Soutien
FAQs
Questions fréquemment posées
1. Pour commencer
2. Données
Le PNUD, le PNUE et le PNUE-WCMC ont adopté des critères pour aider à identifier et à conserver les meilleures couches de données disponibles sur ces thèmes afin de permettre des analyses et des rapports plus rationalisés et standardisés. Ces critères de sélection placeront les données dans l'un des trois niveaux, et prendront en compte des aspects tels que la pertinence des données, l'ouverture et la disponibilité des licences, la transparence et la couverture géographique. Ce système à plusieurs niveaux a pour seul but d'aider à l'élaboration et à la mise en œuvre d’ensembles de données mondiaux adaptés à la réalisation de l'Agenda 2030 pour le développement durable, des objectifs émergents du Cadre mondial pour la biodiversité post-2020 et des objectifs mondiaux connexes.
Les critères peuvent être consultés ici.
Avertissement : Les ensembles de données sur le UNBL et d'autres plateformes de l'ONU n'ont pas encore été formellement évalués par rapport à ces critères. Une première évaluation pilote est en cours.
- Entièrement documenté à l'aide de la spécification Open API 3.0 (officiellement swagger).
- Tout est disponible via une API HTTP RESTful.
- Toutes les interfaces de sécurité ont créé des jetons oAuth 2.0 et JWT.
Veuillez noter que pour toutes les cartes que vous créez sur la plateforme, vous devez citer les fournisseurs de données en suivant le format indiqué dans la section FAQ sur les cartes. Il s'agit d'une exigence pour l'utilisation de nombreux ensembles de données, et d'une bonne pratique standard.
3. Outils et fonctions
4. Espaces de travail UNBL
5. Exportation de cartes
- Les cartes doivent être claires et concises.
- Le texte important sur les cartes doit être clair et lisible (par exemple, les villes, les noms de lieux, les éléments de légende, etc.).
- La carte doit comprendre les éléments cartographiques de base : légende (des couches de données pertinentes) et barre d'échelle.
- La carte doit être affichée avec la citation correcte (voir ci-dessous).
Exemple: Carbone organique du sol de la forêt de mangrove [PDF] Sanderman et al. 2018. 1:25,000. Généré par James Bond. Carte générée par le UN Biodiversity Lab. https://map.unbiodiversitylab.org/earth?basemap=grayscale&coordinates=20,0,2&layers=global-mangrove-soil-carbon-01 . (19 juin 2021).
6. Dépannage
Vous ne trouvez pas une réponse à votre question dans notre FAQ ? N'hésitez pas à contacter notre équipe d'assistance à l'adresse support@unbiodiversitylab.orgVous pouvez également accéder au guide d'utilisation animé en cliquant sur l'onglet "Guide d'utilisation" ci-dessus. Pour une version téléchargeable, cliquez ici. Anglais | Français | Espagnol | Portugais | Russe
Guide de l'utilisateur
Guide de l'utilisateur
Ce guide de l'utilisateur a été conçu pour vous guider à travers les principaux outils et fonctions du UN Biodiversity Lab. Utilisez les onglets ci-dessous pour trouver des guides visuels pour notre plateforme publique et nos espaces de travail sécurisés.
Si vous avez d'autres questions, veuillez nous contacter à l'adresse support@unbiodiversitylab.org.
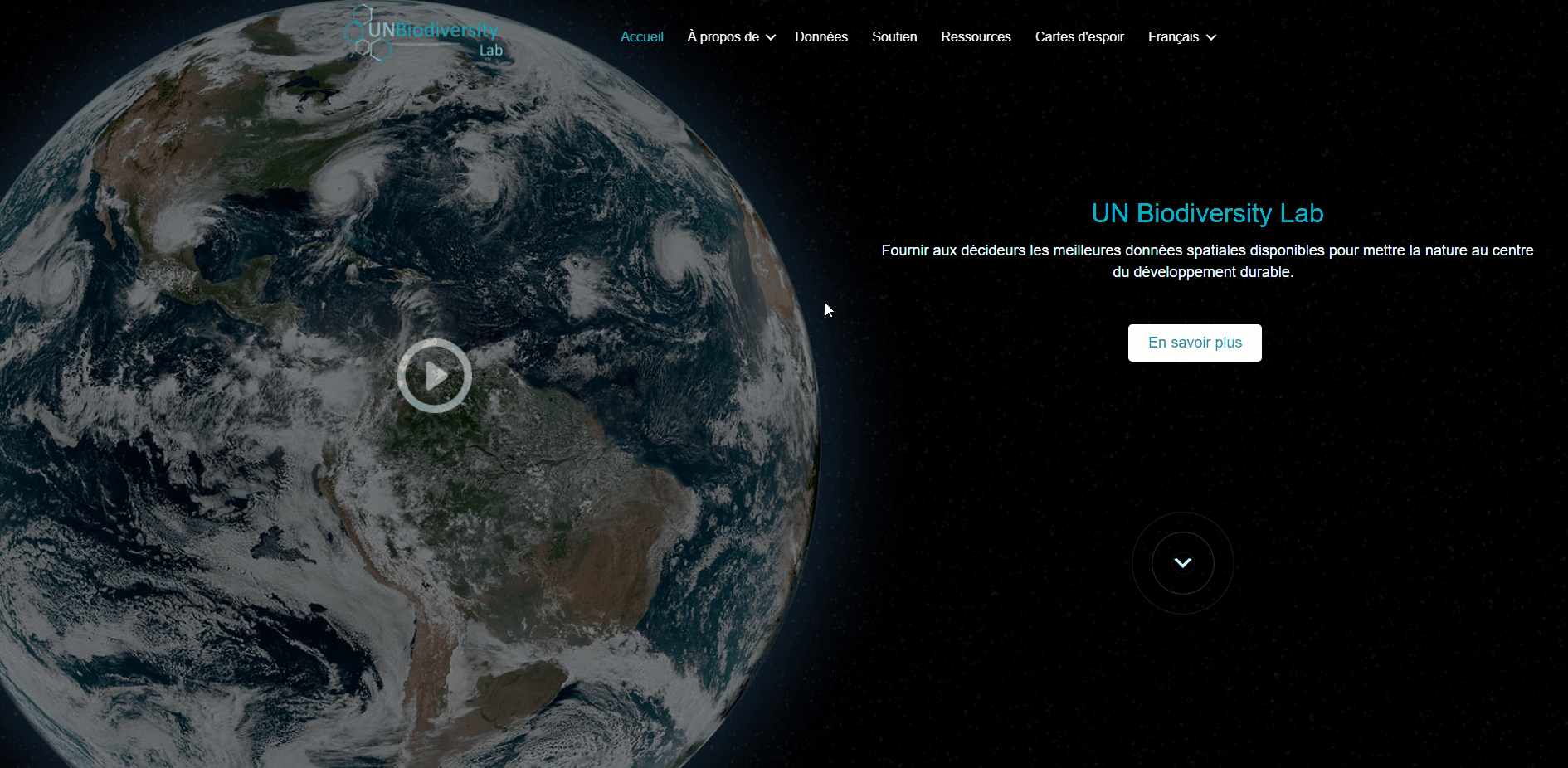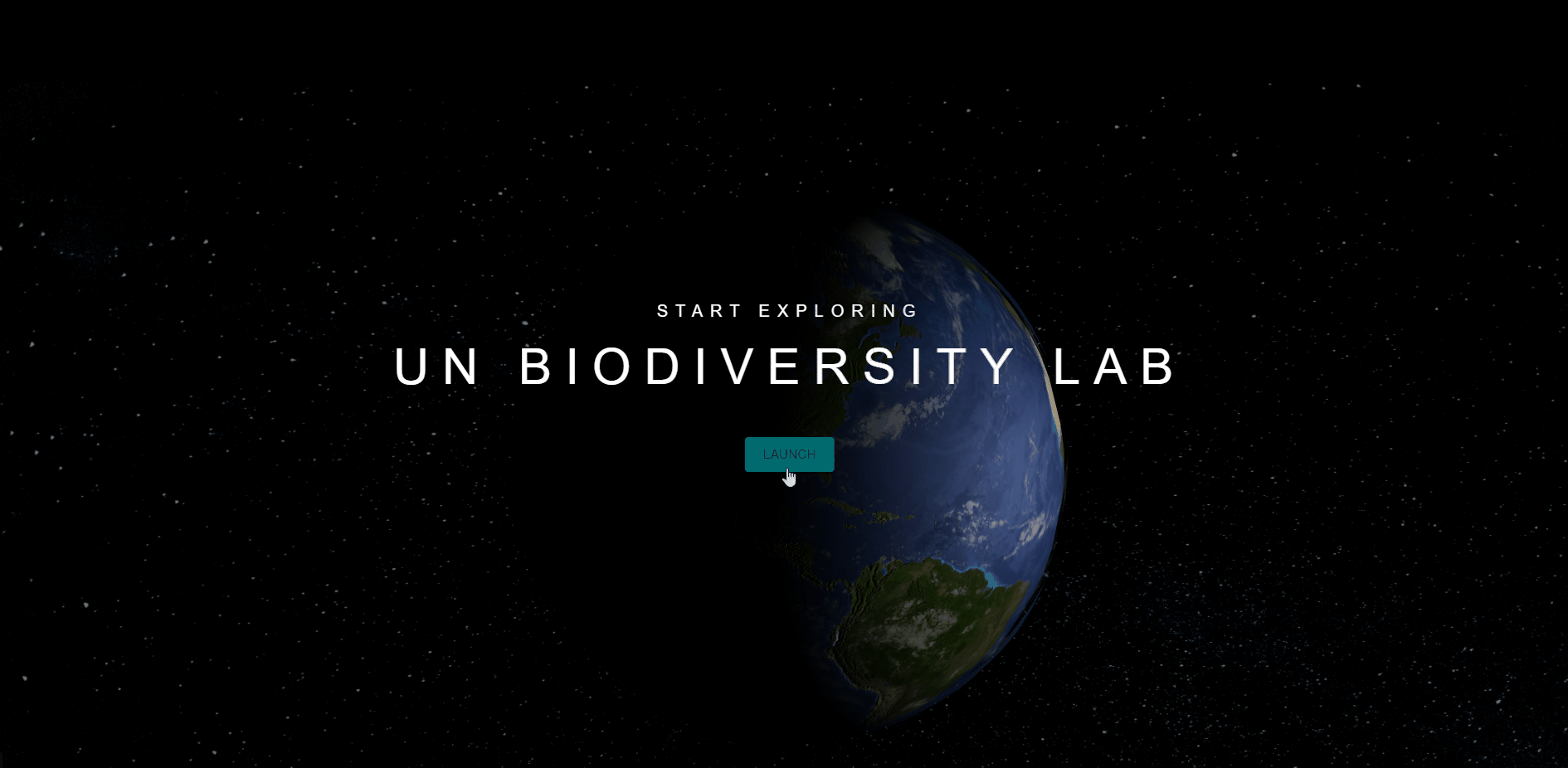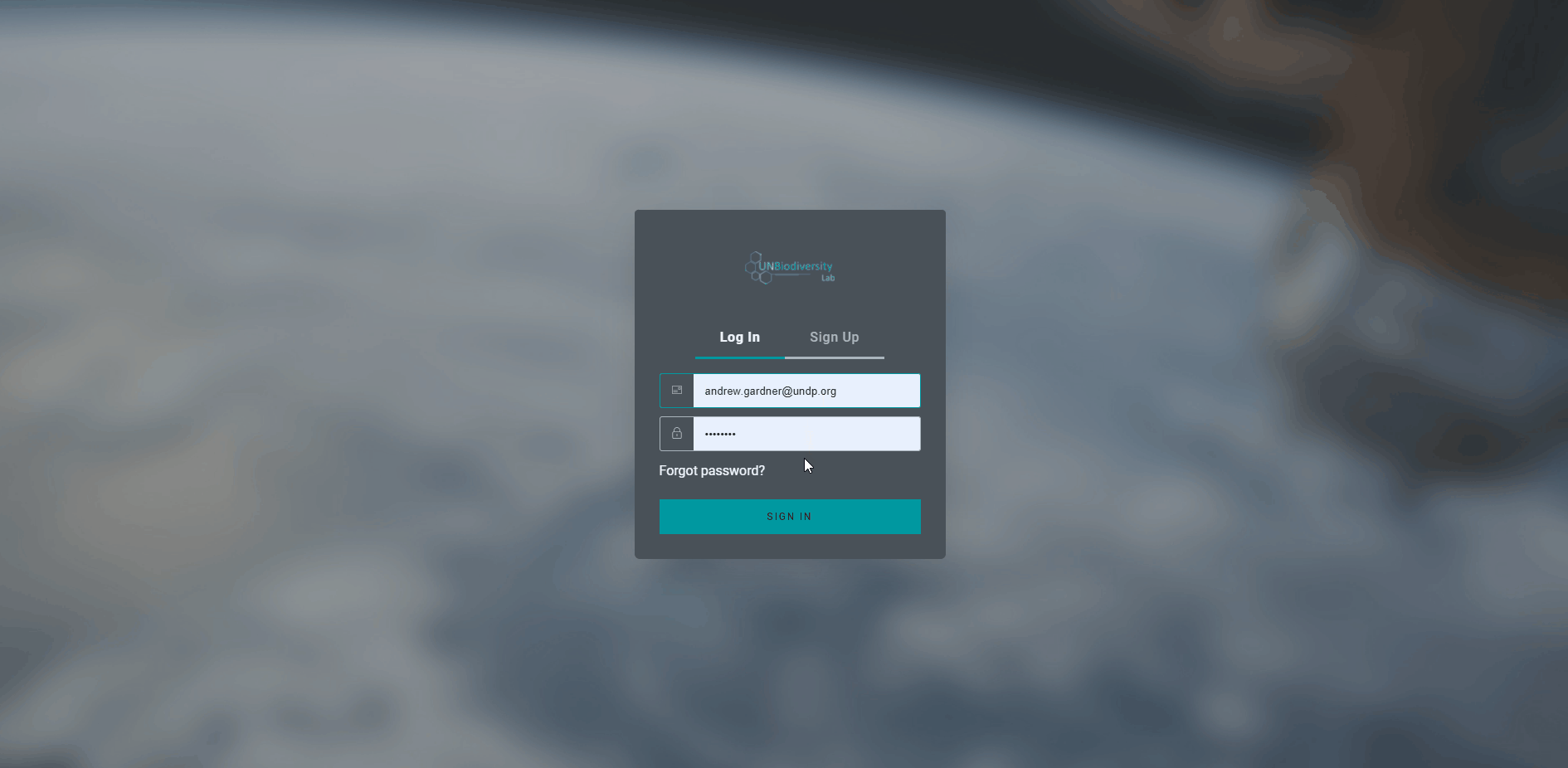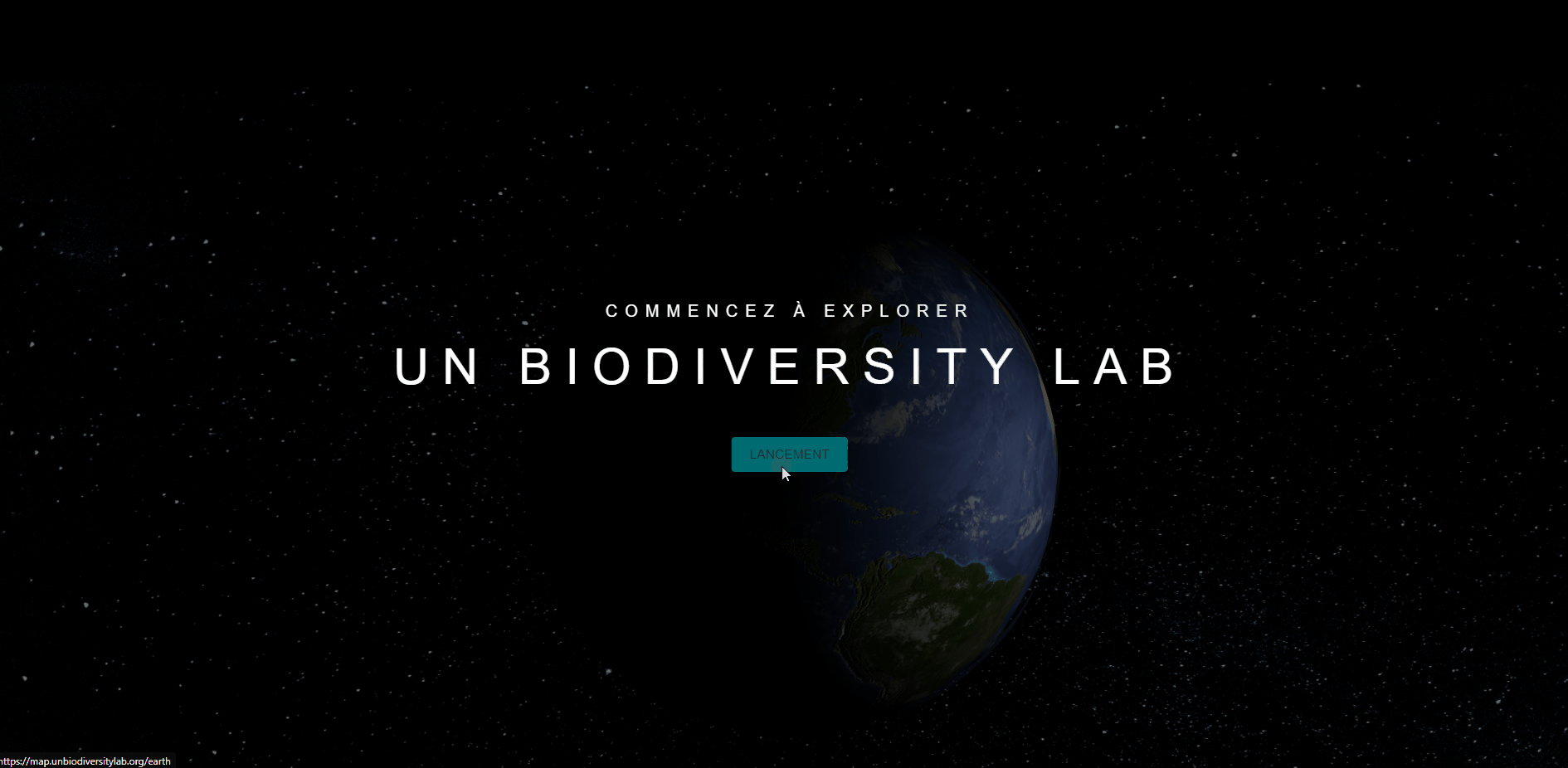
Avant de commencer à explorer les données, inscrivez-vous au UN Biodiversity Lab:
- Cliquez sur la page “données” du site Web du UN Biodiversity Lab, puis sélectionnez le bouton de lancement pour accéder à l’application de données.
- Une fois que celui-ci est chargé, sélectionnez l’icône du compte dans le coin supérieur droit et choisissez “S’inscrire”. Saisissez votre adresse électronique, votre nom, votre pays et votre institution (facultatif), puis définissez votre mot de passe pour vous inscrire.
- Vous recevrez un courriel dans les minutes qui suivent. Suivez les instructions contenues dans ce courriel pour ensuite suivre le courriel afin de vérifier votre compte.
- Une fois votre compte vérifié, vous pouvez vous connecter à l’aide de votre adresse électronique et de votre mot de passe à chaque fois que vous accédez à la plate-forme.
- Vous pouvez vous déconnecter à tout moment en cliquant sur votre icône d’utilisateur et en sélectionnant Déconnexion.
Une fois inscrit au UNBL, vous pourrez gérer votre compte, notamment en modifiant votre nom d’utilisateur, votre adresse électronique, votre mot de passe, votre pays et votre institution. Vous pourrez également consulter et modifier les espaces de travail privés auxquels vous appartenez.
Pour gérer votre compte :
- Cliquez sur l’icône du compte avec vos initiales en haut à droite, puis cliquez sur le profil.
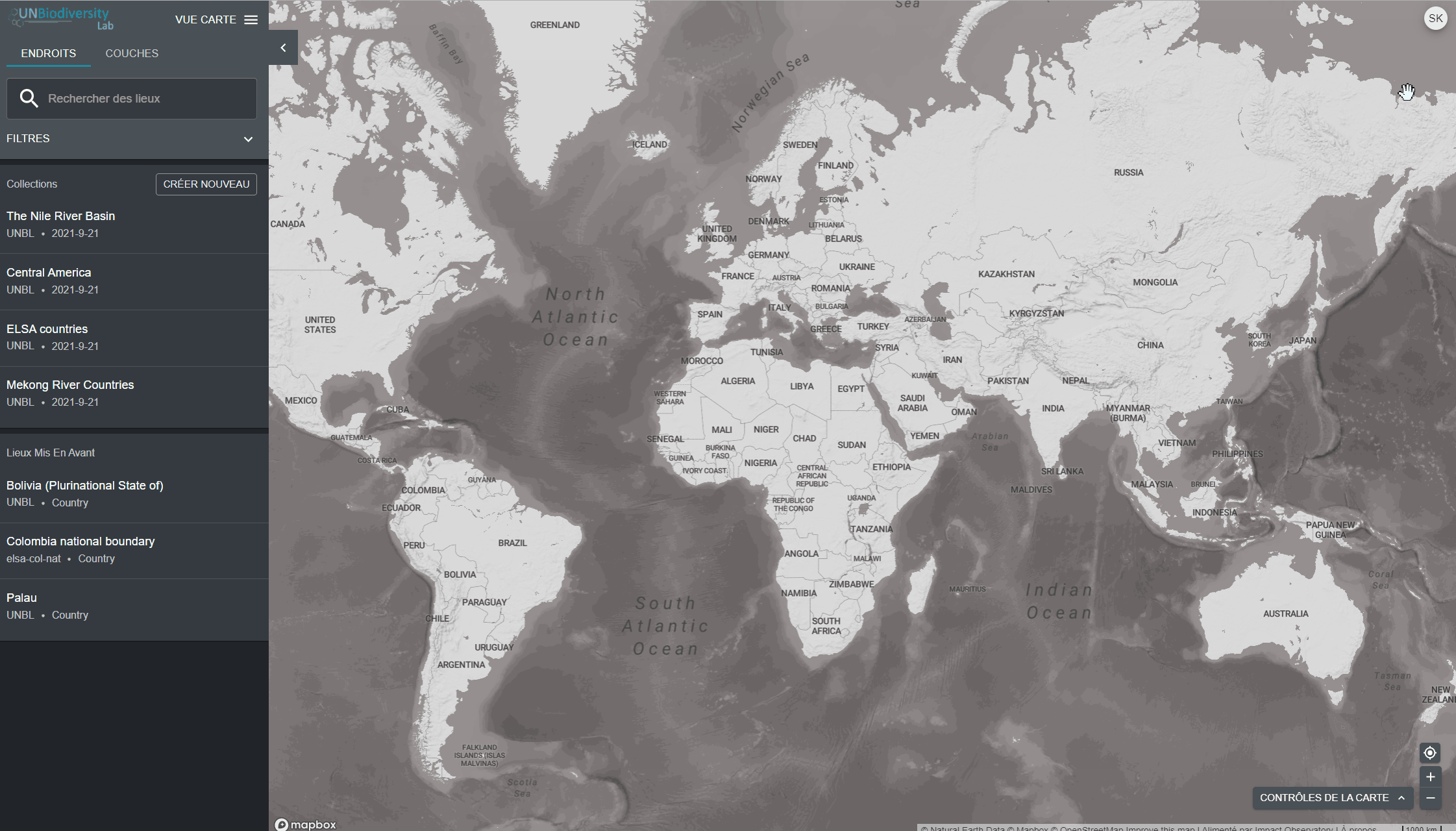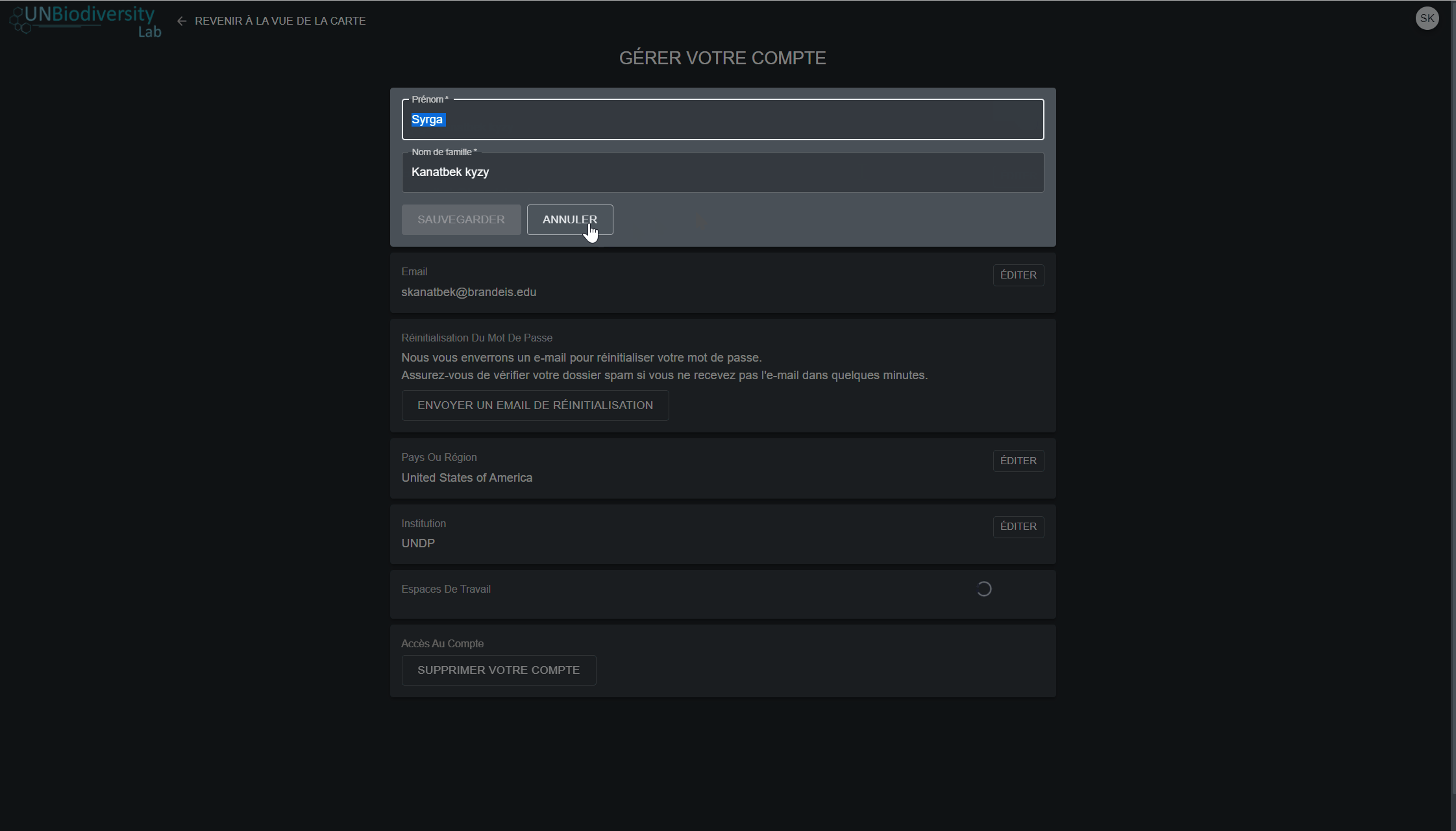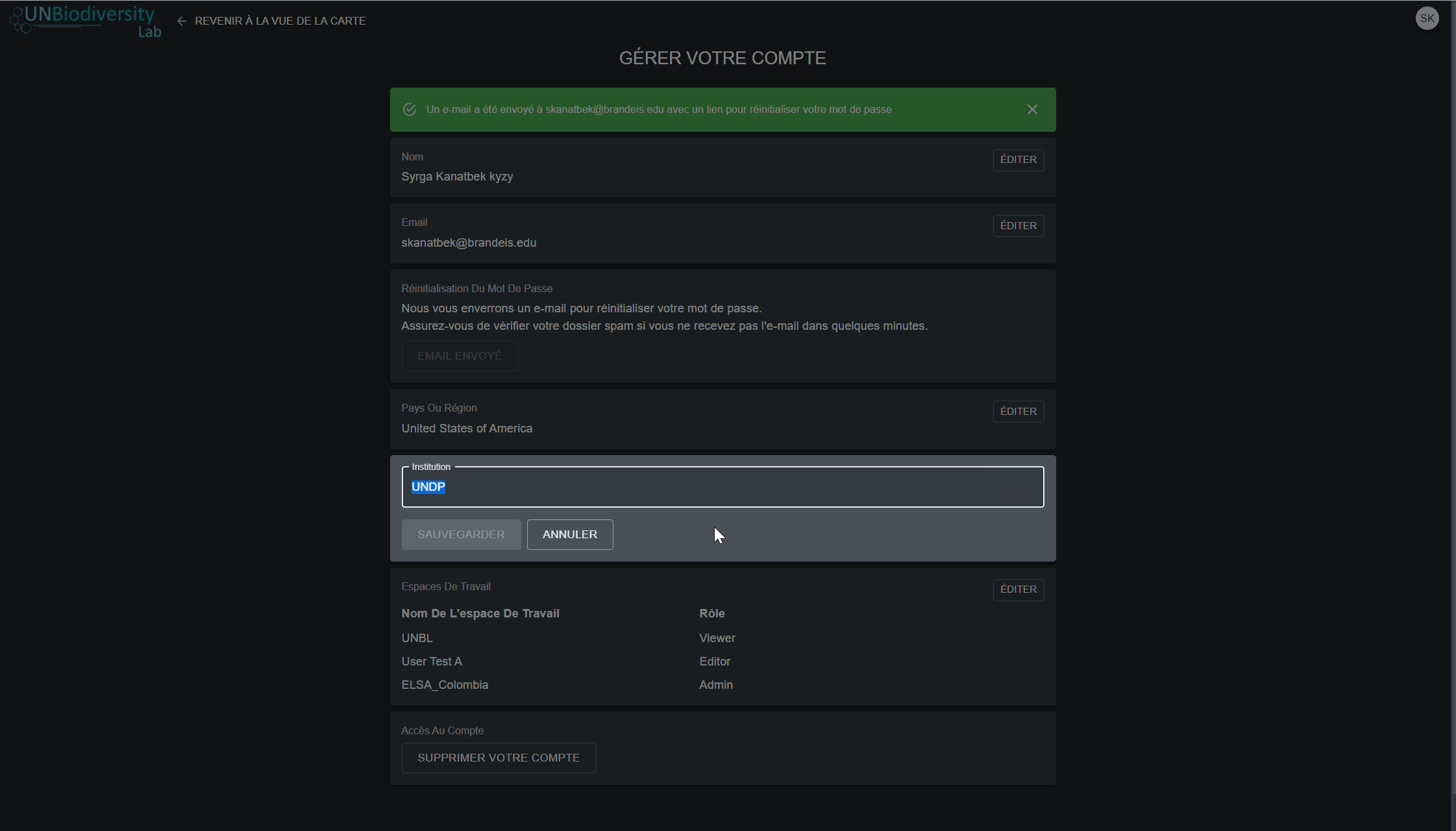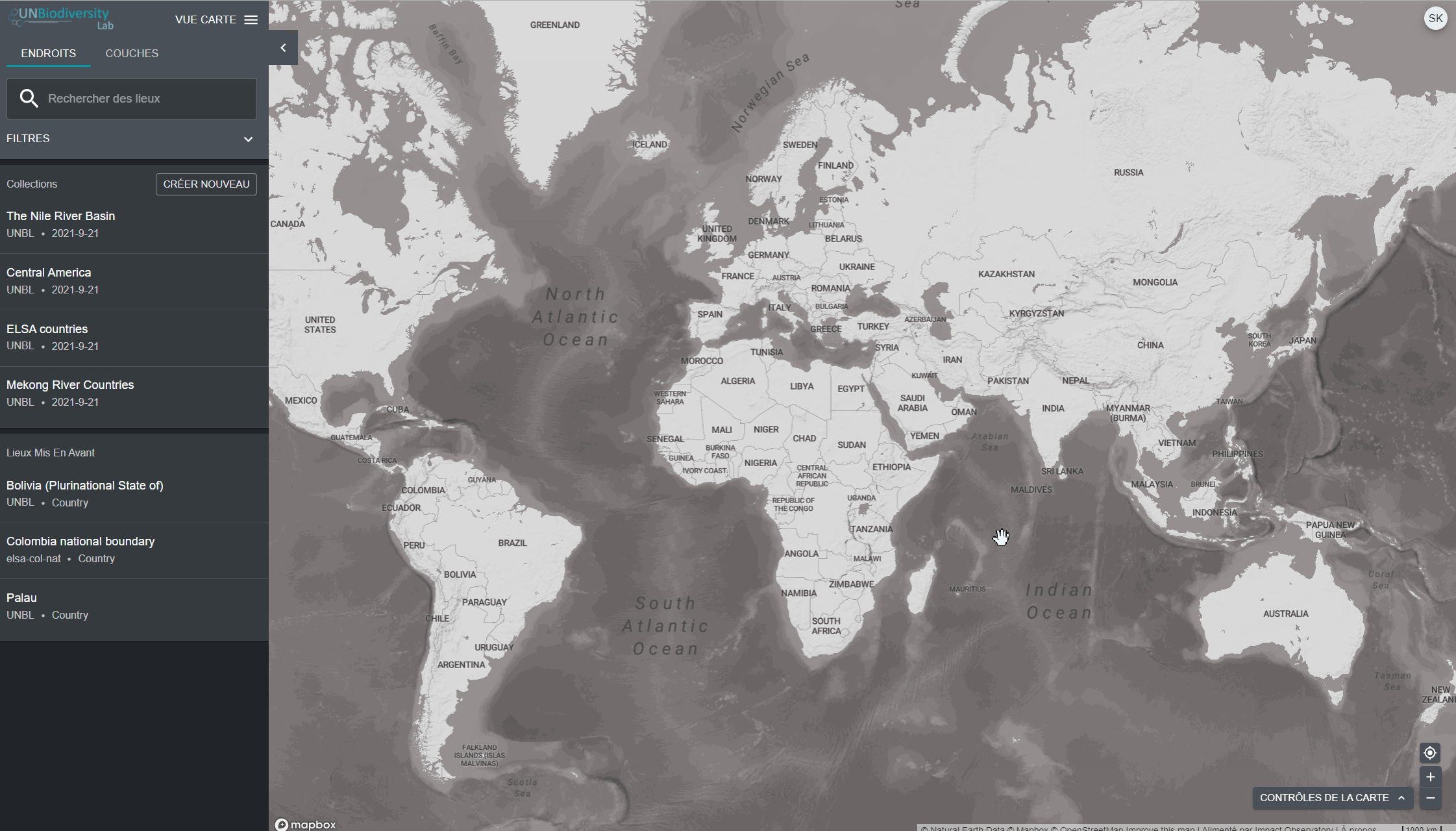
- Cliquez sur l’icône d’édition pour modifier votre nom d’utilisateur, votre adresse électronique, votre pays et votre institution
- Pour réinitialiser votre mot de passe, cliquez sur ENVOYER UN EMAIL DE REINITIALISATION, puis suivez les instructions du courriel.
- Pour quitter l’un des espaces de travail privés auxquels vous appartenez, cliquez sur modifier, puis sur quitter l’espace de travail. Enregistrez vos modifications.
- Si ce compte n’est plus utilisé, vous pouvez cliquer sur SUPPRIMER VOTRE COMPTE en bas de cette page. Après avoir supprimé le compte, vous devrez vous inscrire à nouveau pour obtenir les privilèges d’utilisateur enregistré sur UN Biodiversity Lab.
- Après avoir enregistré vos modifications, cliquez sur REVENIR À LA VUE DE LA CARTE.
La navigation entre les deux pages est simple.
- Pour revenir au site Web du UN Biodiversity Lab à partir de l’application de données, cliquez sur l’option d’affichage de la carte et choisissez l’option d’accueil en haut à droite du panneau.
- Pour accéder à l’application de données à partir du site web du UN Biodiversity Lab, cliquez sur Données.
Le UN Biodiversity Lab est actuellement disponible en anglais, français, espagnol, portugais , et russe. La langue par défaut est l’anglais.
Pour changer la langue, cliquez sur l’icône du compte dans le coin droit de la carte et cliquez à nouveau pour sélectionner la langue que vous préférez dans le menu déroulant.
Vous pouvez changer de langue sur le site Web UN Biodiversity Lab ou sur l’application de données
Il existe plusieurs fonctions qui peuvent vous aider à naviguer sur l’écran de la carte. Il s’agit notamment des éléments suivants:
- Déplacer la carte: Utilisez votre souris pour faire glisser la partie de la carte que vous souhaitez visualiser au milieu de l’écran.
- Effectuer un zoom en avant/arrière:: Cliquez sur les icônes +/- en bas à droite de la carte.
- Placer de manière centrale: Cliquez sur le bouton de la place centrale au-dessus de +/-. Cela recentrera la carte sur le lieu sélectionné.
- Cacher la barre de menu de gauche: Cliquez sur la flèche en haut du menu de gauche pour réduire le panneau des couches et obtenir une vue agrandie de la carte. Cliquez à nouveau pour agrandir le panneau.

Plusieurs options s’offrent à vous pour personnaliser la carte de base. Il s’agit notamment des options suivantes:
- Étiquettes: Les étiquettes indiquent le nom des lieux, y compris les pays, les états, les villes et les points de repère représentatifs. Cliquez sur le bouton pour activer les étiquettes, et pour les masquer.
- Routes: Cliquez sur le bouton pour afficher les routes, ou sur le bouton pour les masquer.
- Fond de carte: Nous proposons des options en niveaux de gris et par satellite pour l’arrière-plan de la carte. Pour basculer entre ces options, cliquez sur la petite fenêtre en bas à gauche et à droite de l’écran.
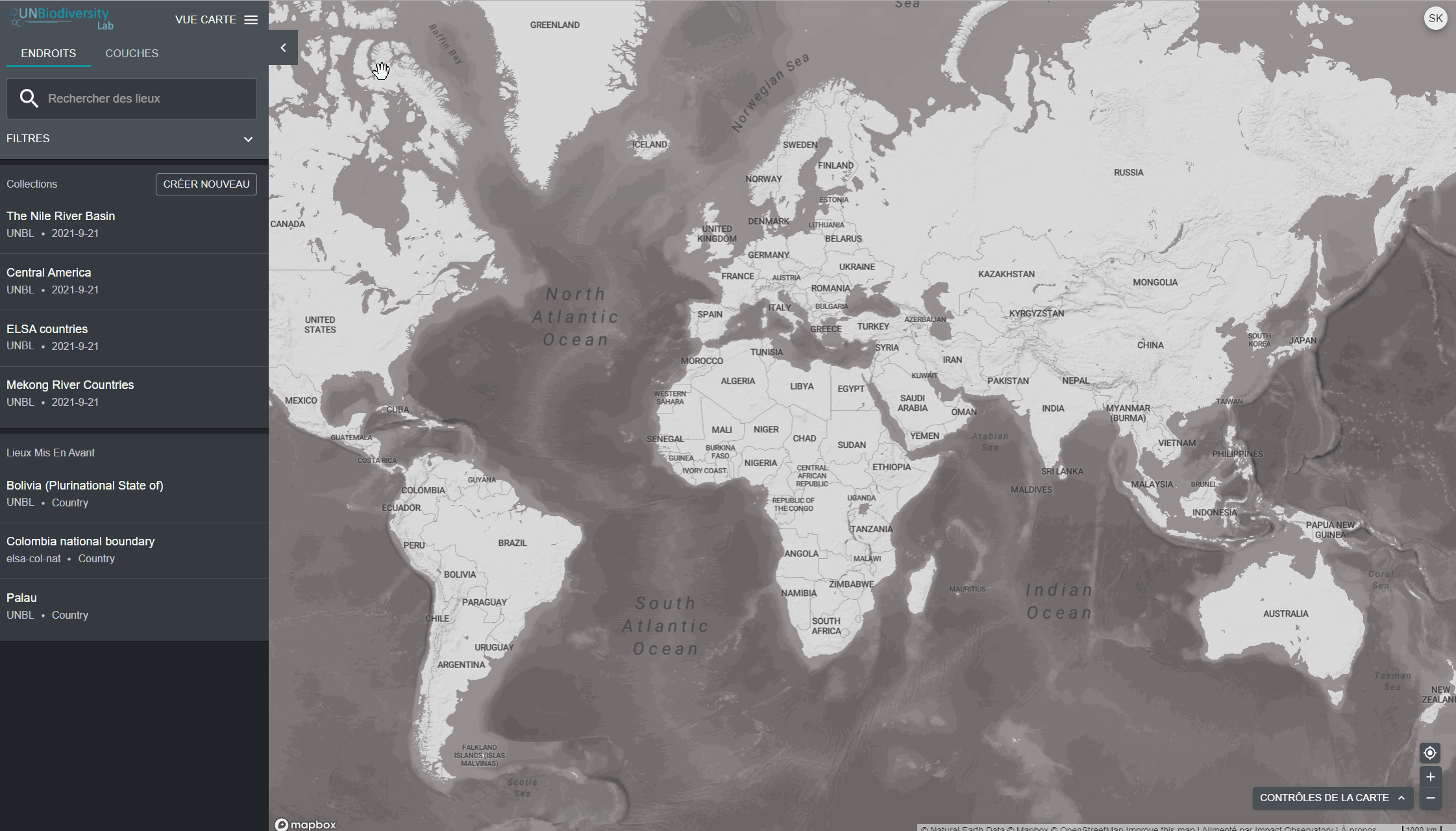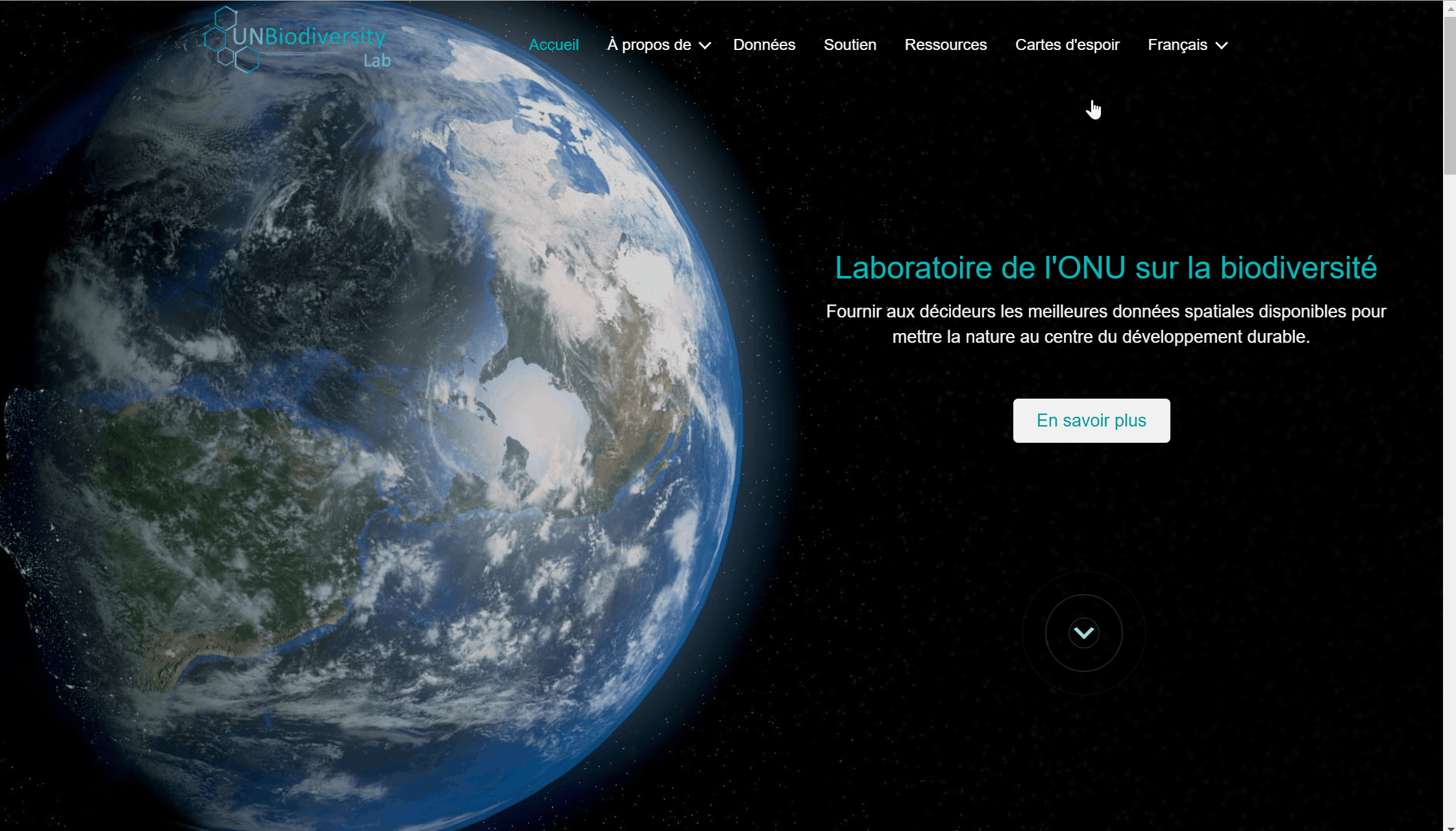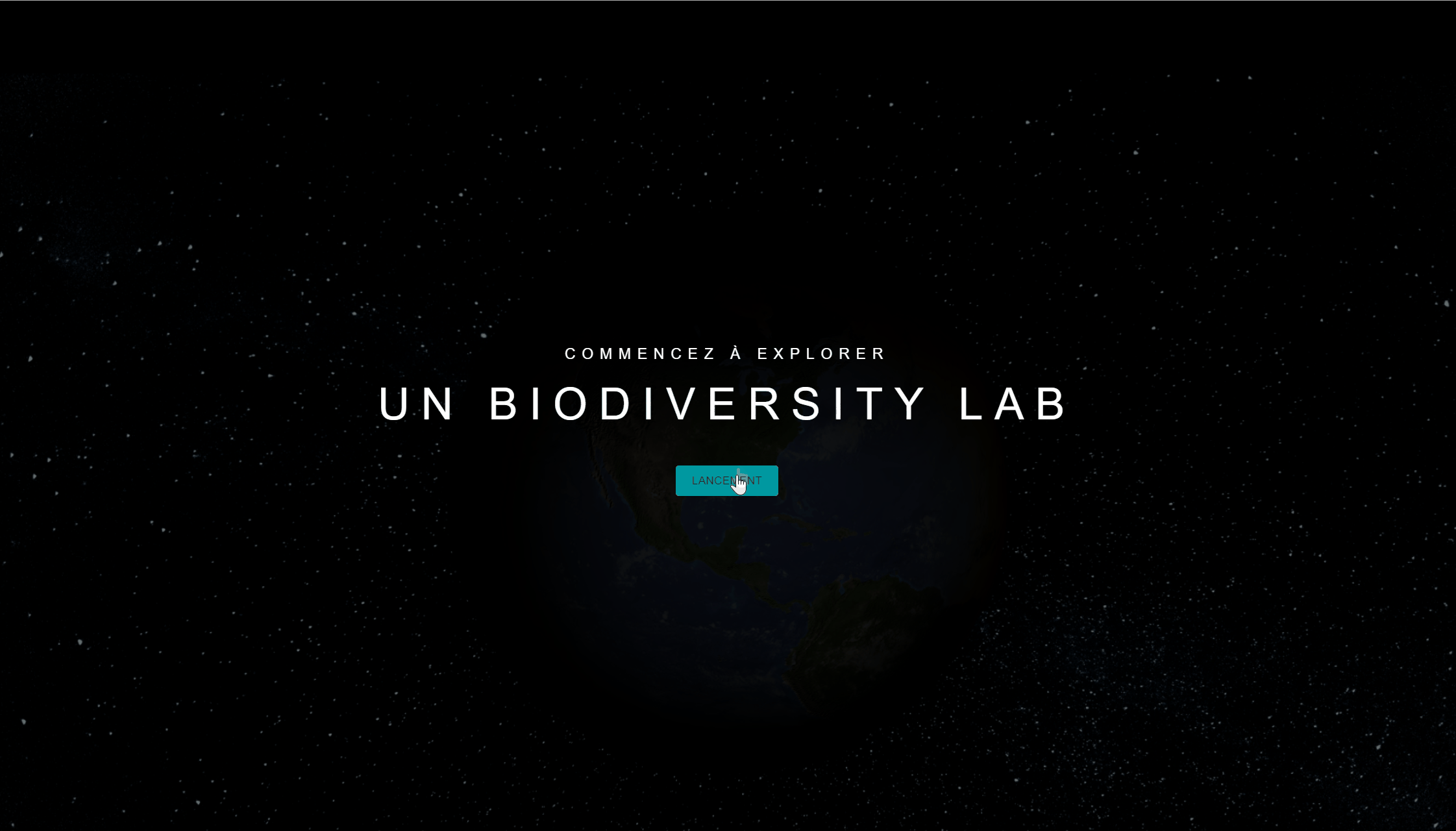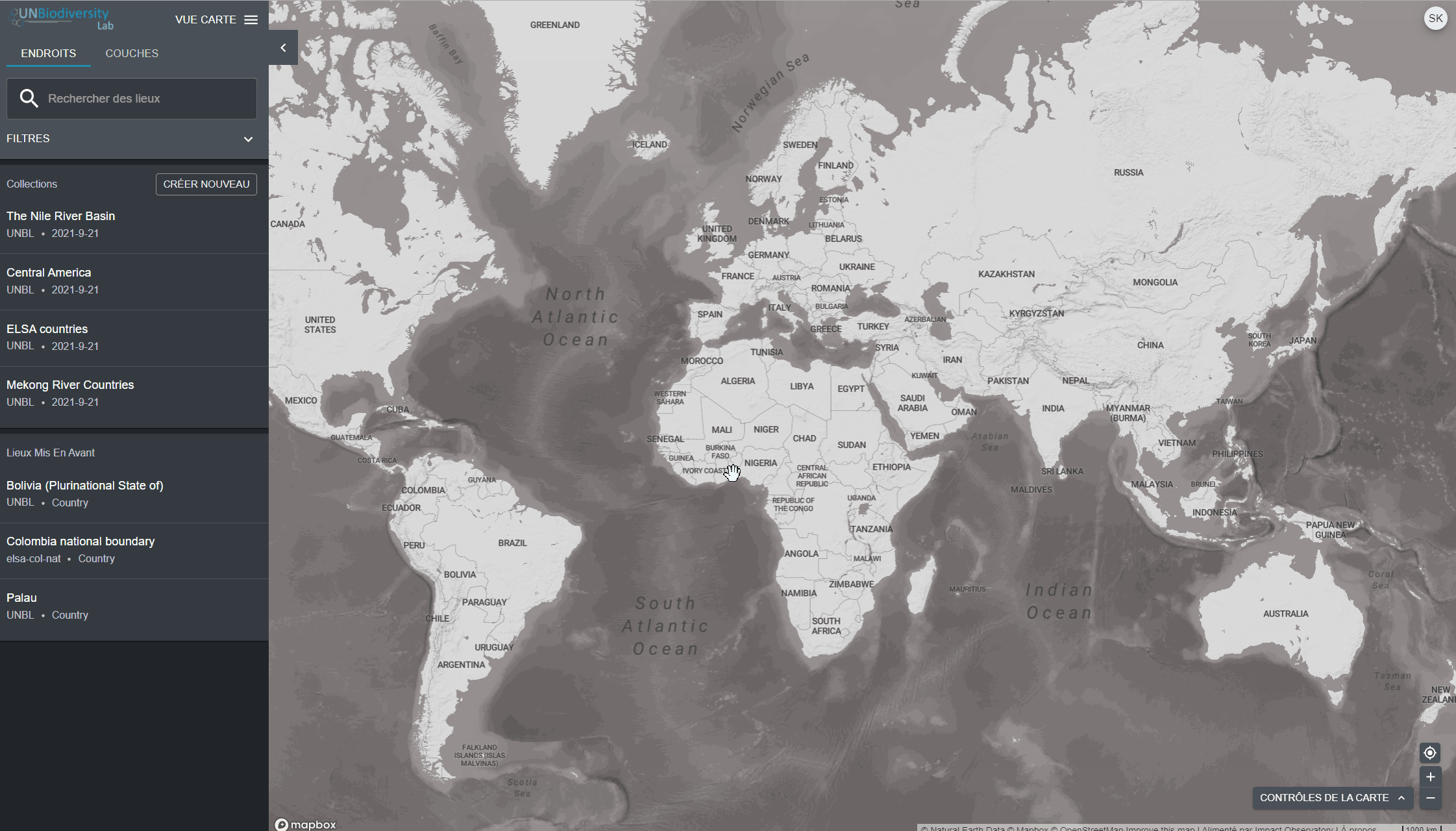
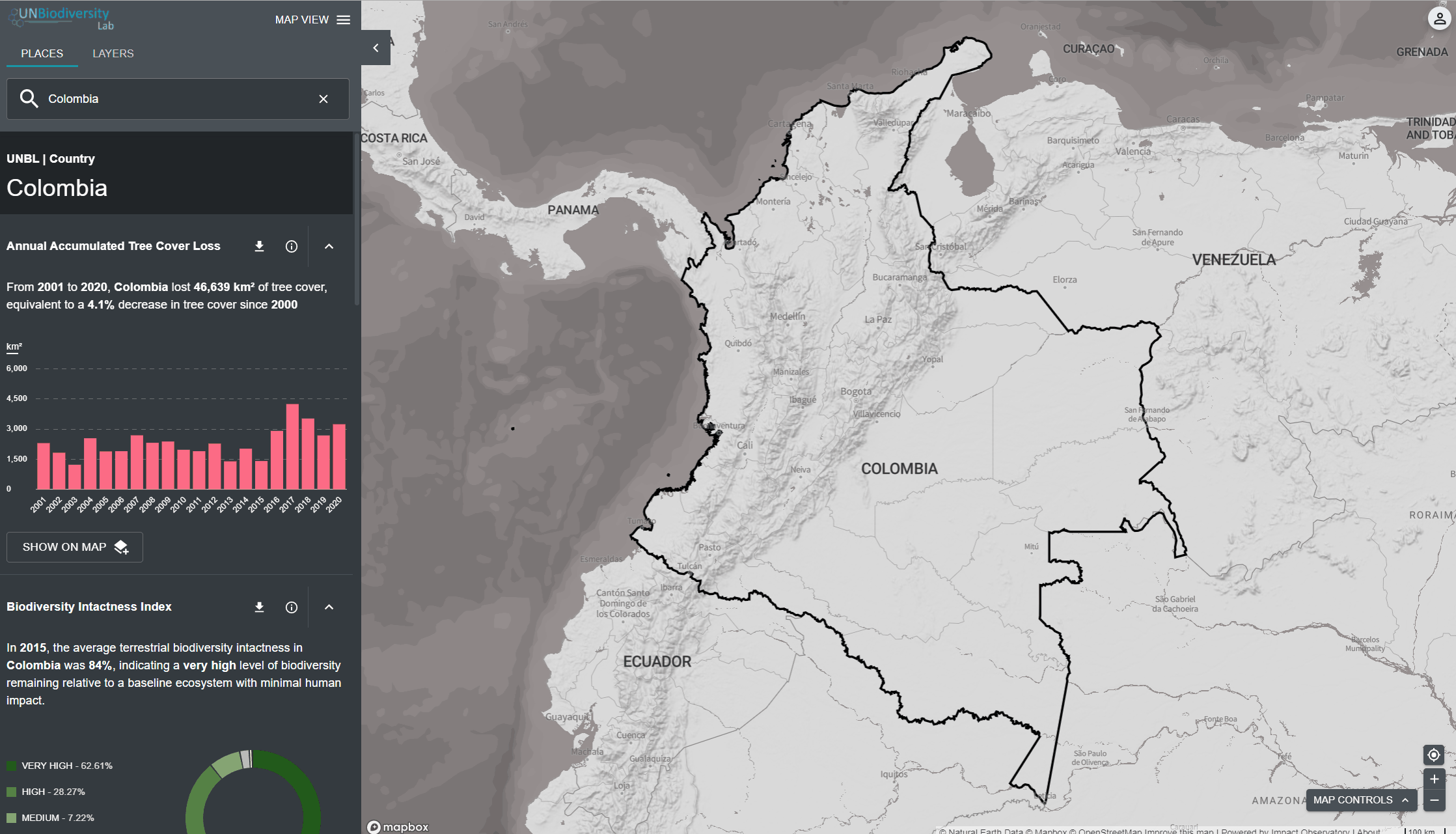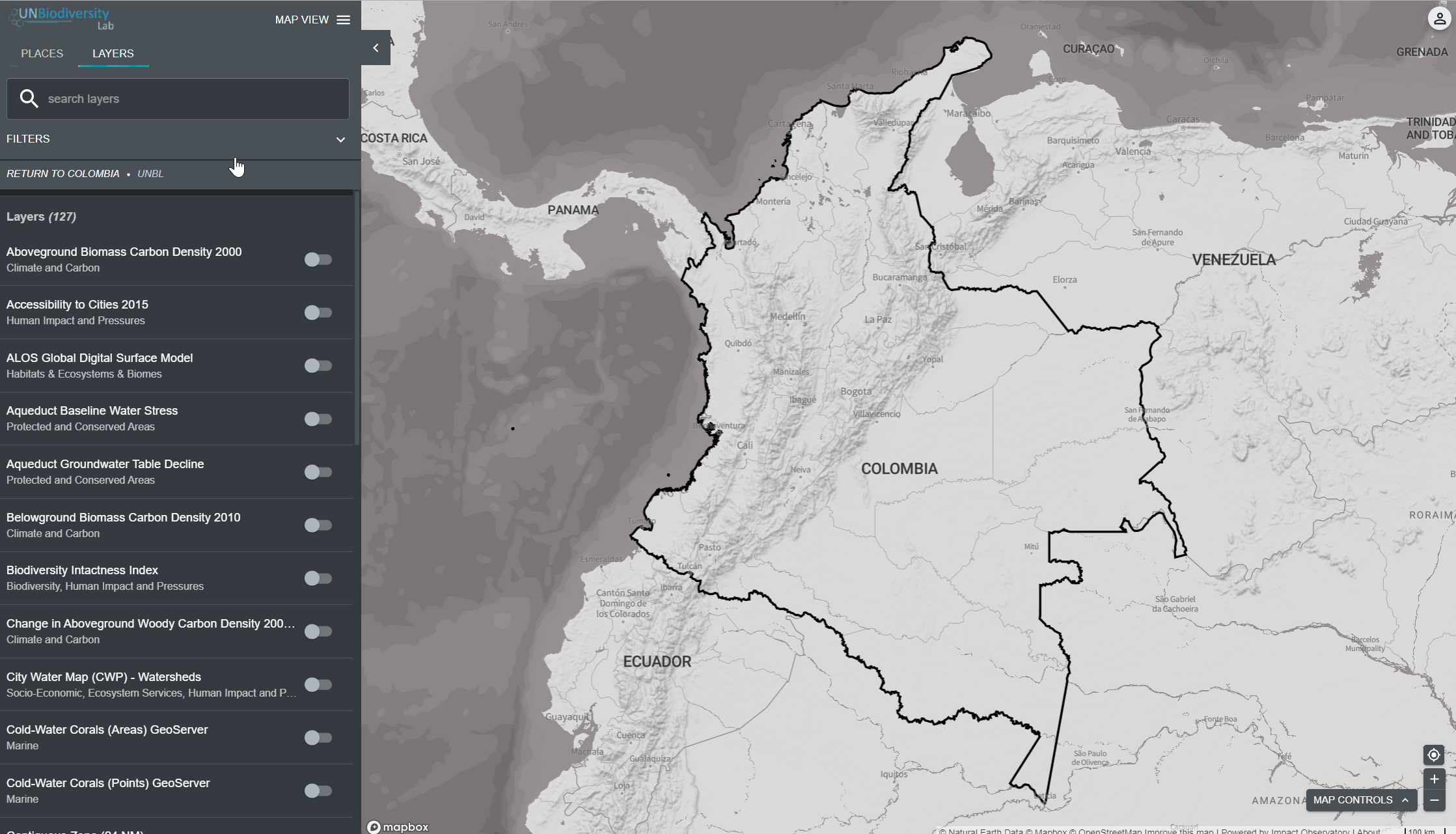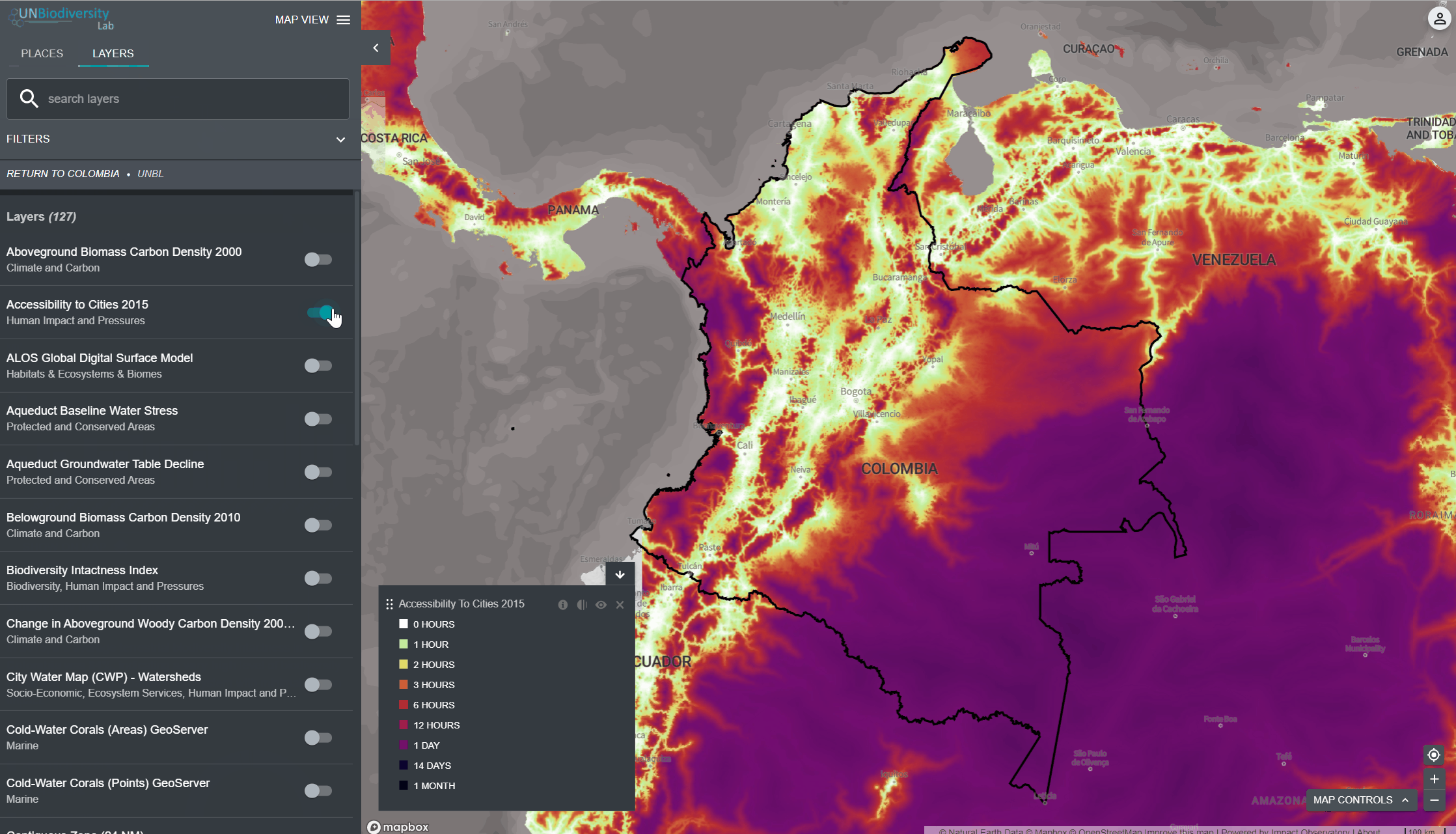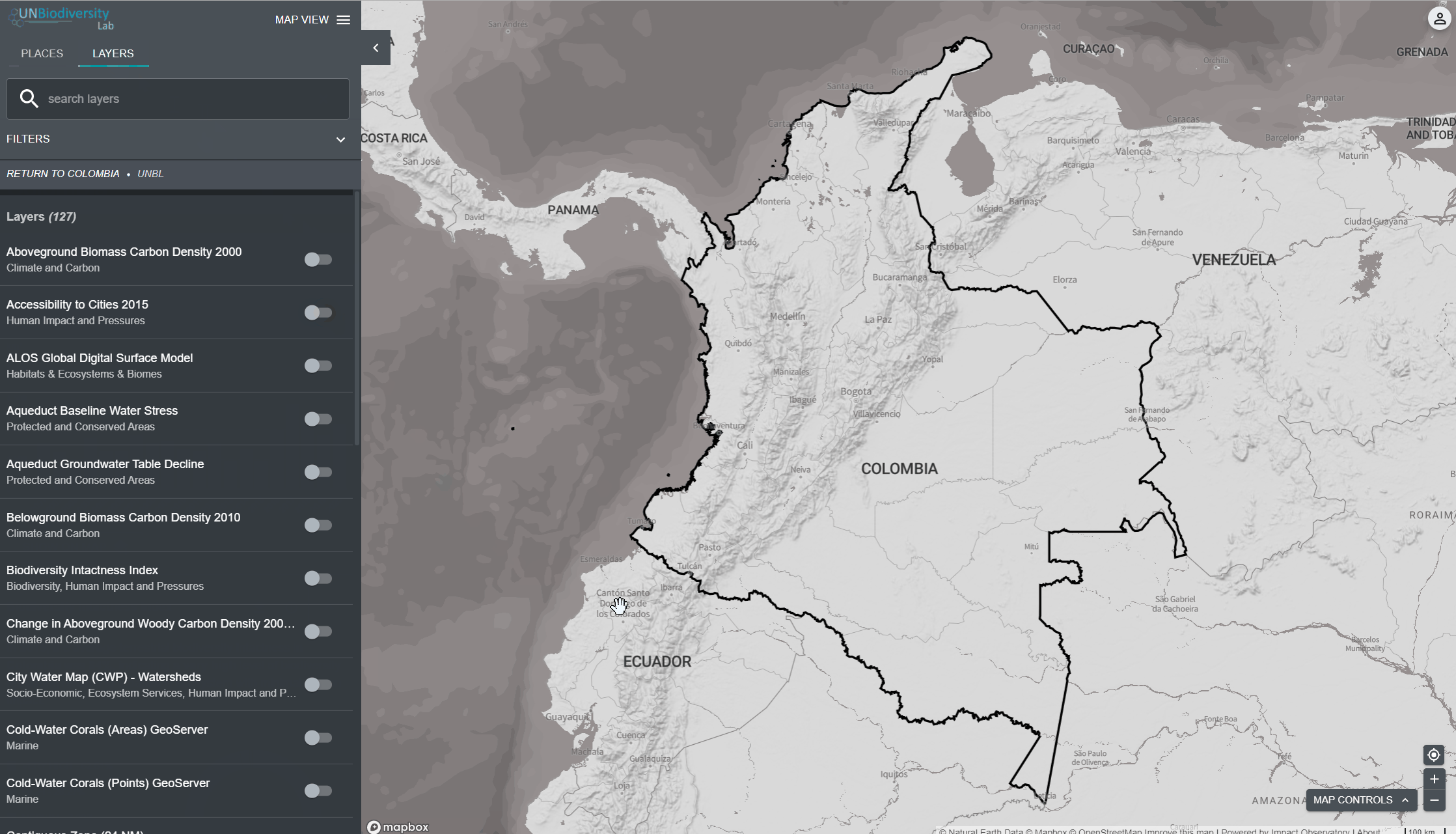
Le UN Biodiversity Lab peut vous aider à naviguer vers une zone d’intérêt spécifique et à accéder à des ensembles de données et des mesures dynamiques pour cette zone. Sur notre plateforme publique, les domaines d’intérêt comprennent les pays, les juridictions et certaines zones transfrontalières. Pour rechercher une zone d’intérêt, vous pouvez soit:
- Cliquez sur l’icône ENDROITS, tapez le nom du pays ou de la juridiction que vous souhaitez consulter dans la boîte de recherche, et sélectionnez le résultat souhaité dans la liste des résultats de la recherche.
OU
- Cliquez sur l’icône ENDROITS, cliquez pour développer la boîte de filtres et sélectionnez le filtre qui vous intéresse, puis sélectionnez le lieu souhaité dans la liste des résultats de la recherche.
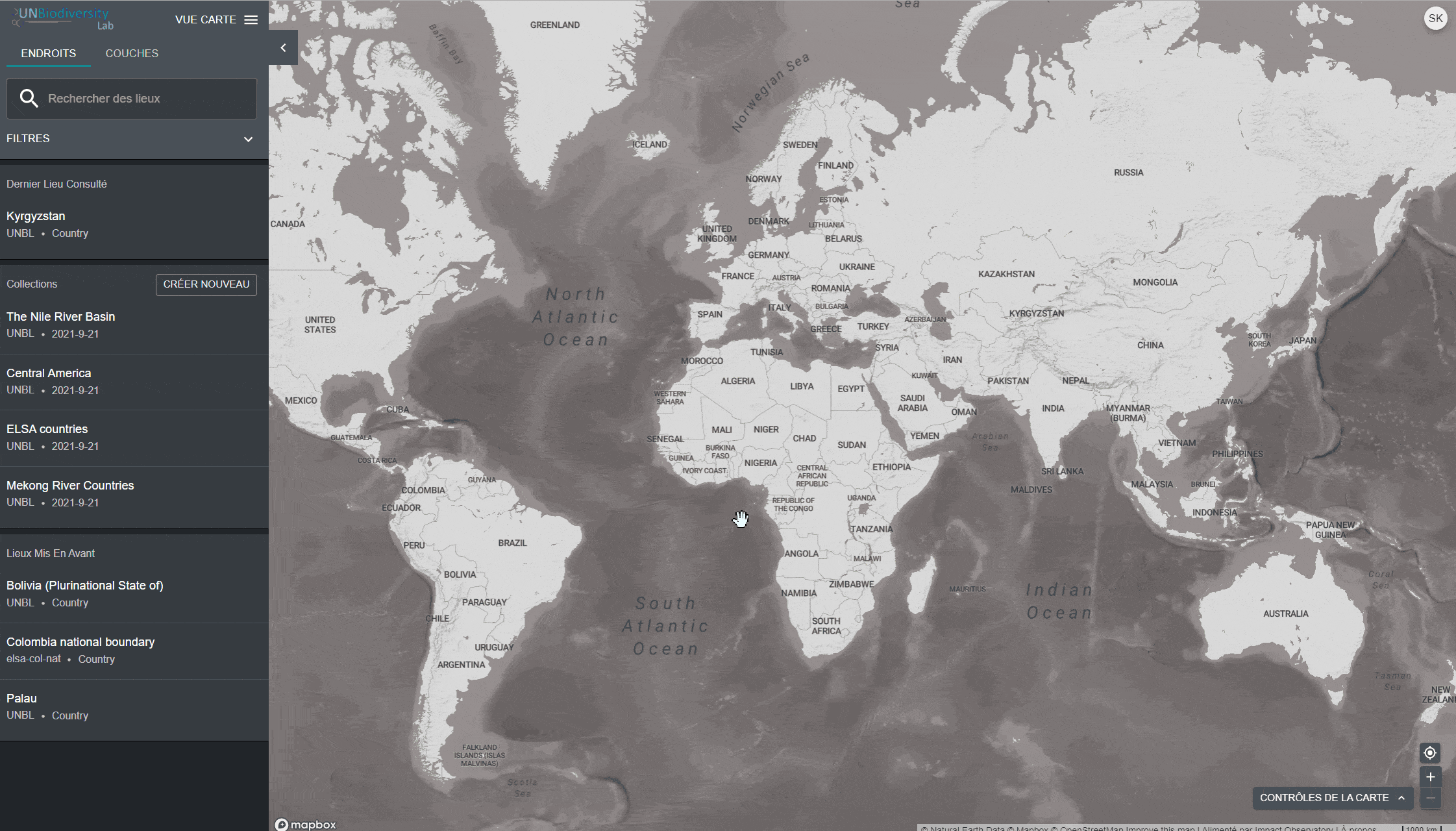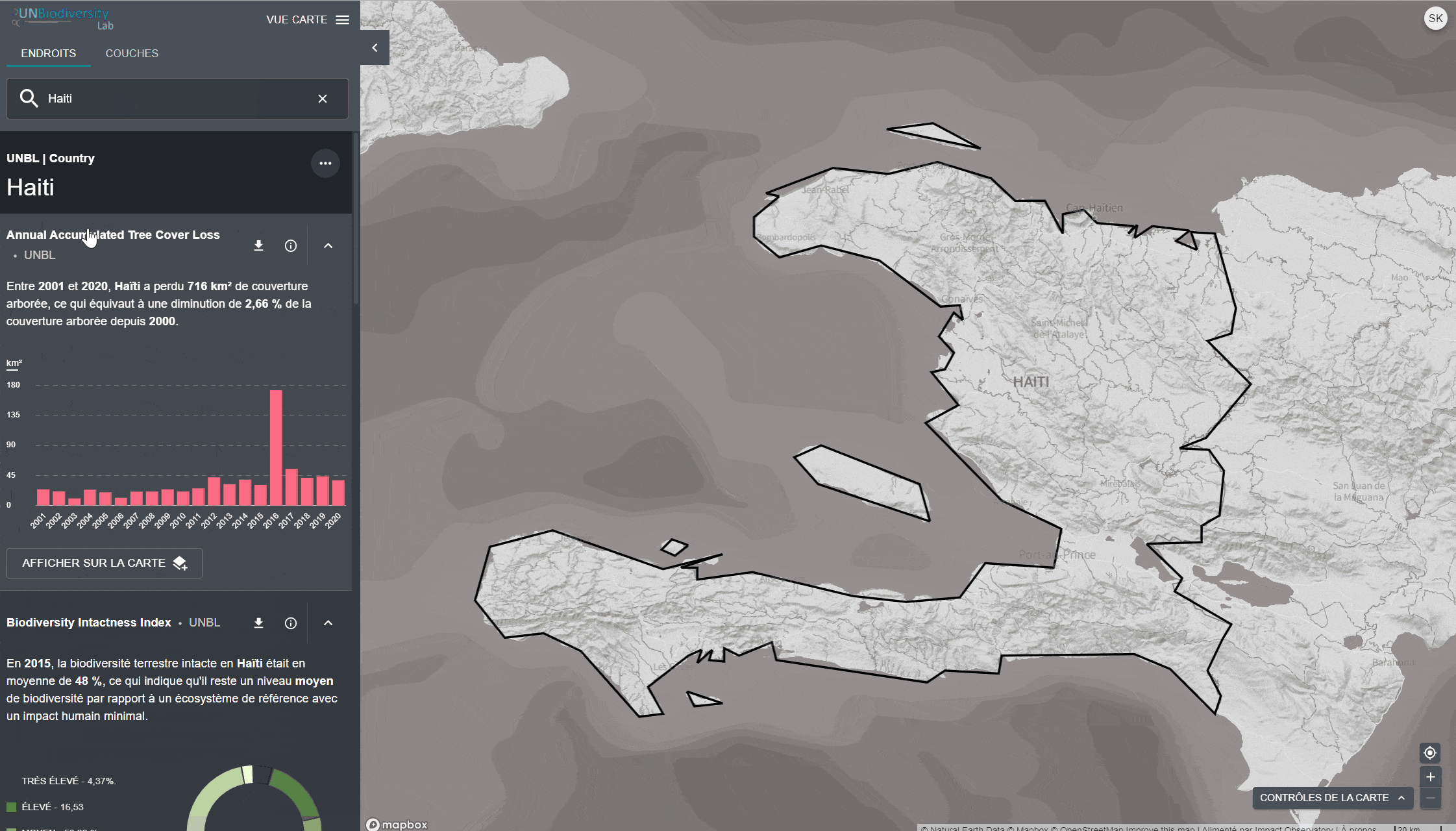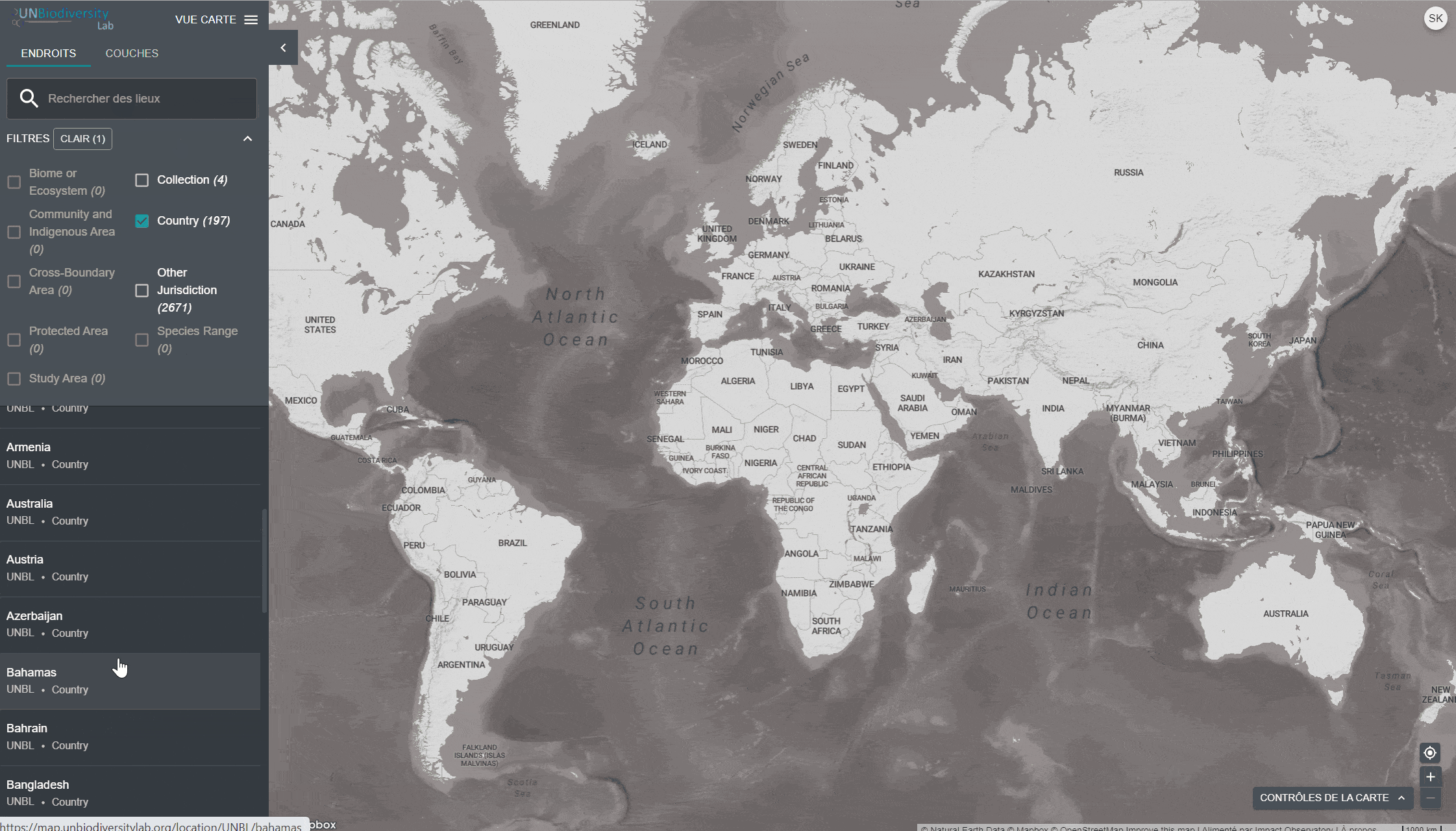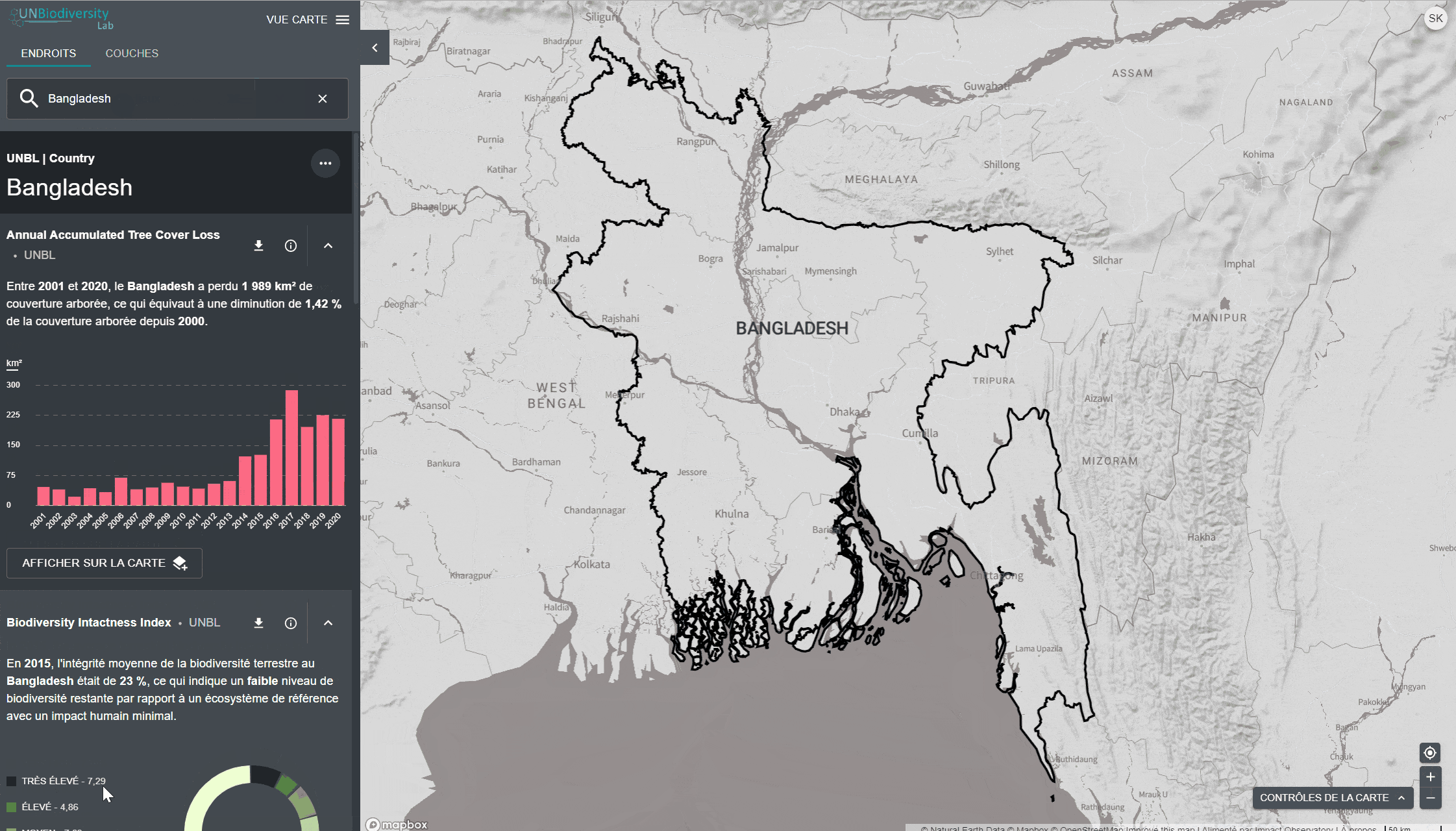
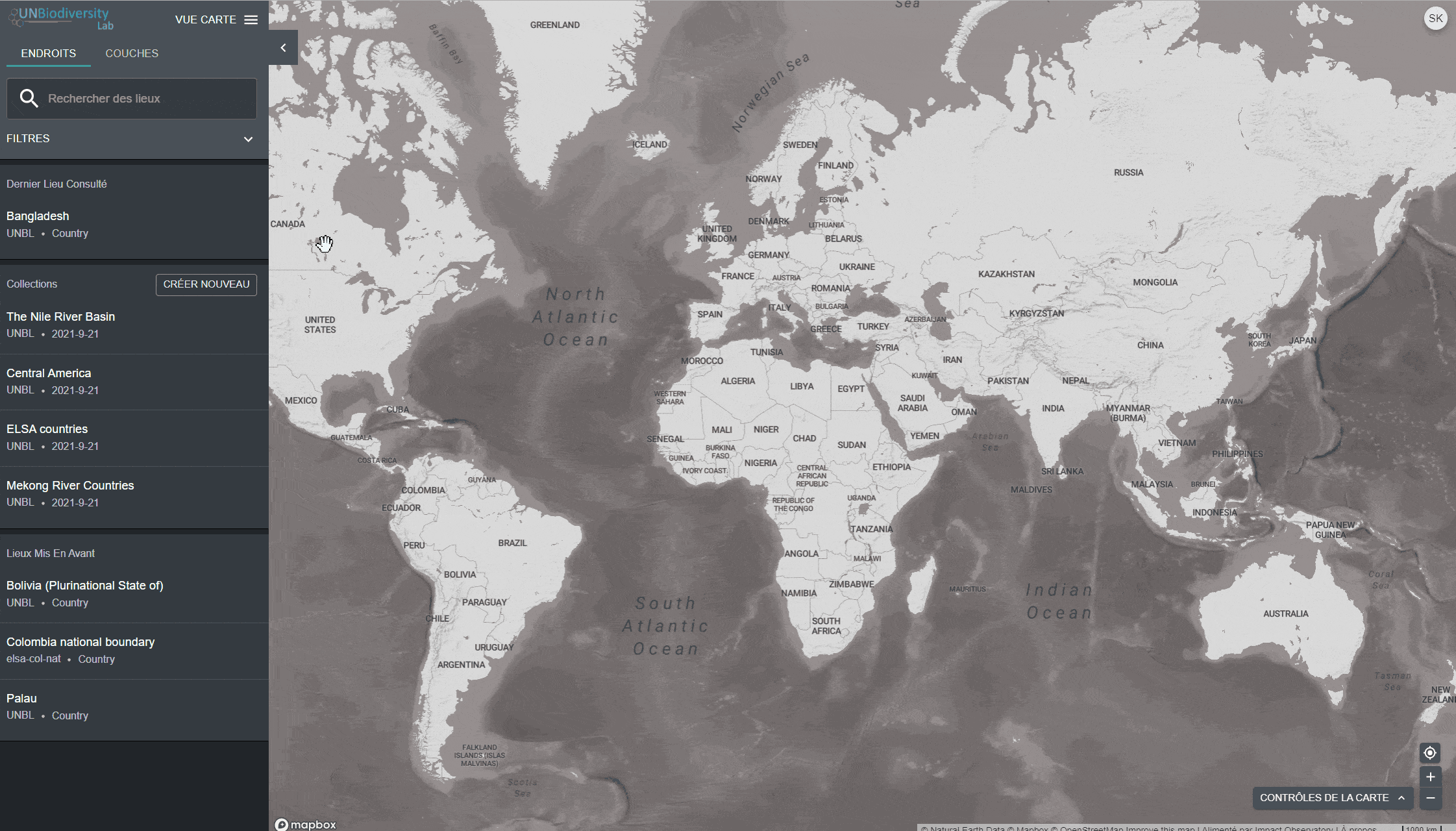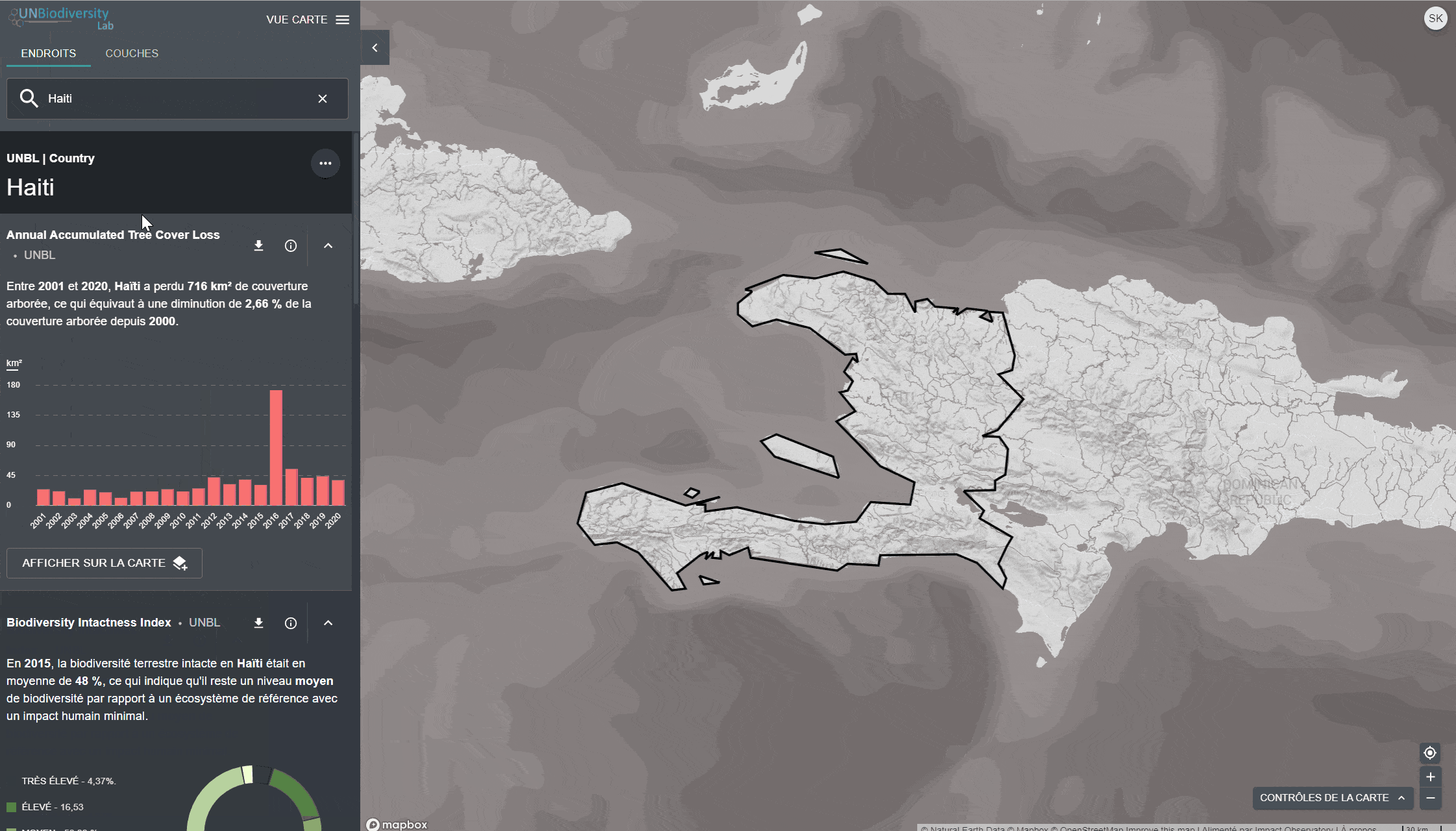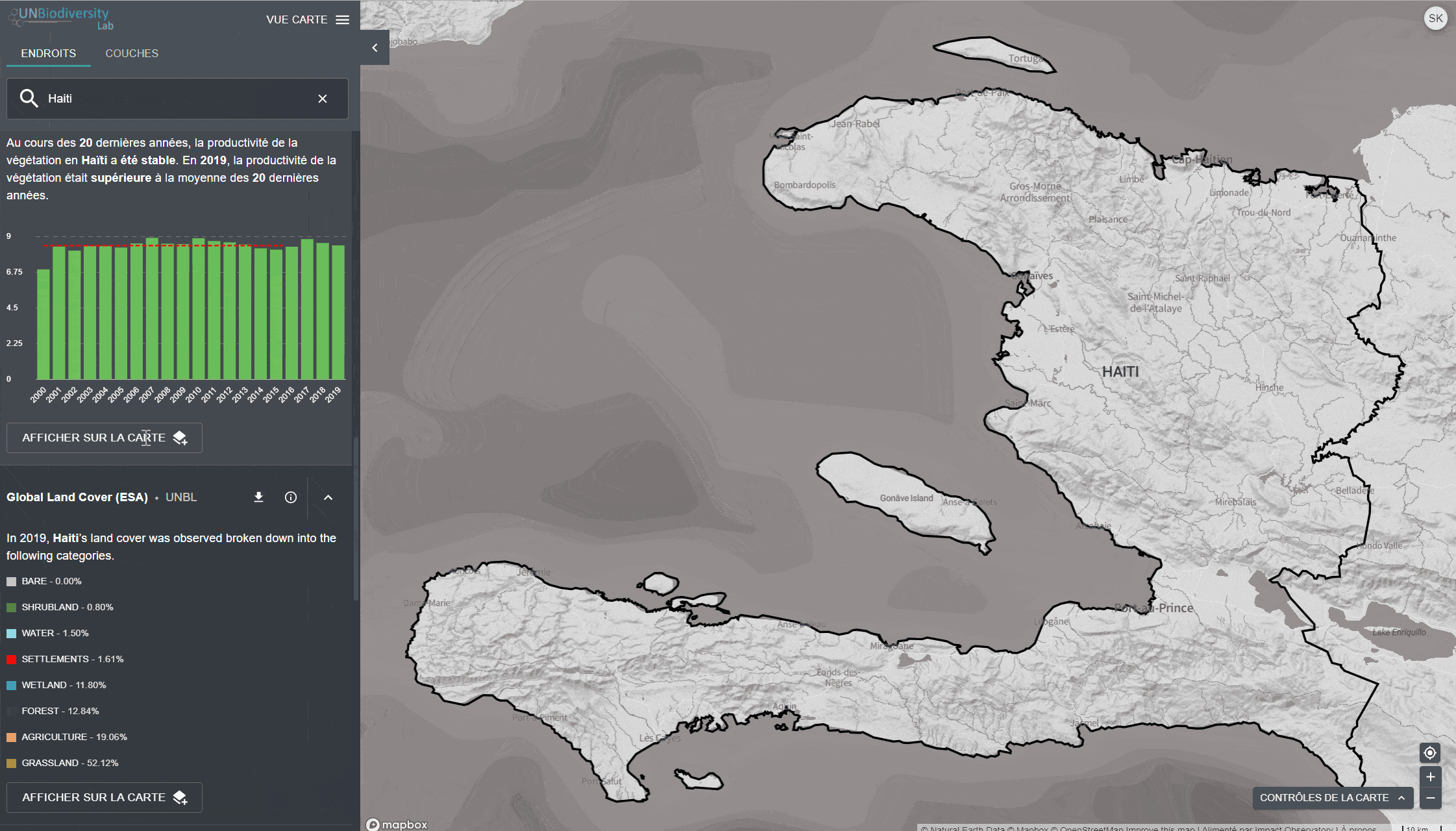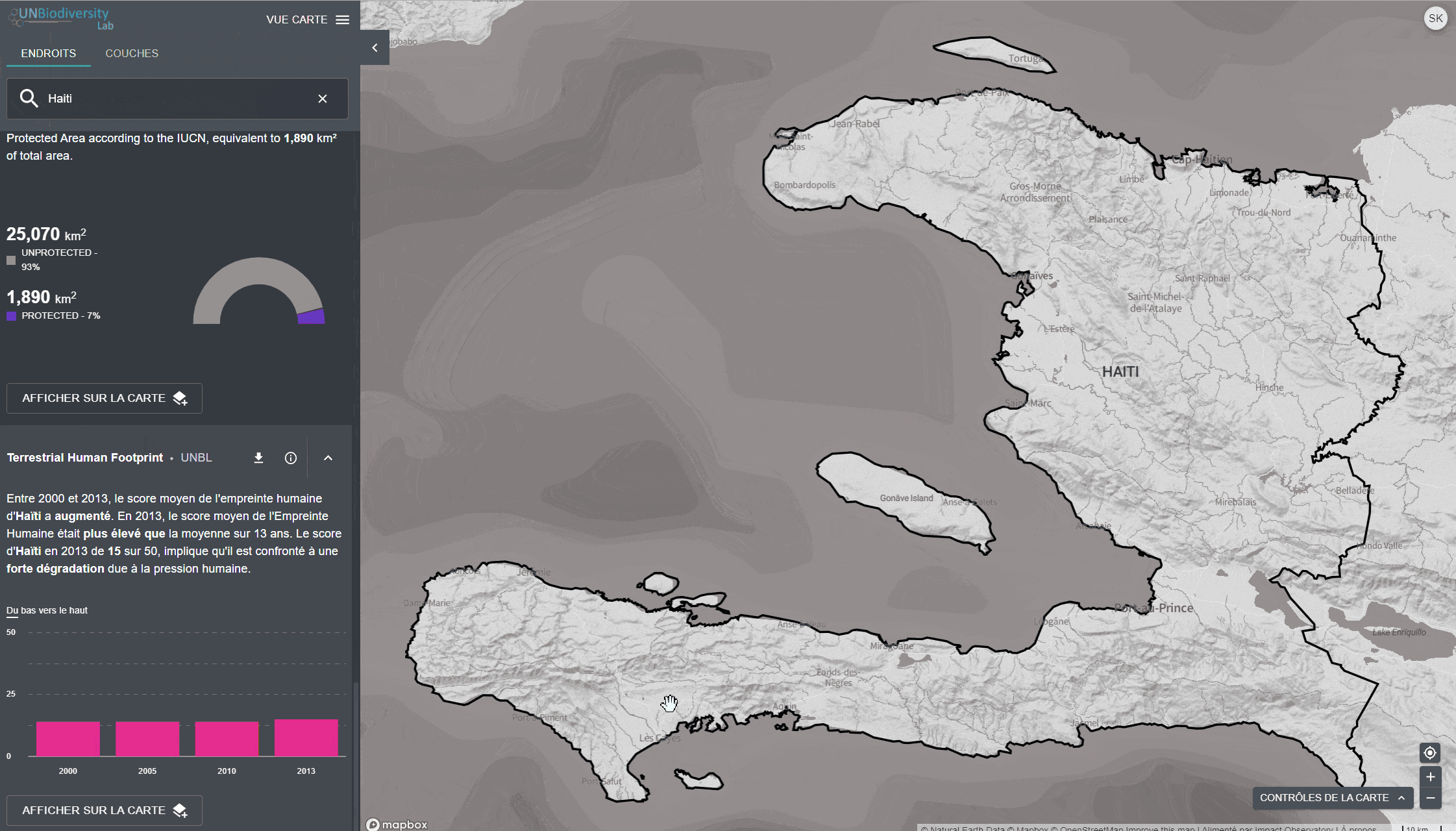
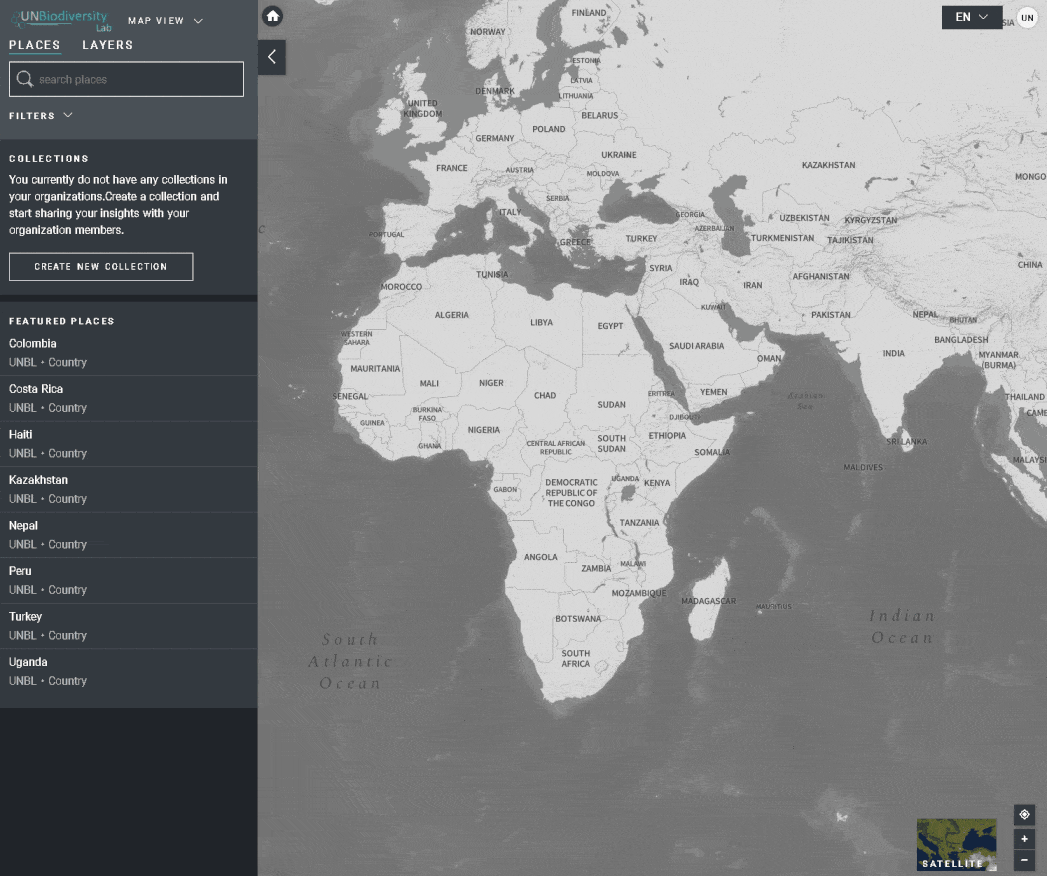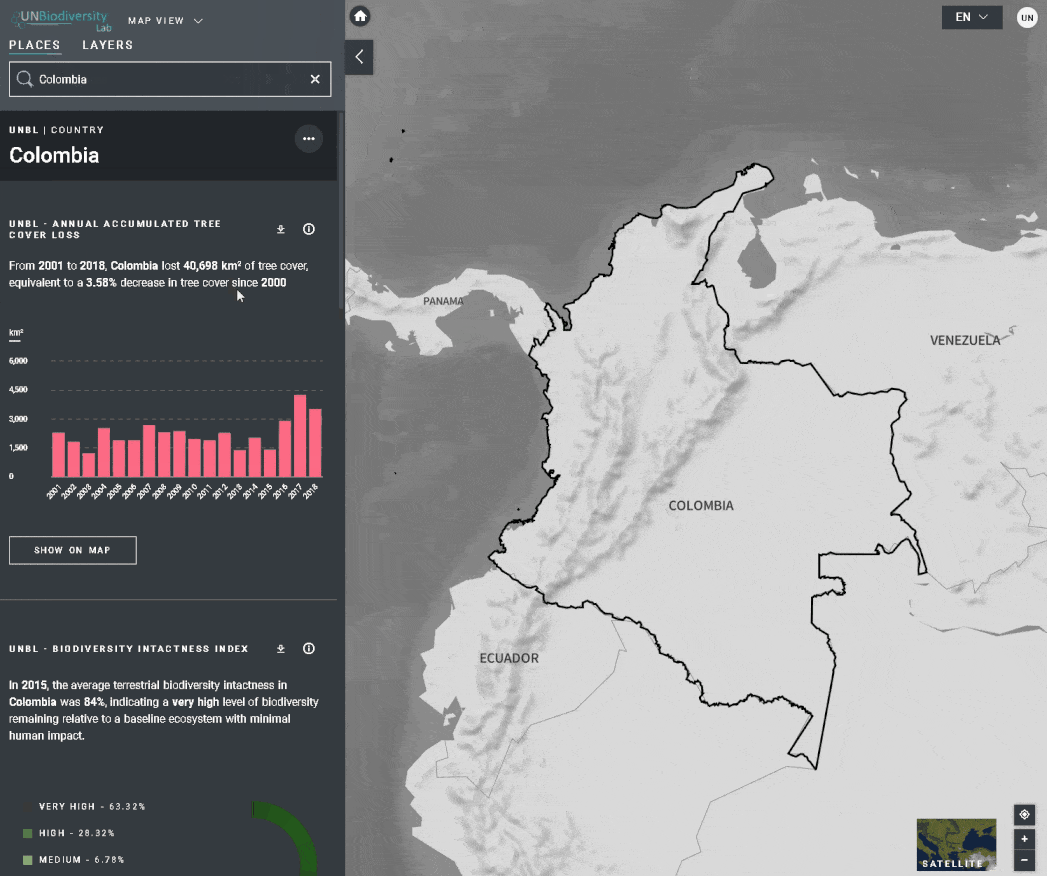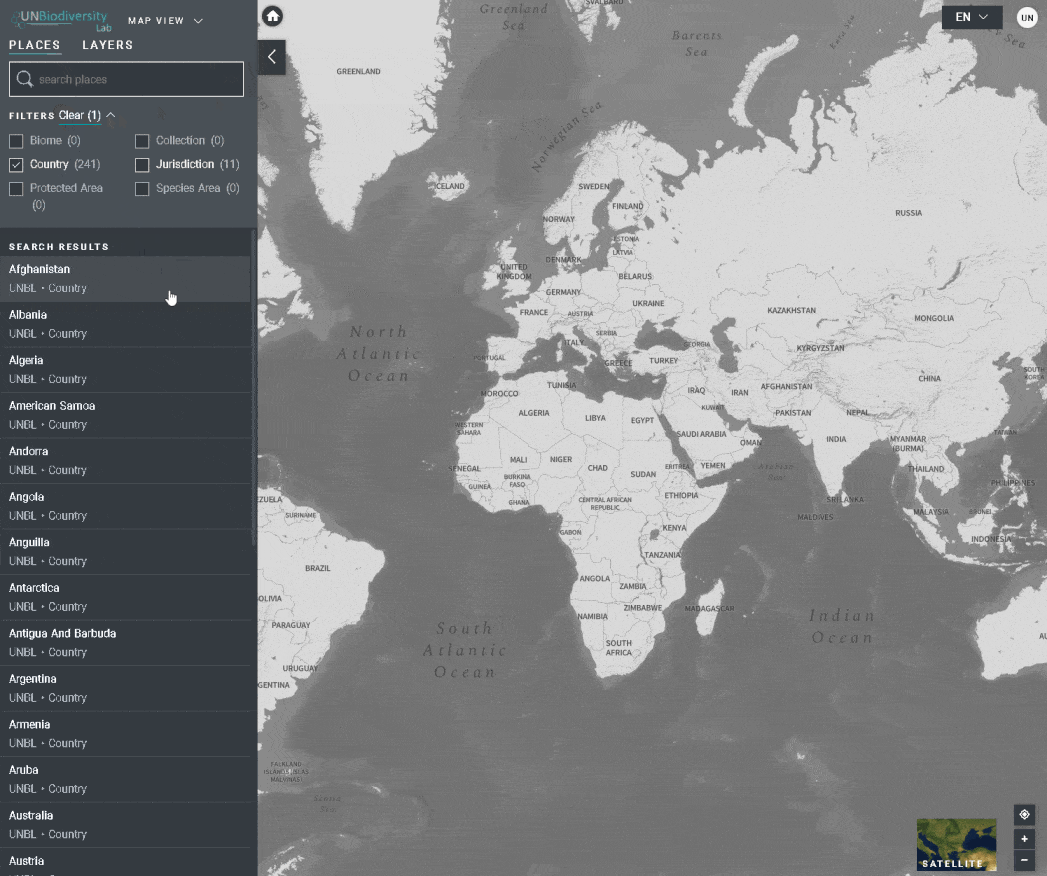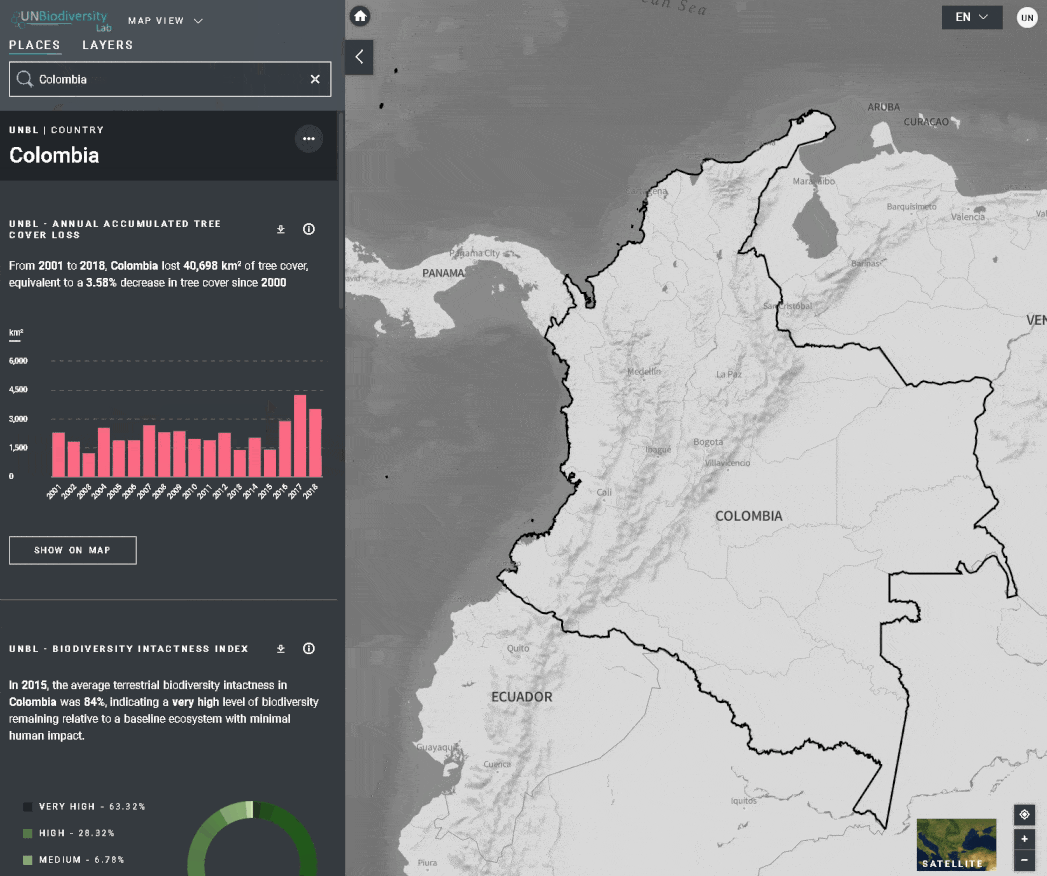
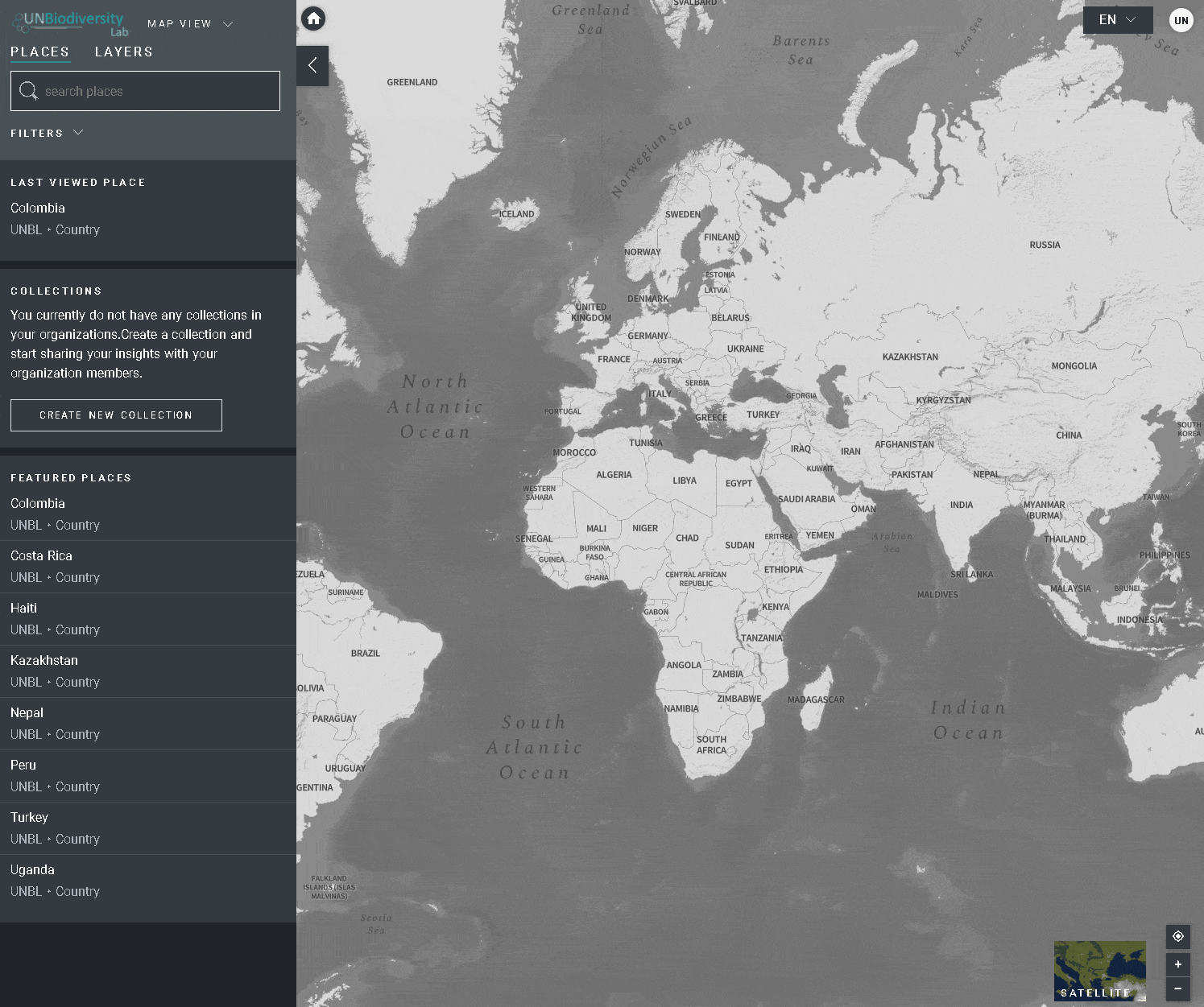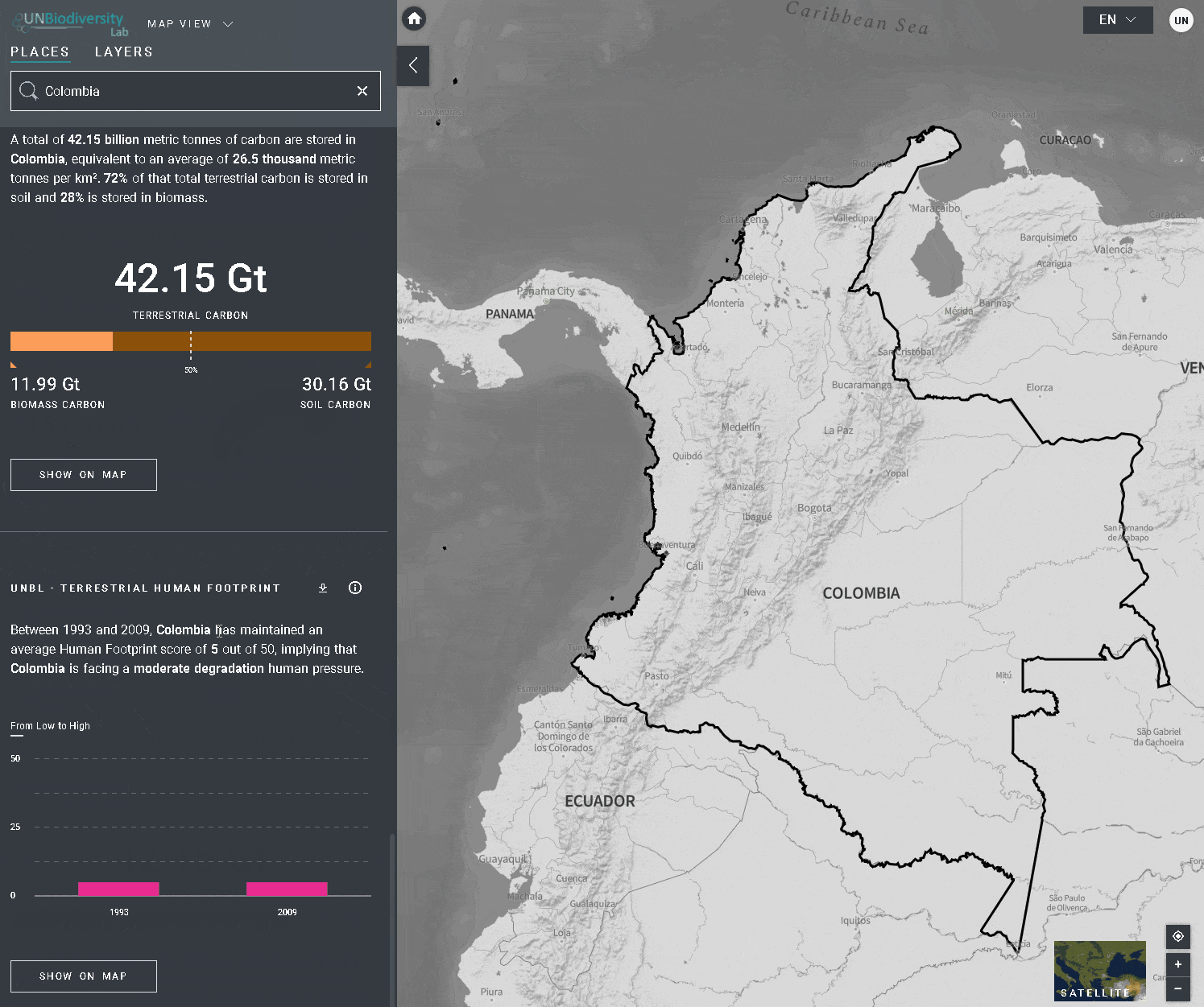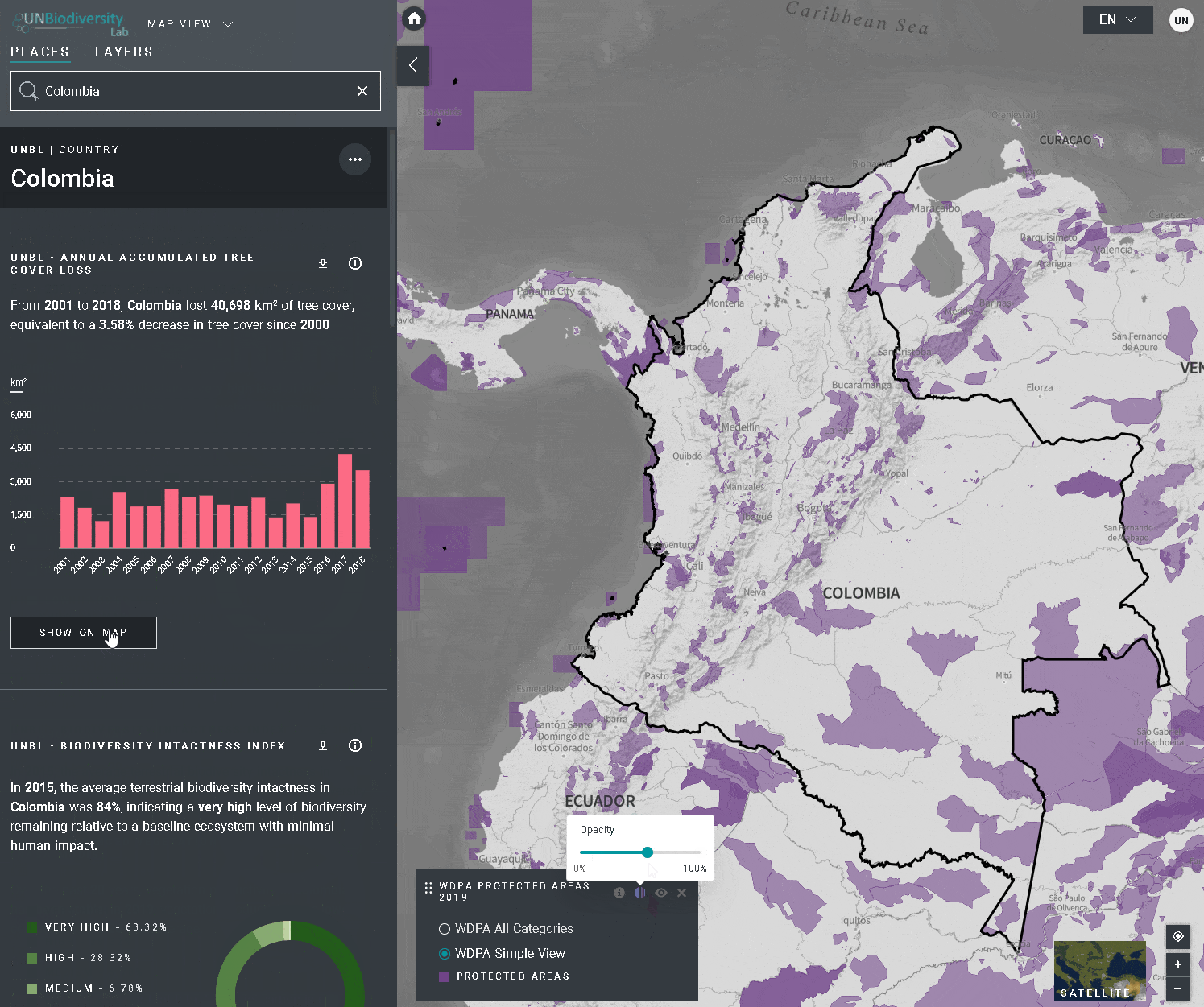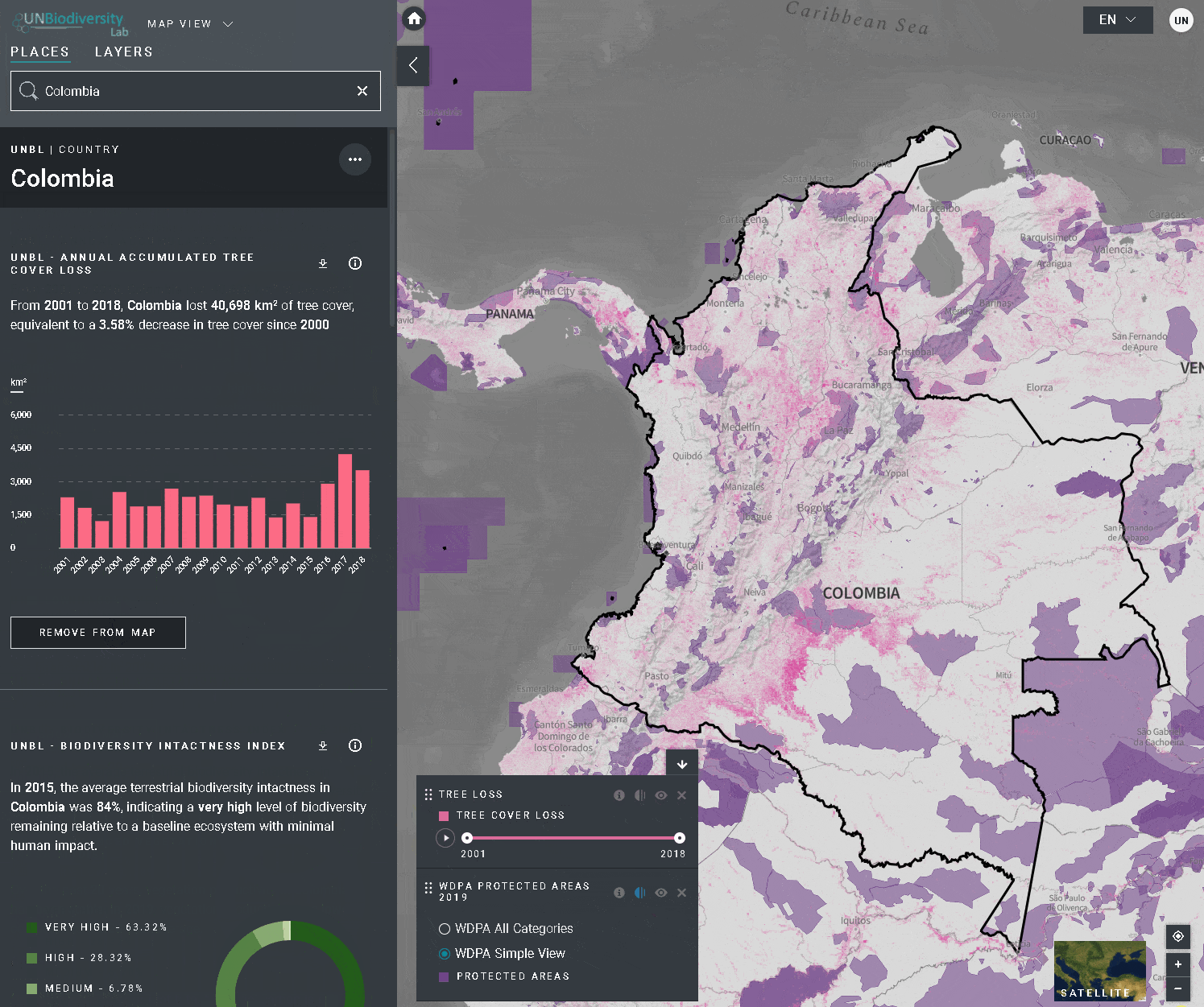
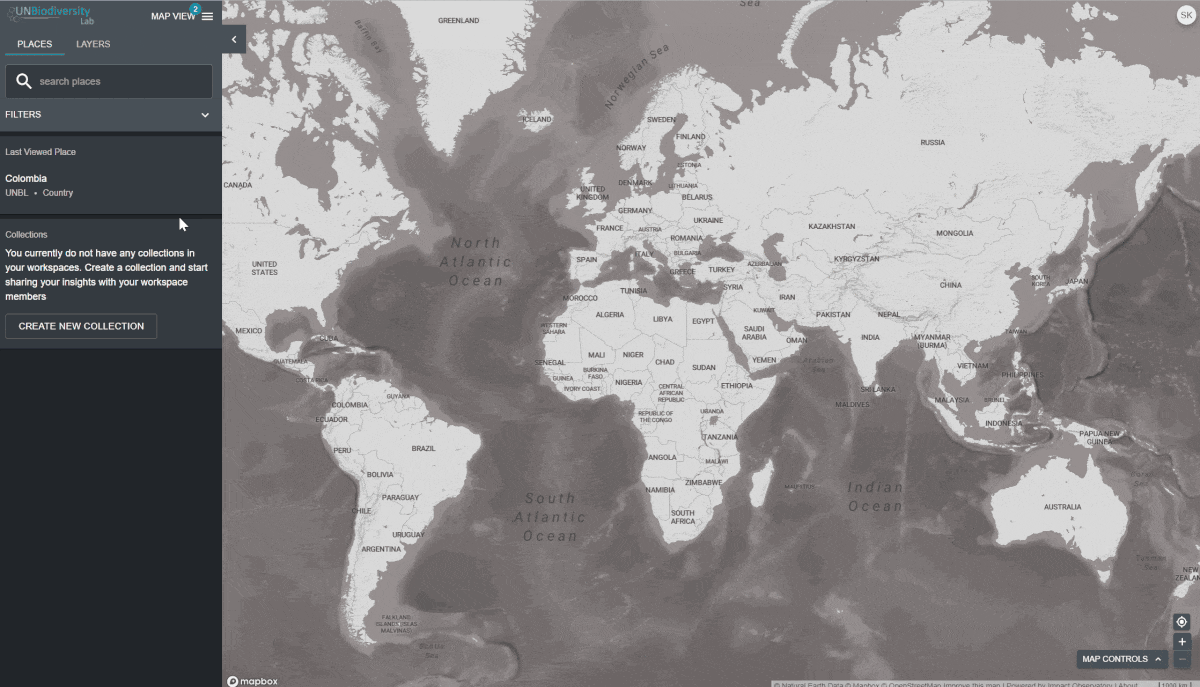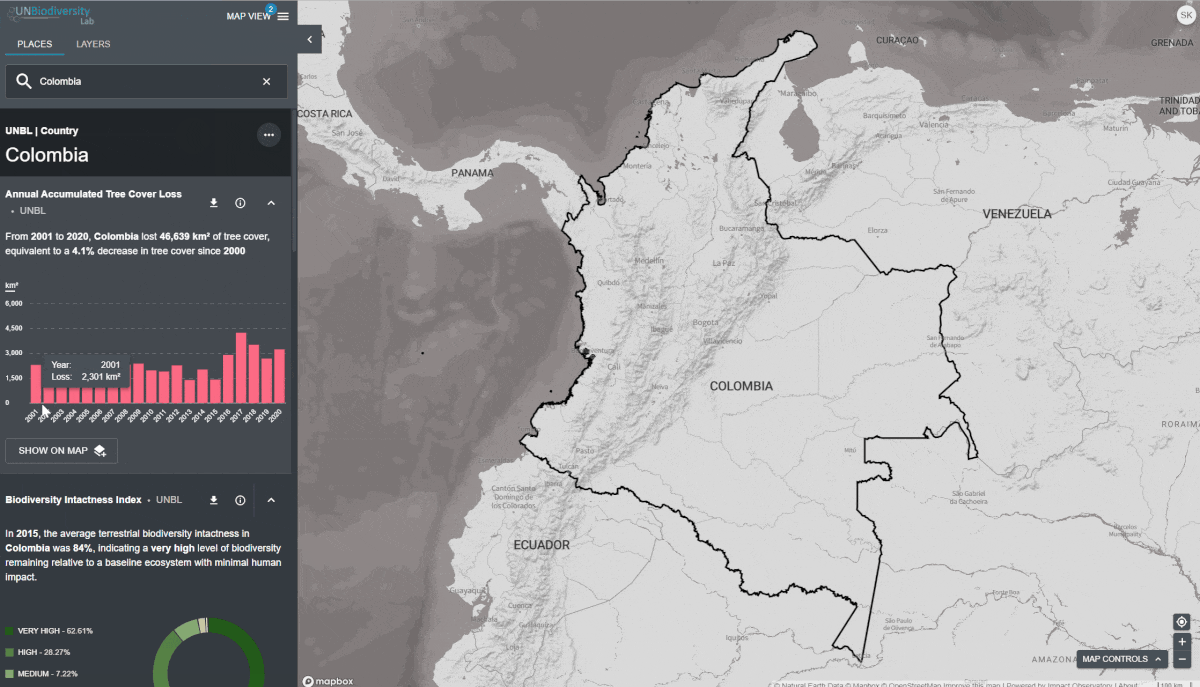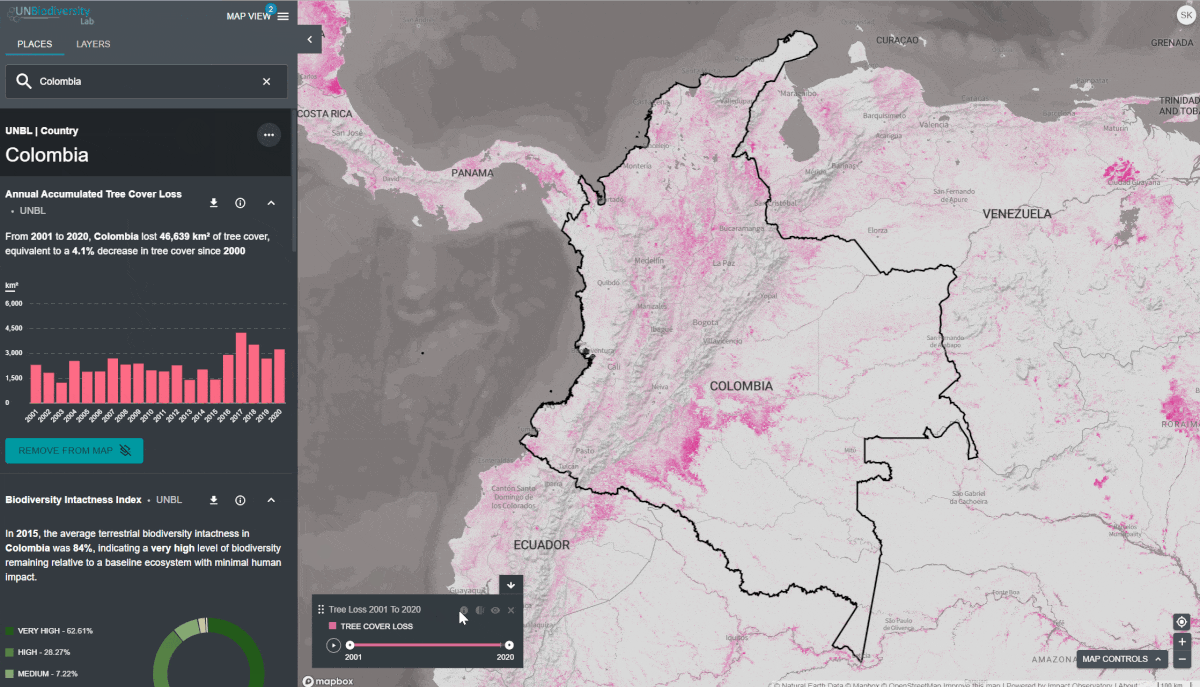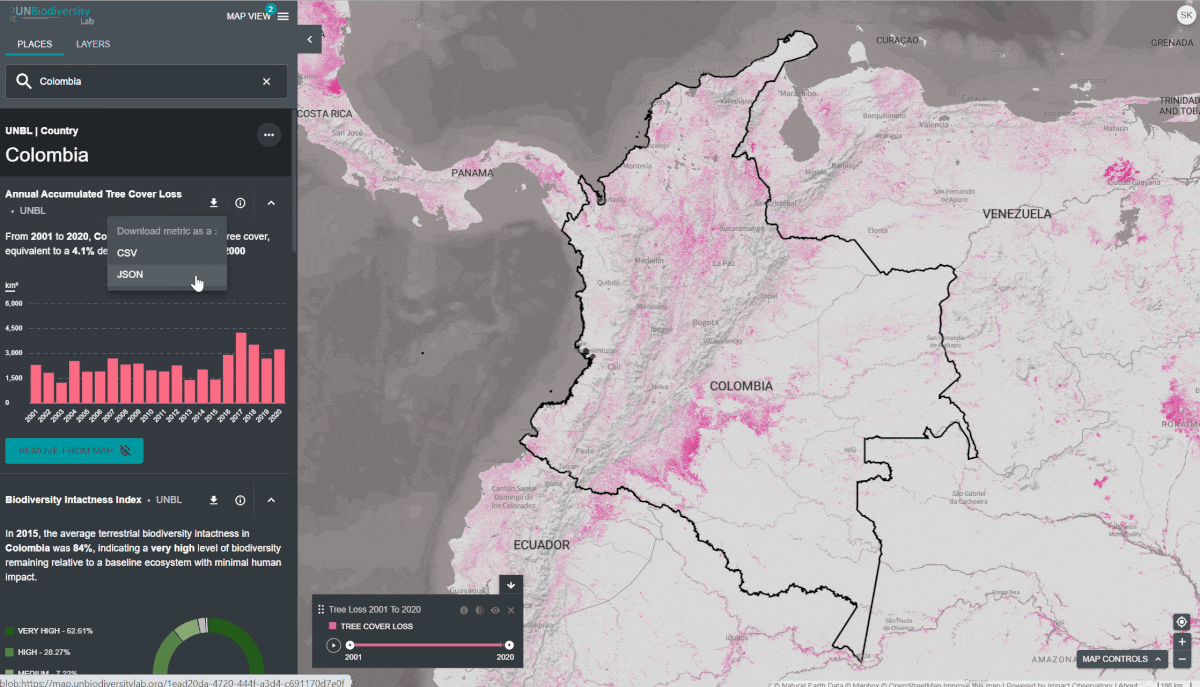
Le UN Biodiversity Lab offre des mesures d’un coup d’œil basées sur les meilleures séries de données spatiales mondiales disponibles. Ces métriques peuvent être utilisées pour rendre compte de l’état de la nature et du développement humain dans votre pays. Les métriques disponibles comprennent:
- Perte de la couverture forestière (2001-2018)
- Indice d’intégrité de la biodiversité (2015)
- Indice de végétation amélioré (2000-2019)
- Couverture terrestre mondiale (2015)
- Nombre d’incendies par mois (2018)
- Zones protégées (2019)
- Densité de carbone terrestre (2010)
- Empreinte humaine terrestre (1993 et 2009)
Pour consulter les métriques sur le site du UNBL:
- Sélectionnez un domaine d’intérêt.
- Examinez les métriques dans le panneau de gauche.
- Cliquez sur l’icône “AFFICHER SUR LA CARTE” si vous souhaitez visualiser cette couche sur la carte. Cliquez sur l’icône SUPPRIMER DE LA CARTE ou sur l’icône de suppression de couche dans la légende pour effacer ce qu’il y a sur l’écran.
- Cliquez sur l’icône
 pour afficher les informations sur les couches. Les pages d’information fournissent une brève description des données, des documents à lire et des liens vers les sources.
pour afficher les informations sur les couches. Les pages d’information fournissent une brève description des données, des documents à lire et des liens vers les sources. - Pour télécharger les données de synthèse de la métrique au format .csv ou .json, cliquez sur l’icône en forme de flèche
 . Vous pouvez également télécharger les données à partir des liens de source sur les pages d’information des couches.
. Vous pouvez également télécharger les données à partir des liens de source sur les pages d’information des couches.
- Sélectionnez la couche et chargez-la sur la carte.
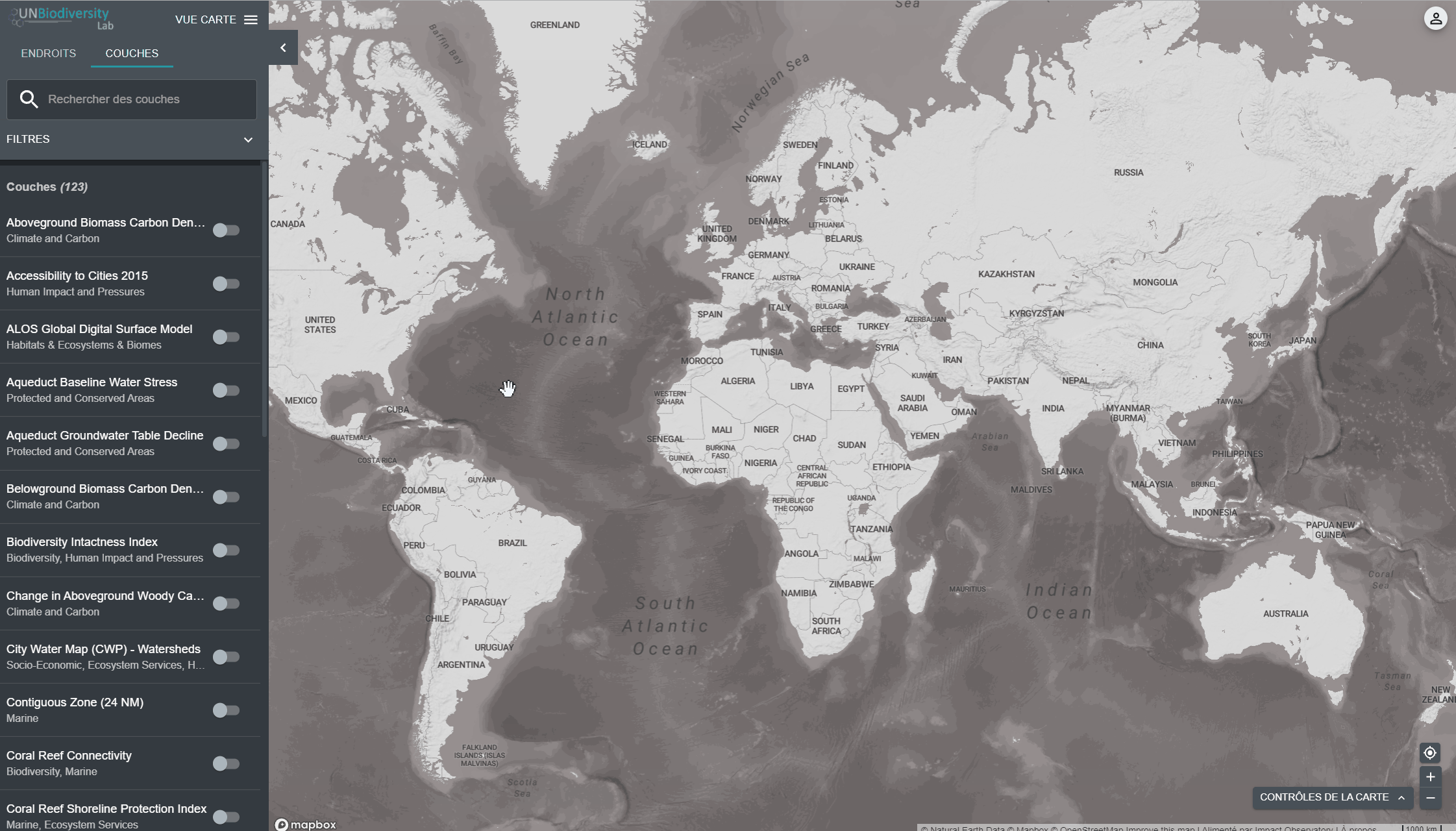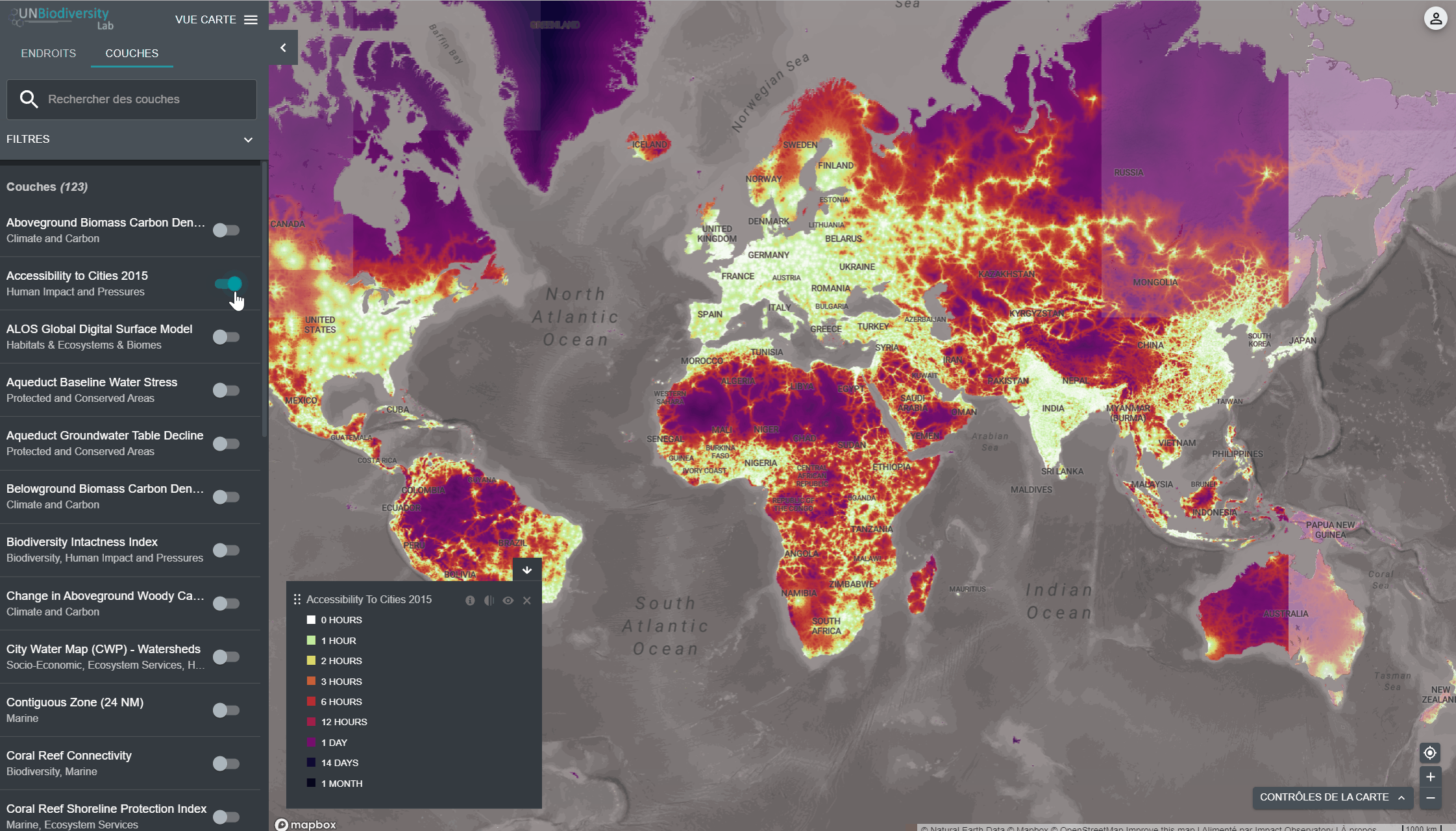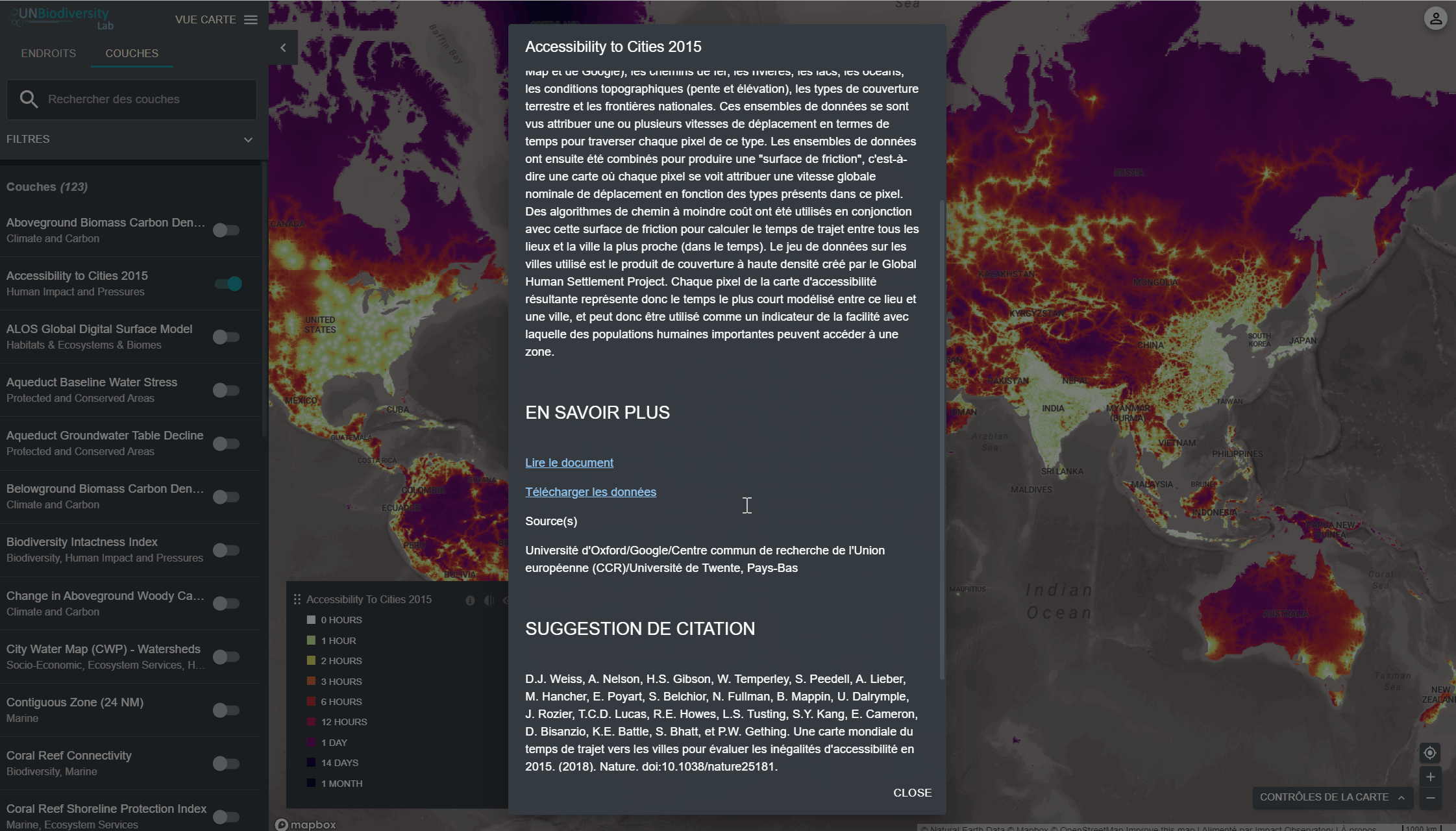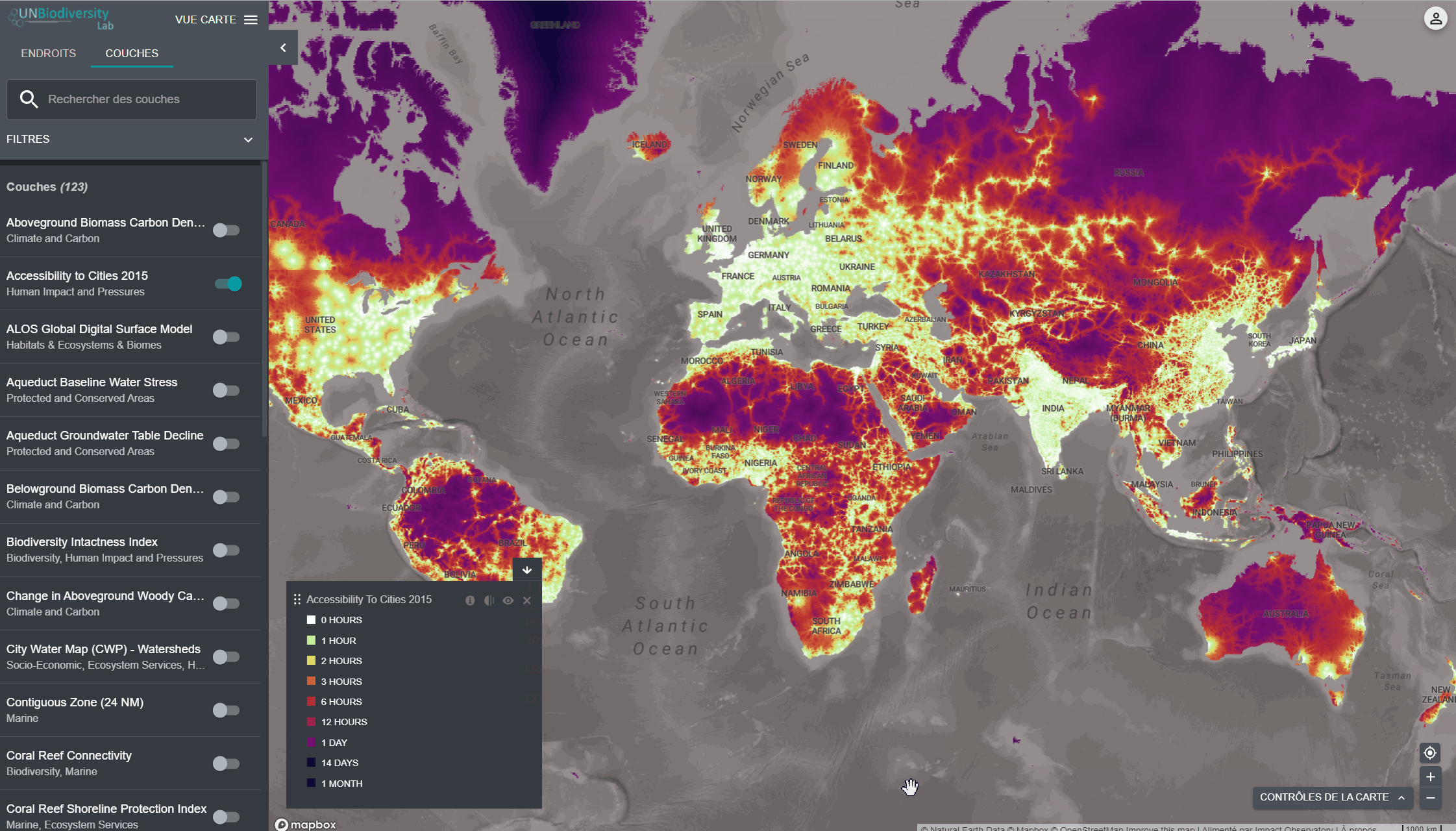
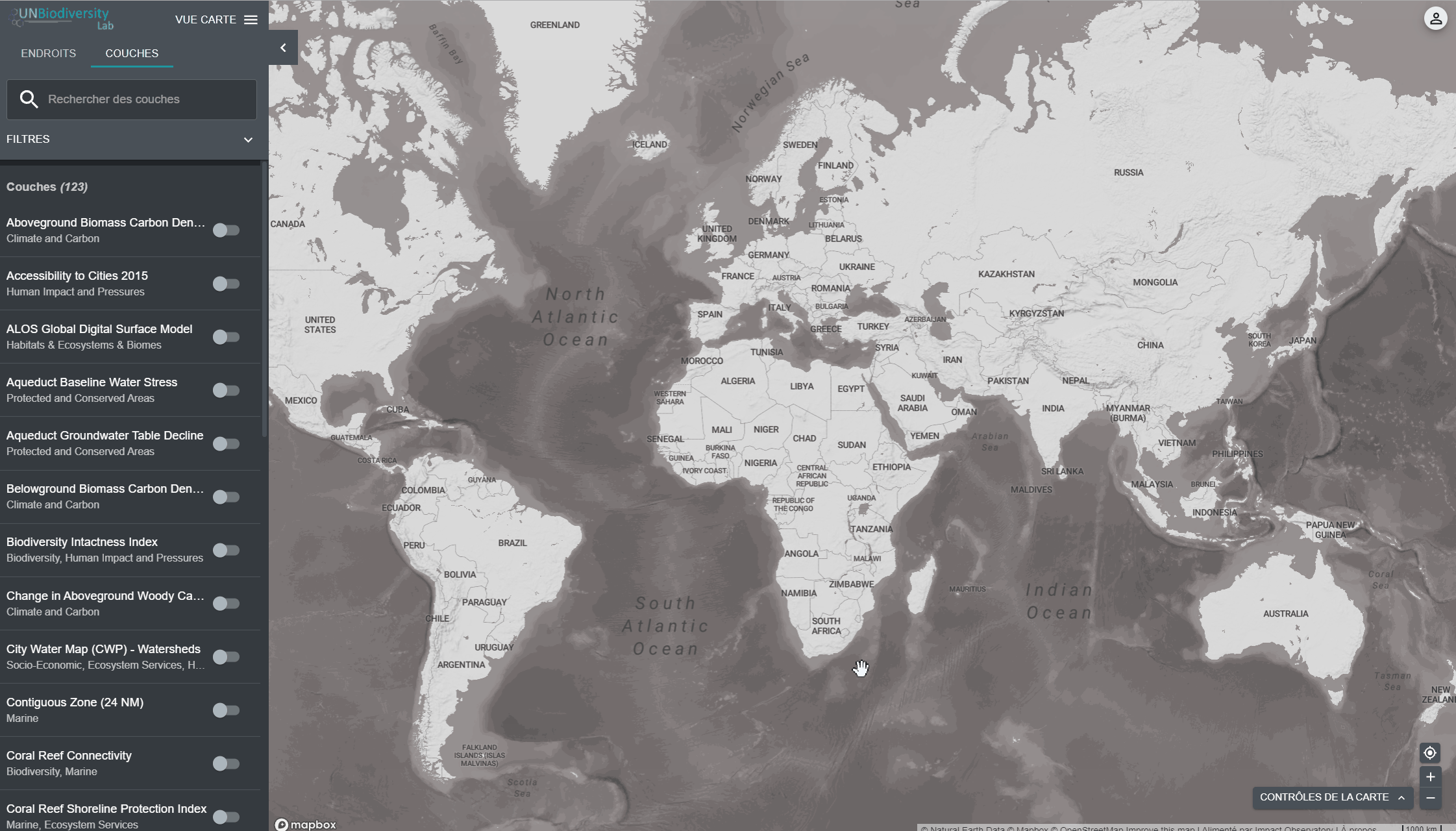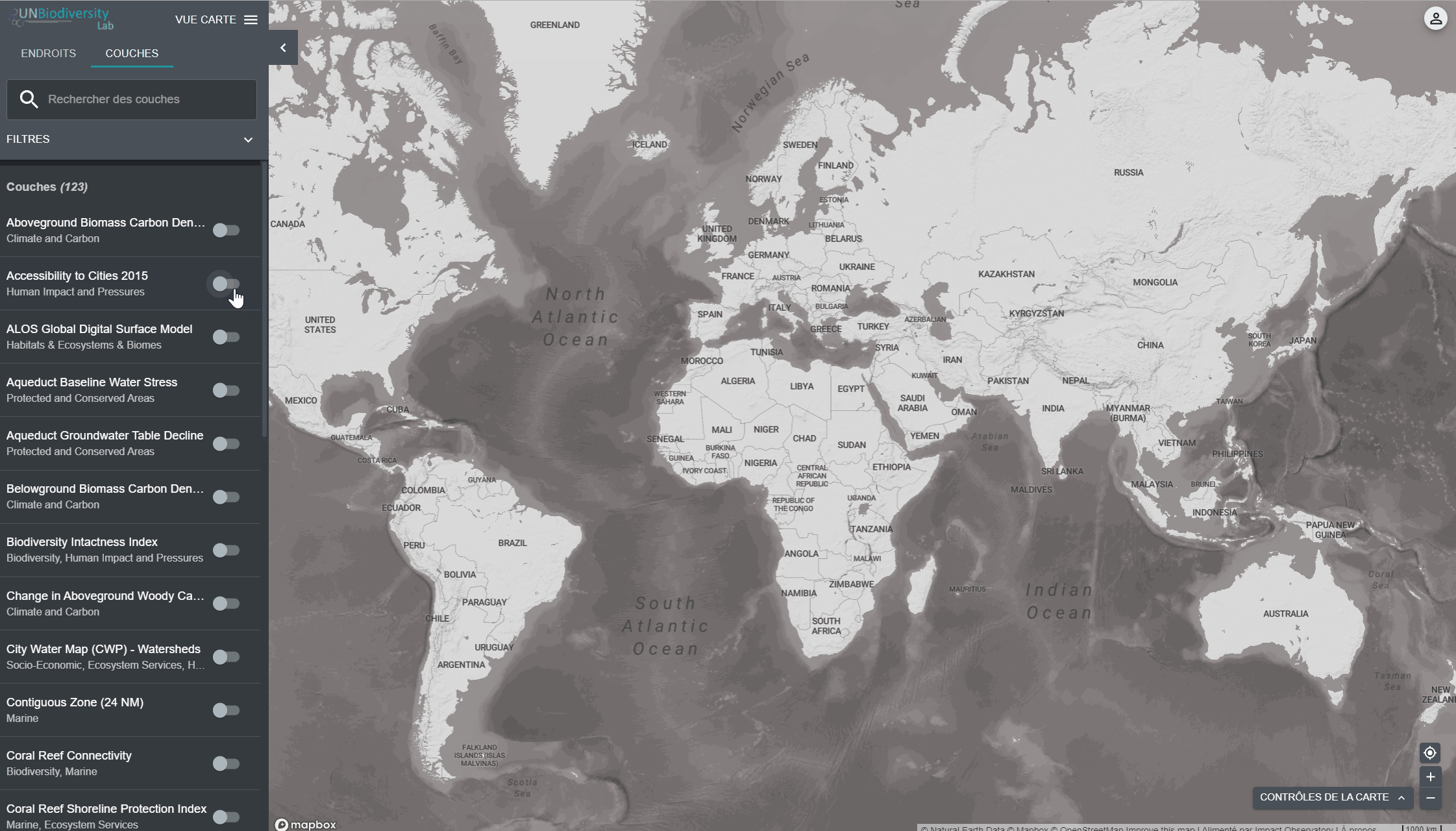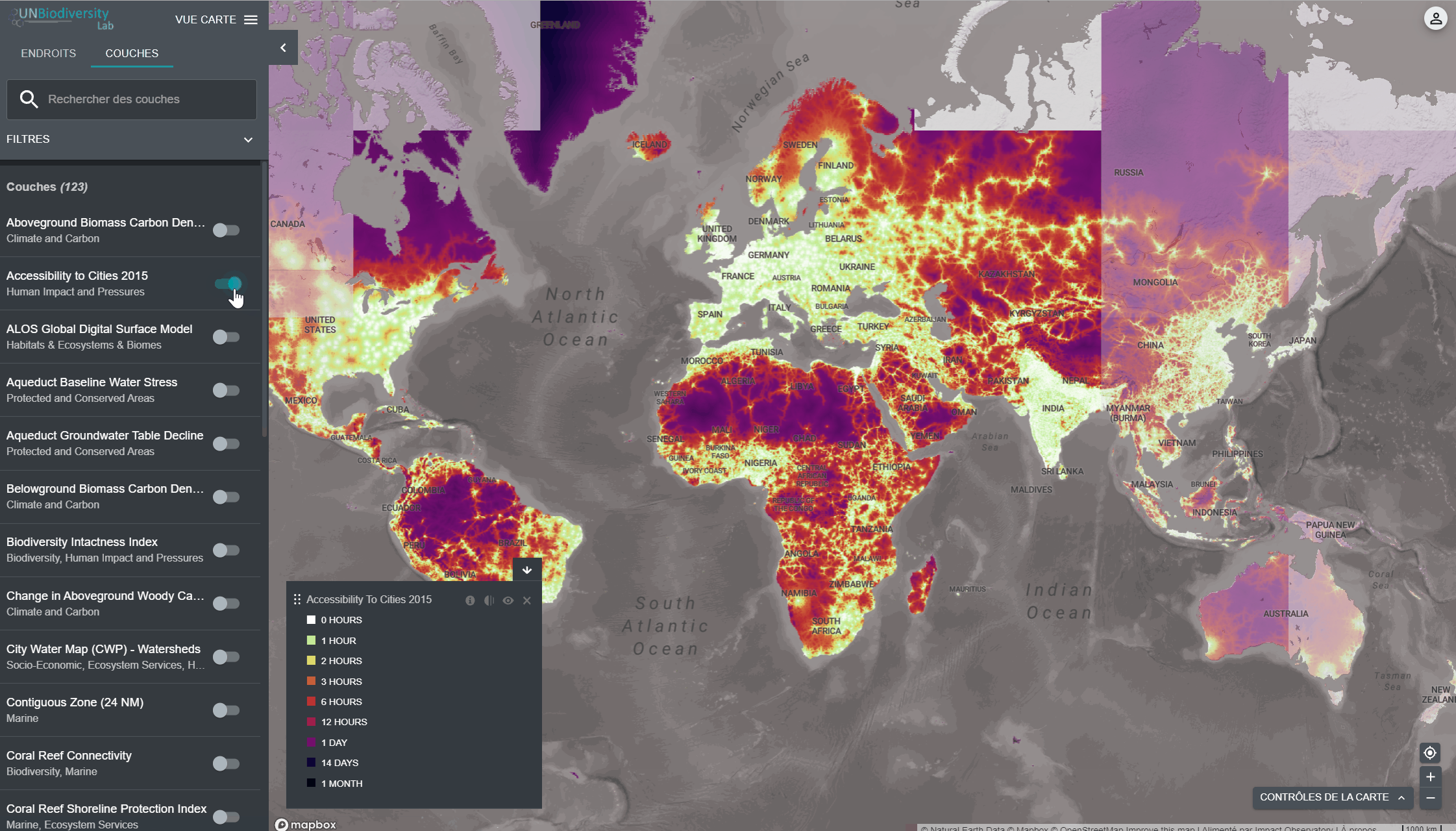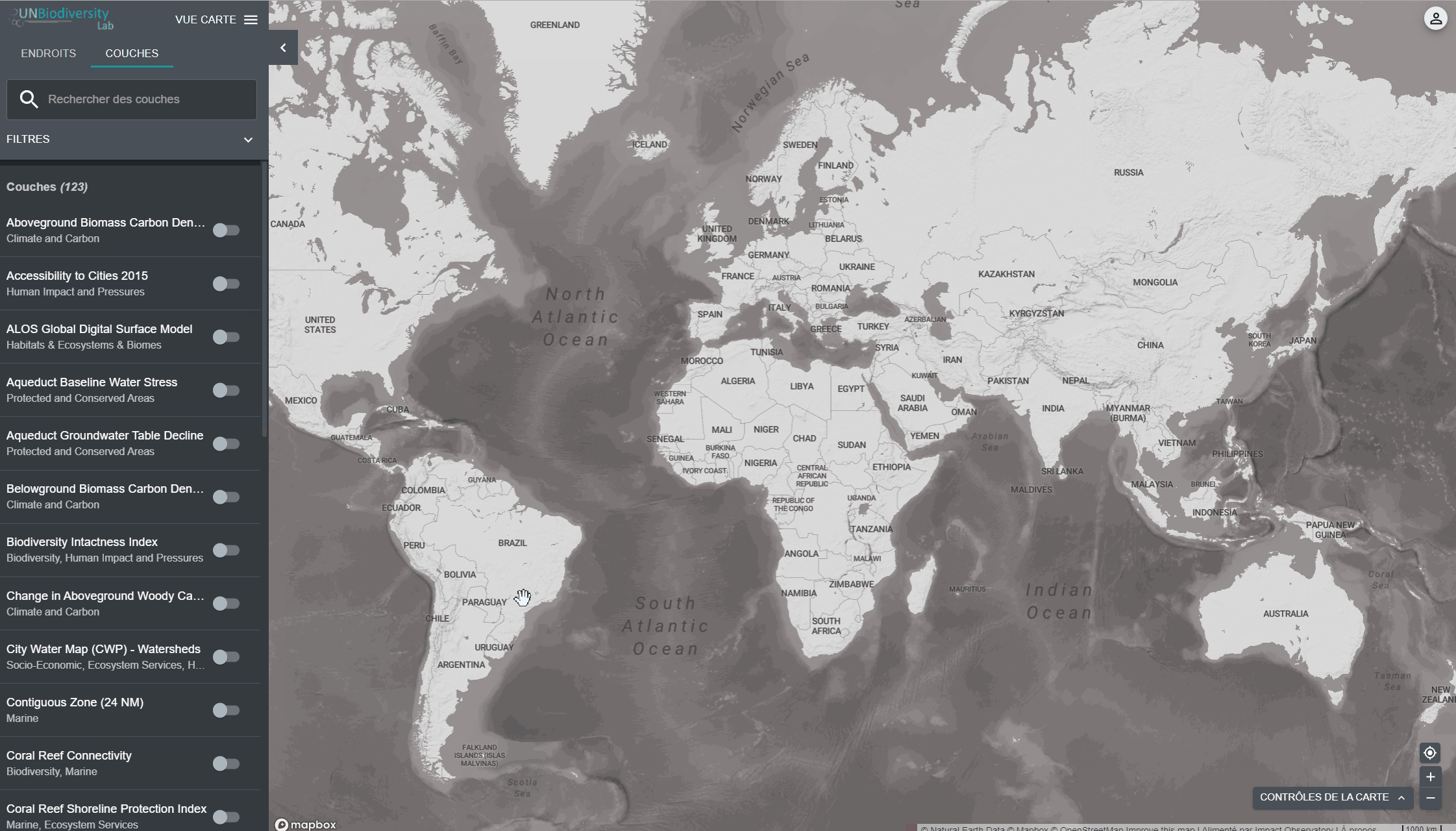
- Dans le coin gauche de la carte, il y aura une légende montrant le nom et la symbologie des couches de données sur la carte.
- Cliquez sur l’icône pour afficher les informations sur les couches. Les informations fournissent une description de la couche, l’organisation de la source, les citations et les liens pour télécharger les données.
Lorsque vous sélectionnez plusieurs couches, vous pouvez personnaliser la carte en ajustant leur ordre de superposition et leur opacité:
- Pour changer l’ordre de superposition, cliquez sur l’icône
 à gauche du nom de la couche dans la légende et déplacez l’icône vers le haut ou vers le bas, selon votre préférence. La couche supérieure de la légende sera la couche supérieure de la carte.
à gauche du nom de la couche dans la légende et déplacez l’icône vers le haut ou vers le bas, selon votre préférence. La couche supérieure de la légende sera la couche supérieure de la carte. - Pour modifier l’opacité, cliquez sur l’icône
 . La réduction de l’opacité augmente la transparence de la couche. Par exemple, pour visualiser à la fois la perte de couverture des arbres et les zones protégées, vous pouvez positionner la couche de perte de couverture des arbres au-dessus de la couche des zones protégées, et ajuster l’opacité des zones protégées à 60 %. Cela permet de créer une carte qui montre la perte de couverture arborée dans les zones protégées, ainsi que la perte globale à travers le pays.
. La réduction de l’opacité augmente la transparence de la couche. Par exemple, pour visualiser à la fois la perte de couverture des arbres et les zones protégées, vous pouvez positionner la couche de perte de couverture des arbres au-dessus de la couche des zones protégées, et ajuster l’opacité des zones protégées à 60 %. Cela permet de créer une carte qui montre la perte de couverture arborée dans les zones protégées, ainsi que la perte globale à travers le pays. - Pour masquer temporairement une couche sur la carte, cliquez sur l’icône
 . Pour la rendre à nouveau visible, cliquez sur l’icône
. Pour la rendre à nouveau visible, cliquez sur l’icône 
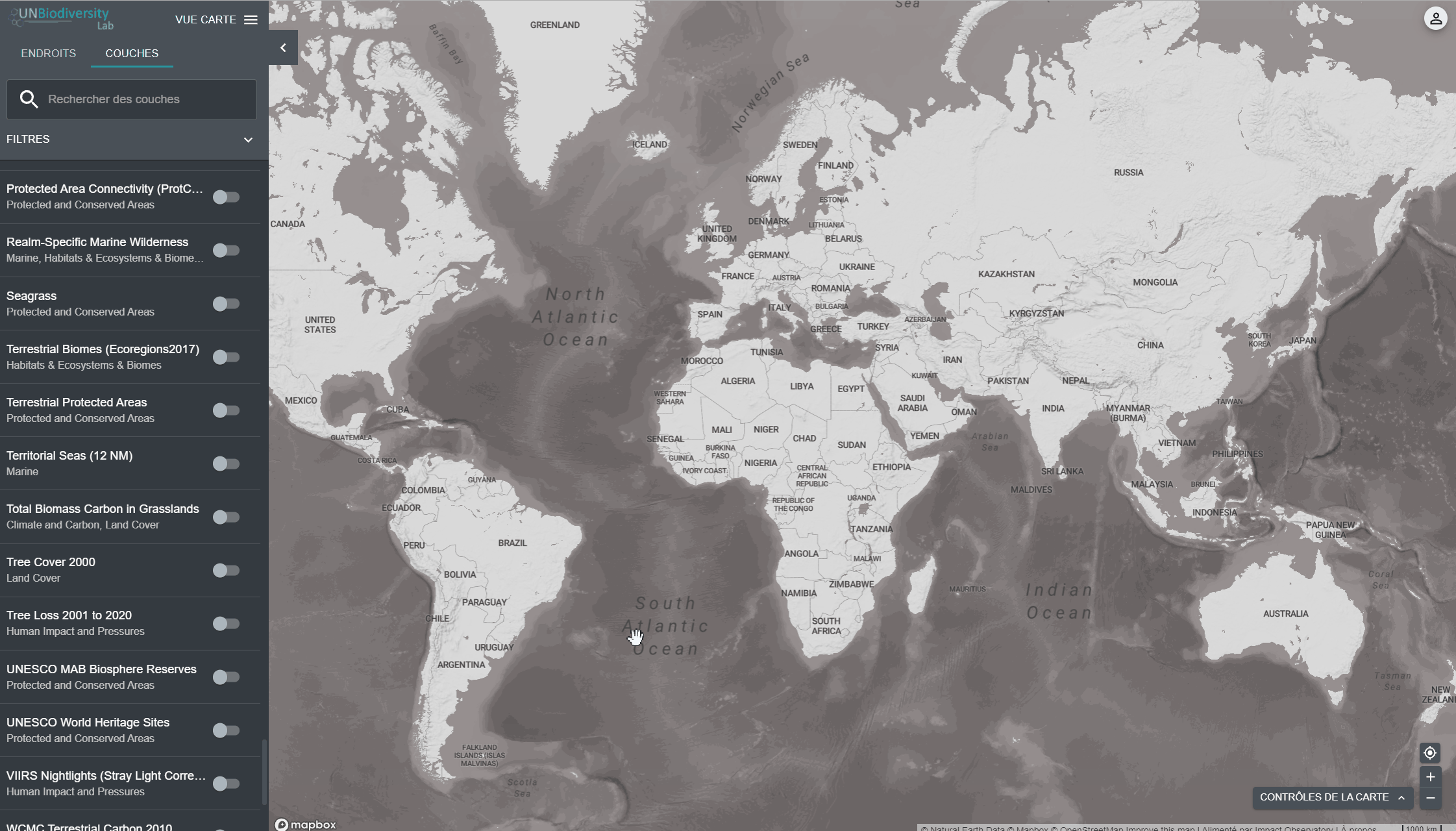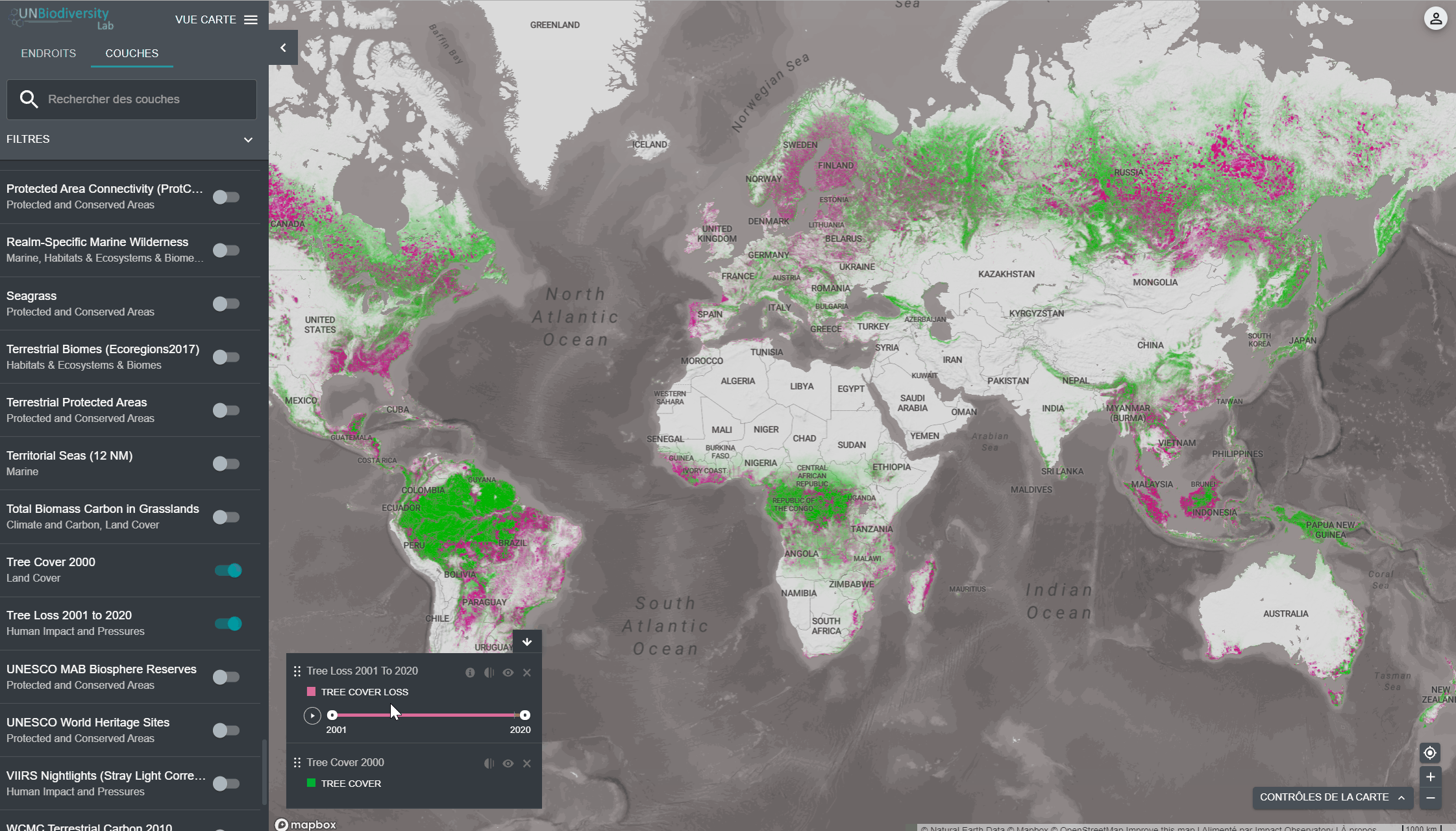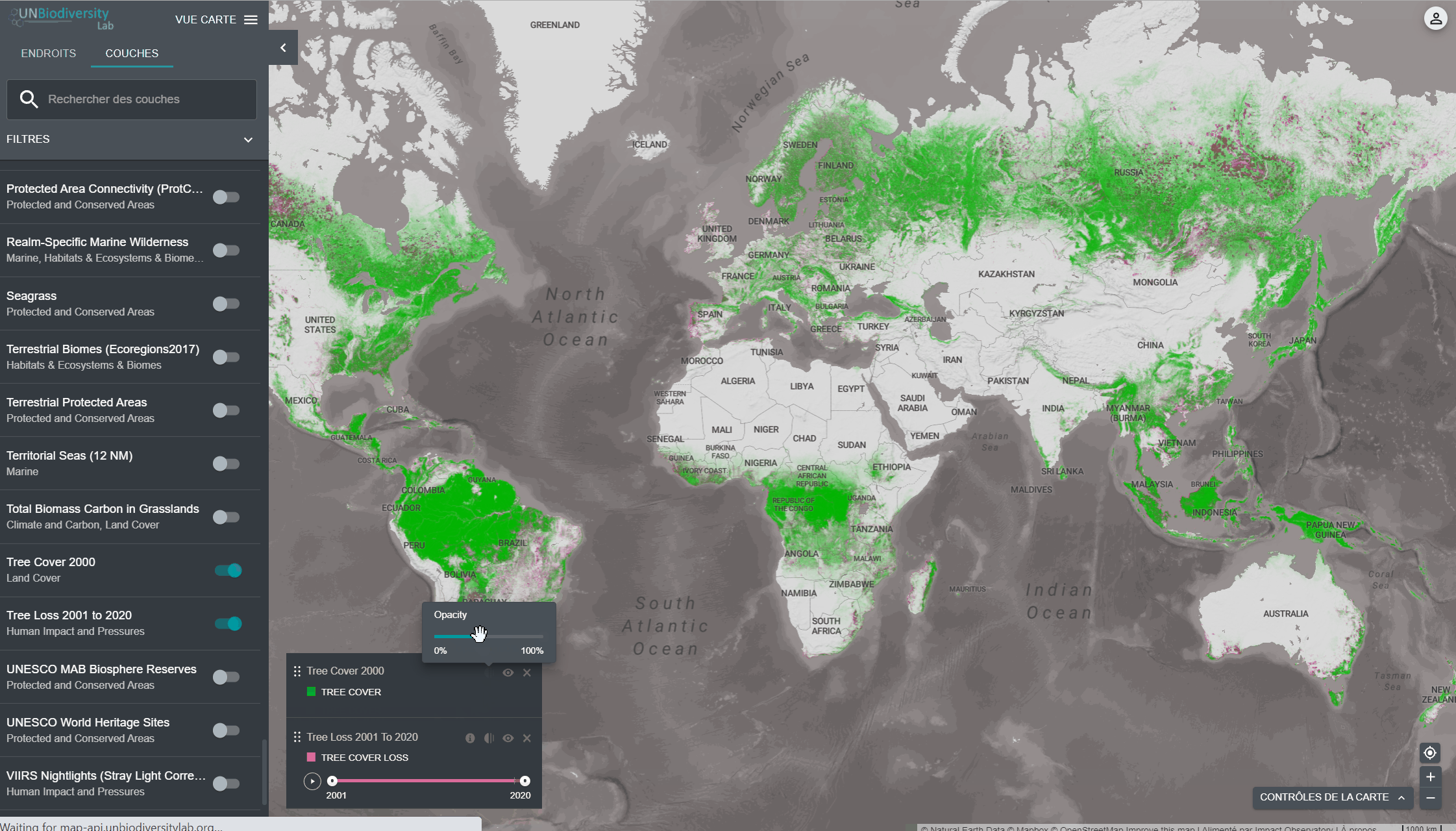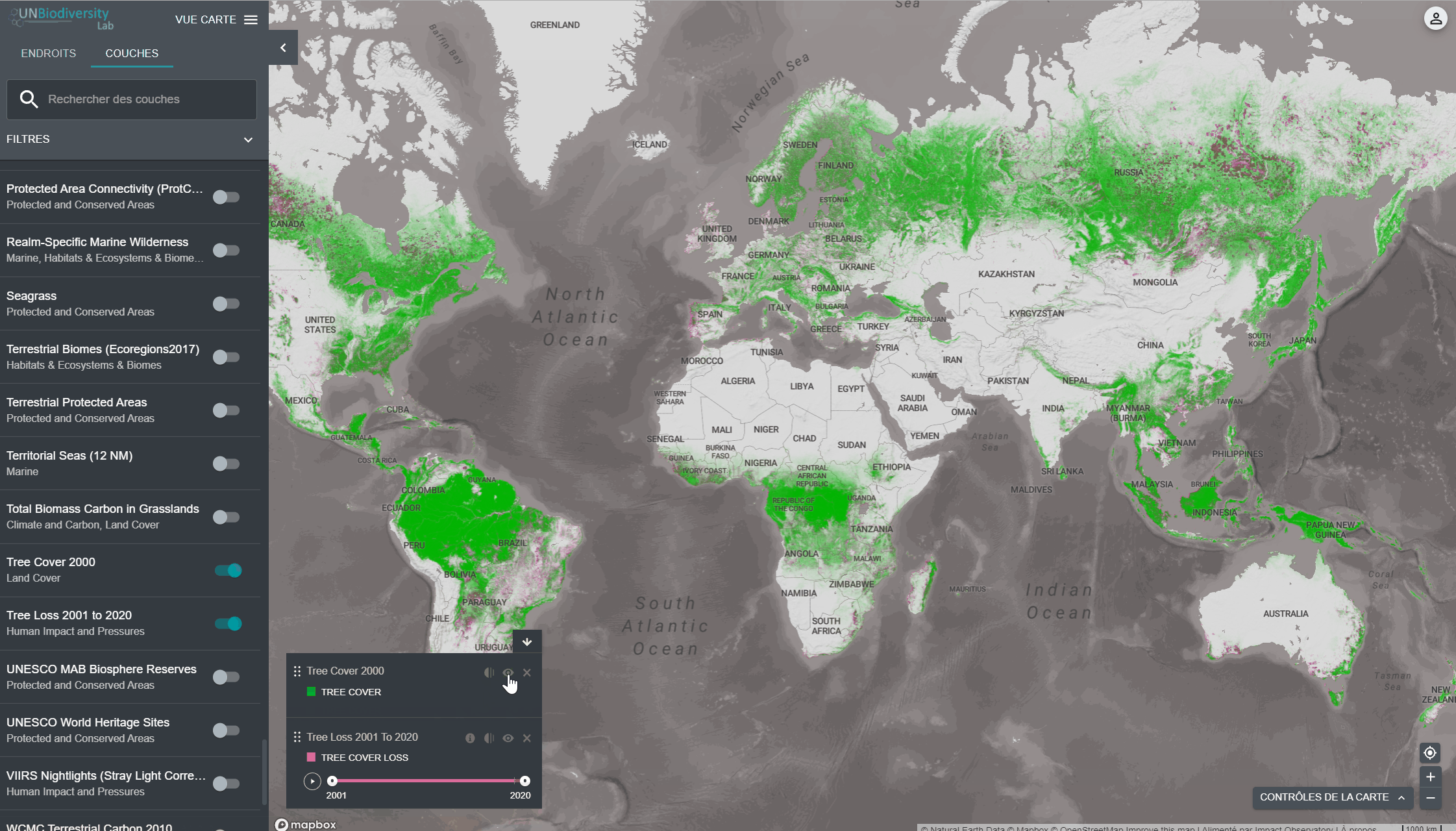
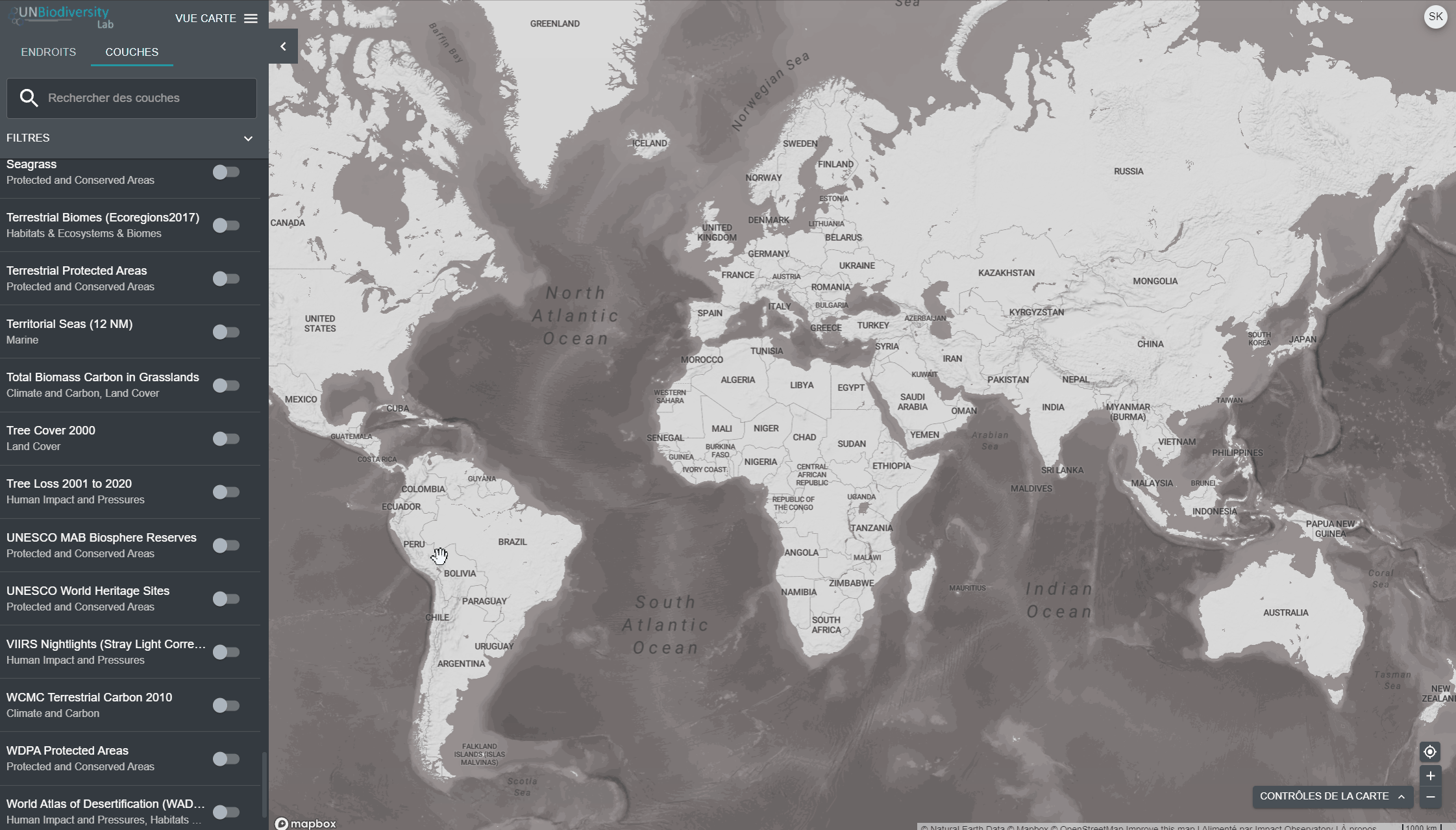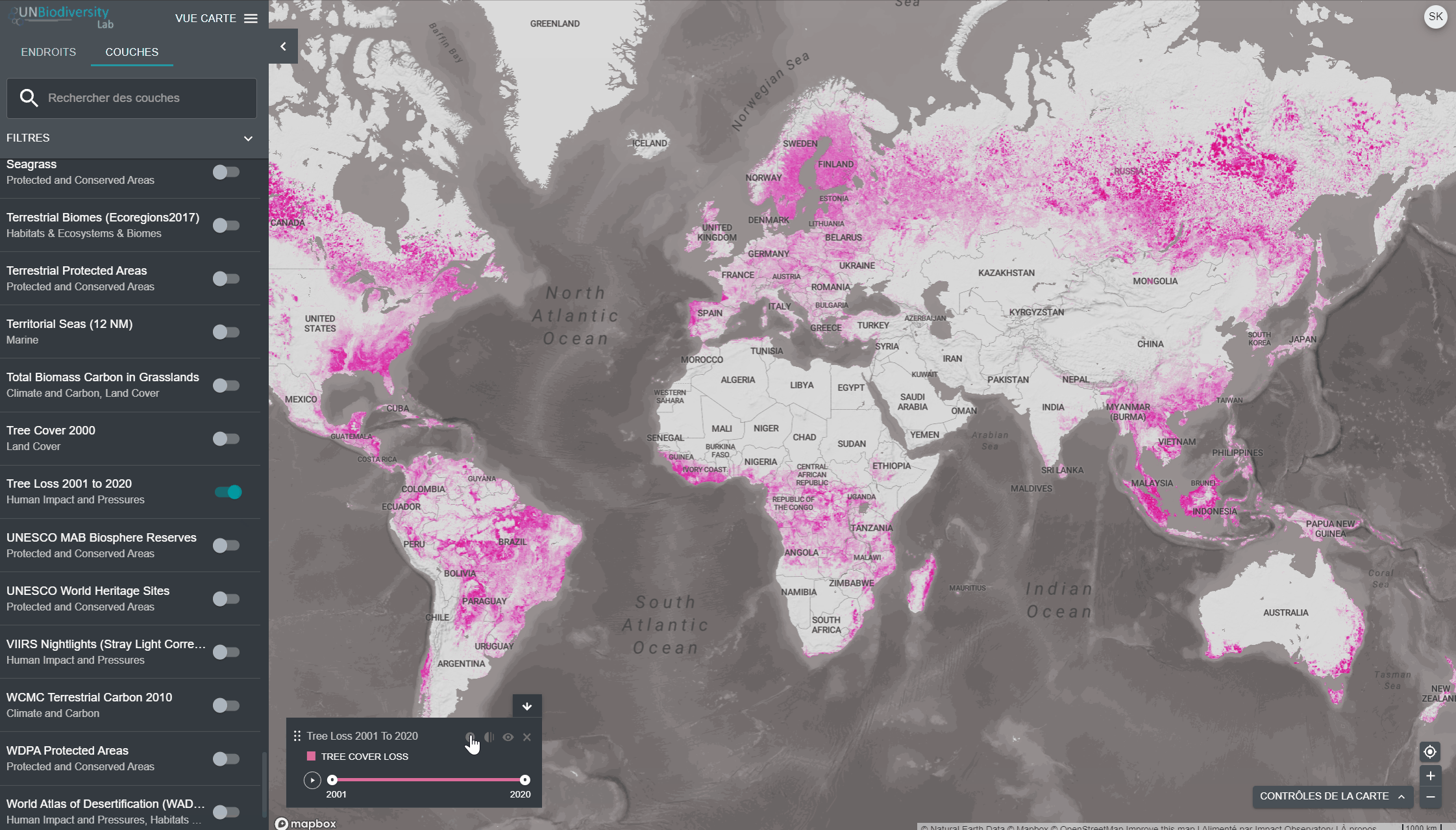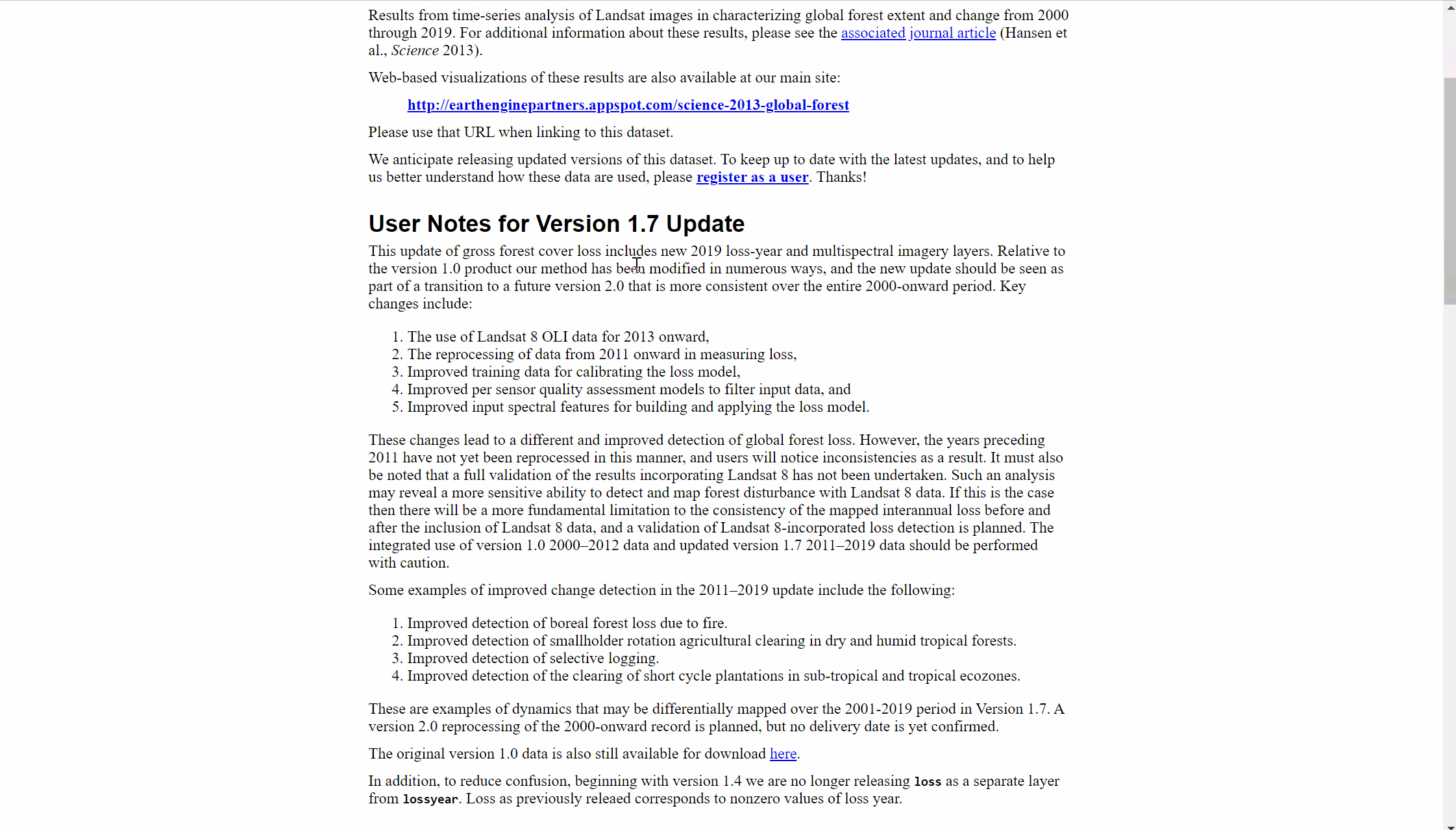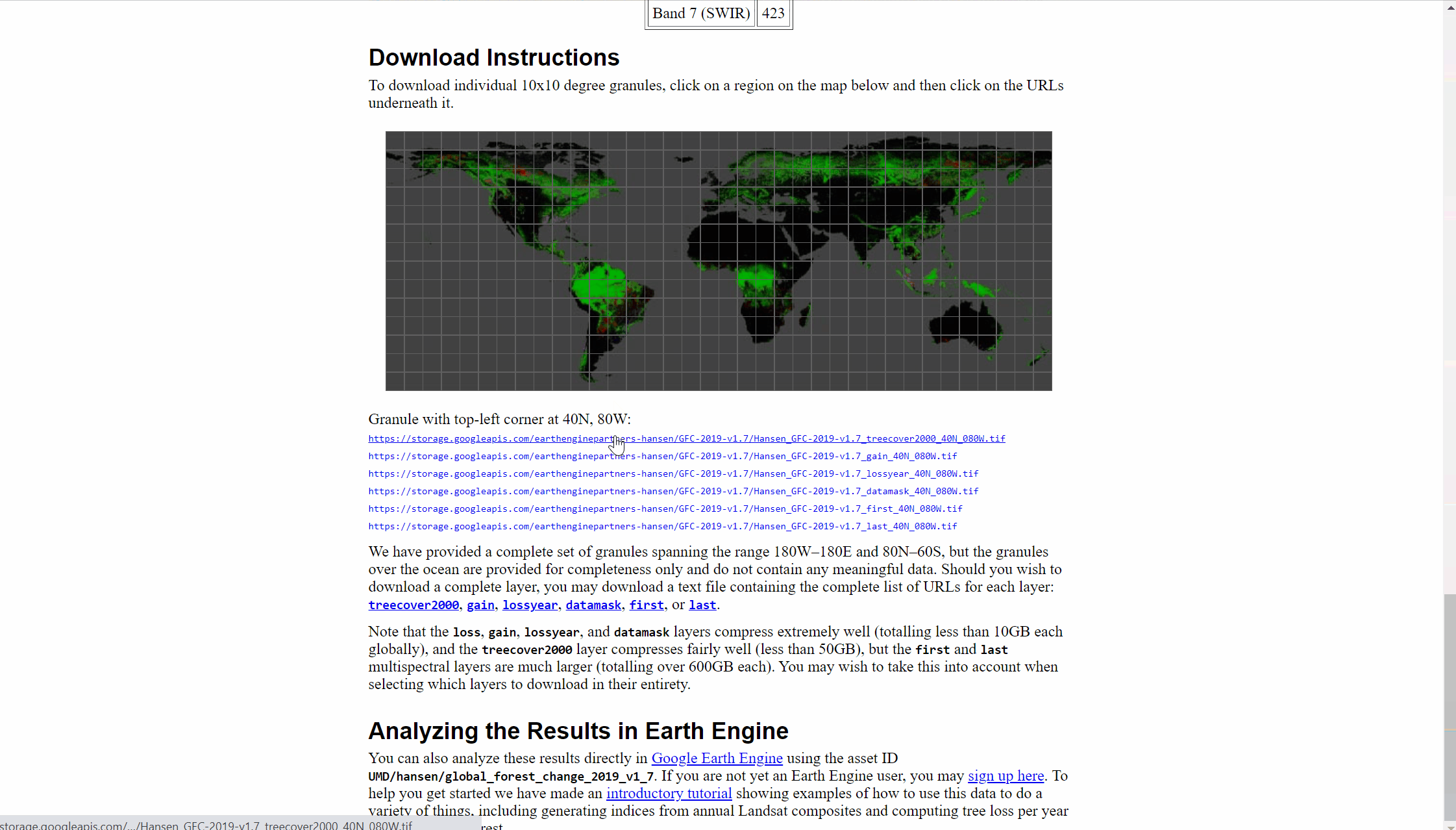
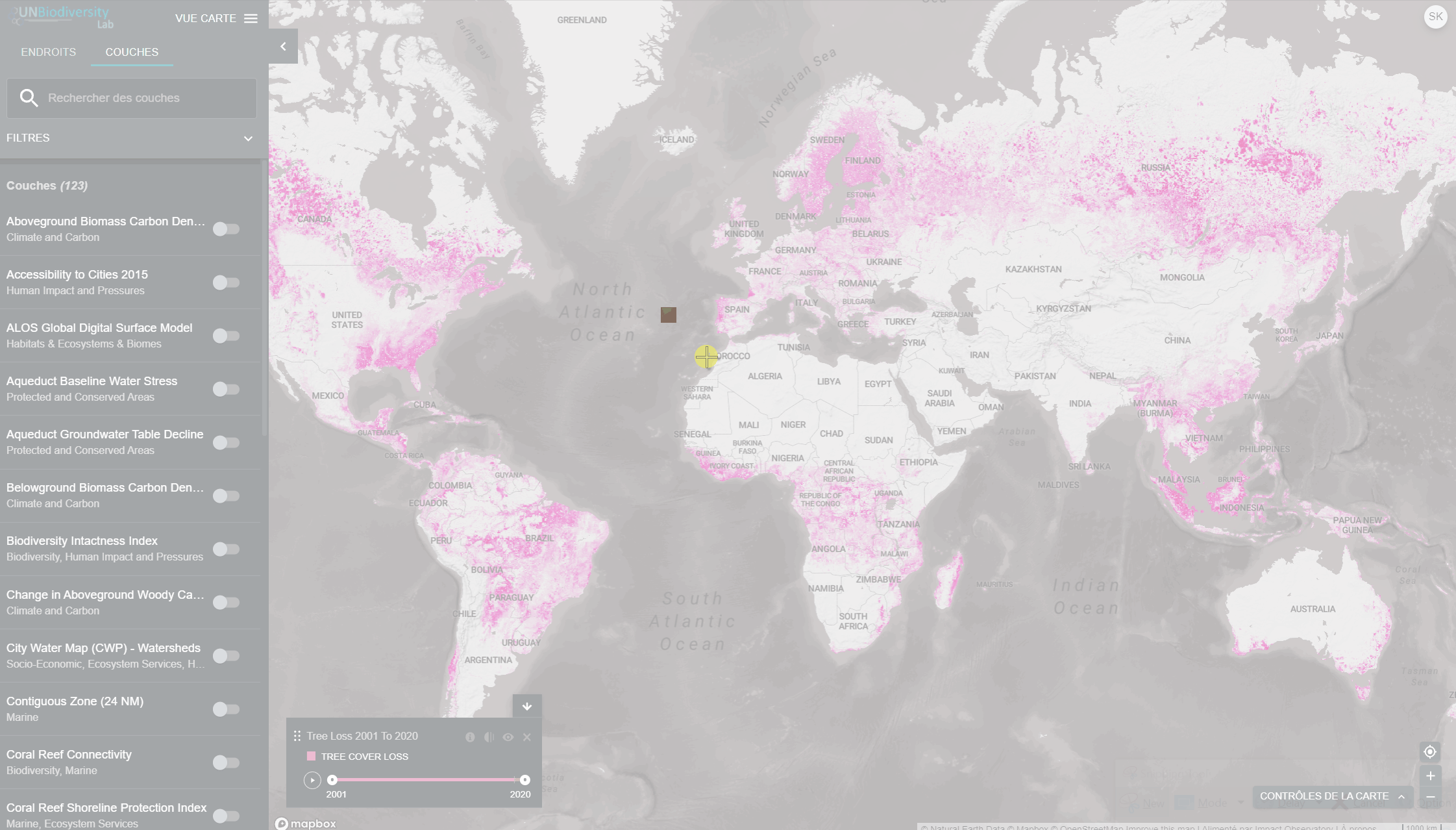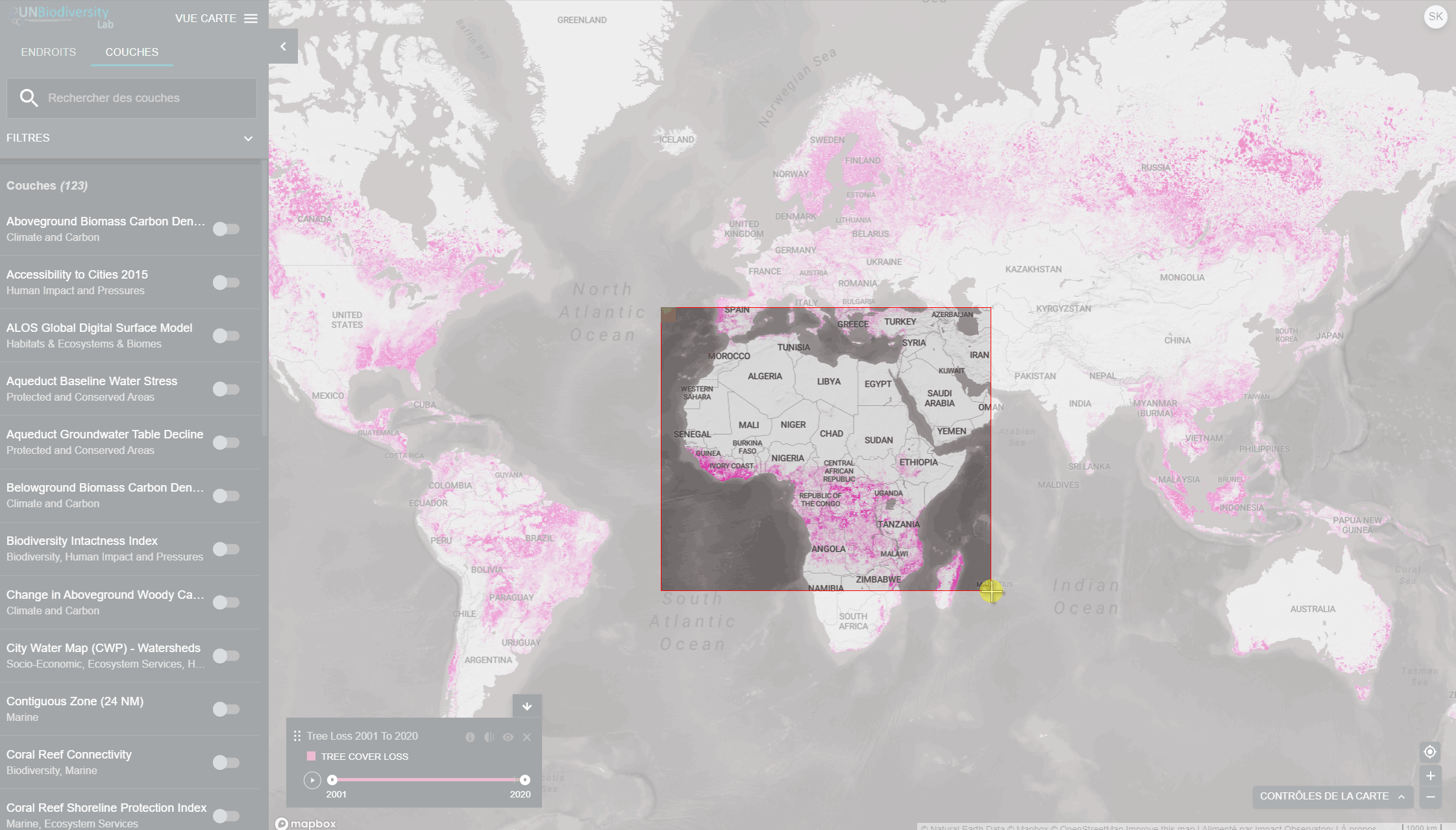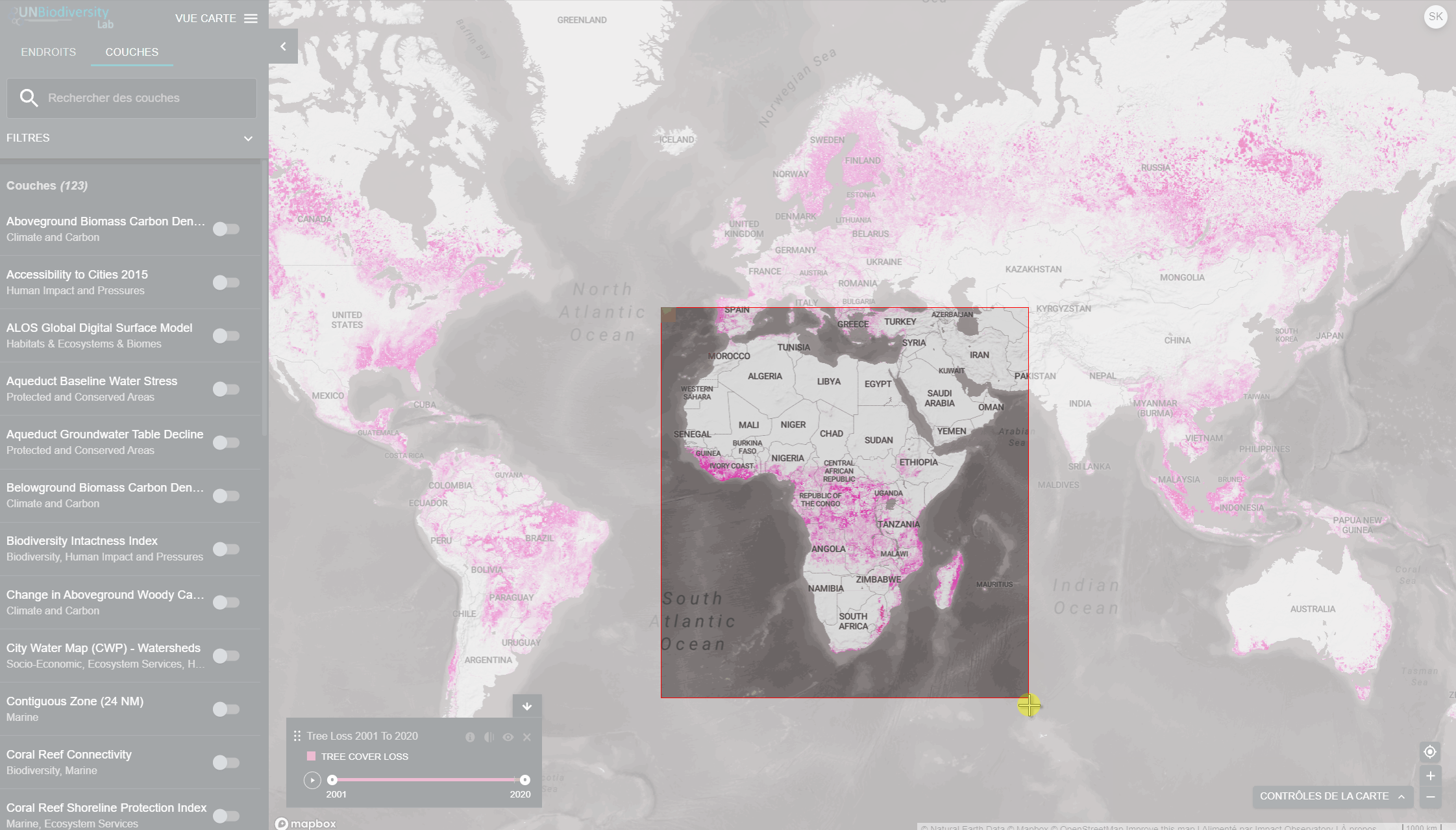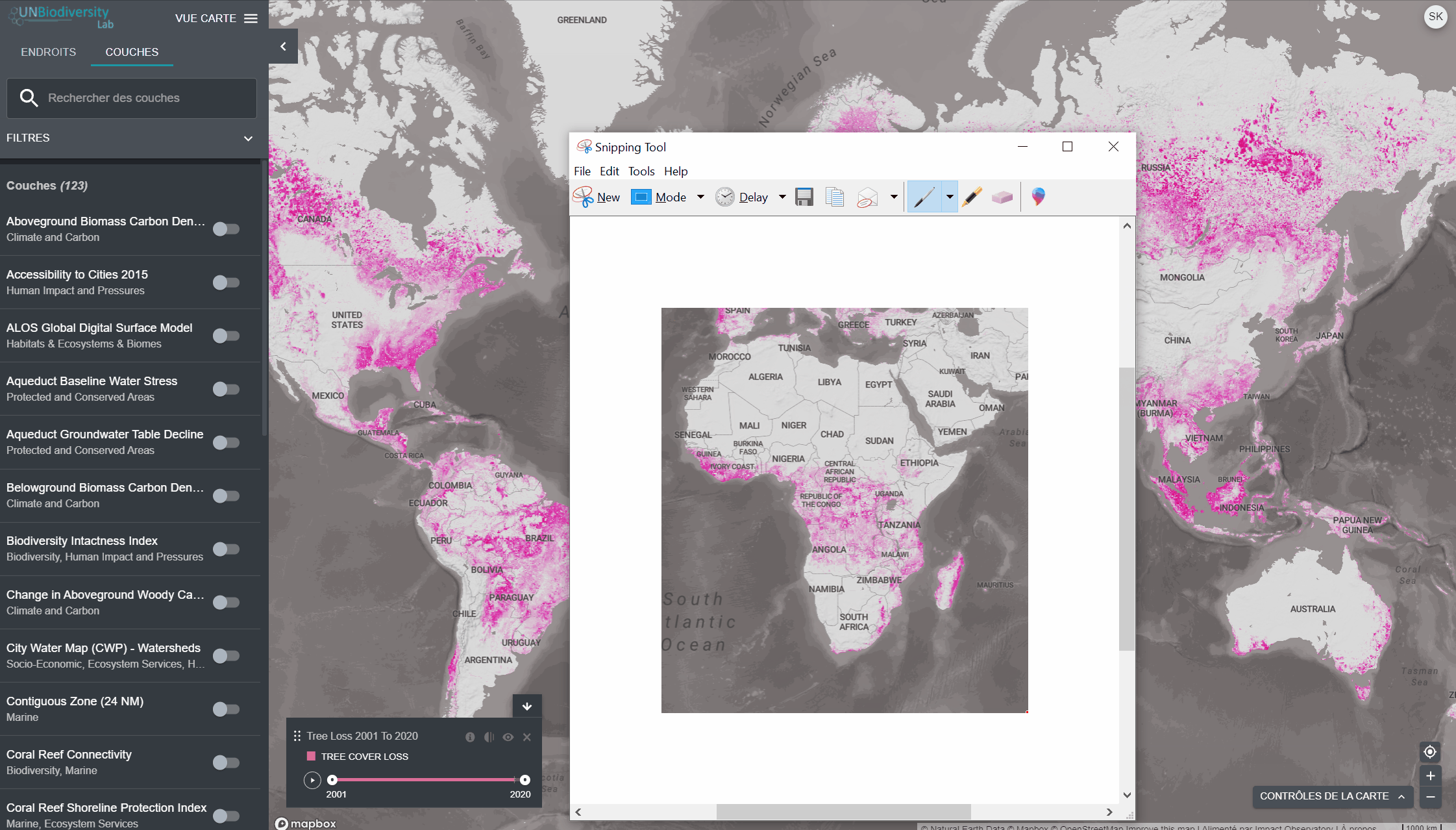
Pour visualiser les couches de séries chronologiques:
-
- Examinez notre liste de données pour confirmer quelles couches sont disponibles sous forme de séries chronologiques.
- Sélectionnez la couche d’intérêt.
- Personnaliser en fonction des options disponibles:
Animation uniquement: Cliquez sur l’icône de jeu à gauche pour voir l’animation des changements survenus au cours de cette période.
-
- Année spécifique uniquement: Sélectionnez l’heure (année, mois ou date) que vous souhaitez faire apparaître sur la carte en cliquant sur la barre de temps.
- Animation personnalisée: Sélectionnez la période (année, mois ou date) que vous souhaitez faire apparaître sur la carte en cliquant sur la barre de temps. Cliquez sur l’icône de jeu à gauche pour voir l’animation des changements sur cette période de temps.
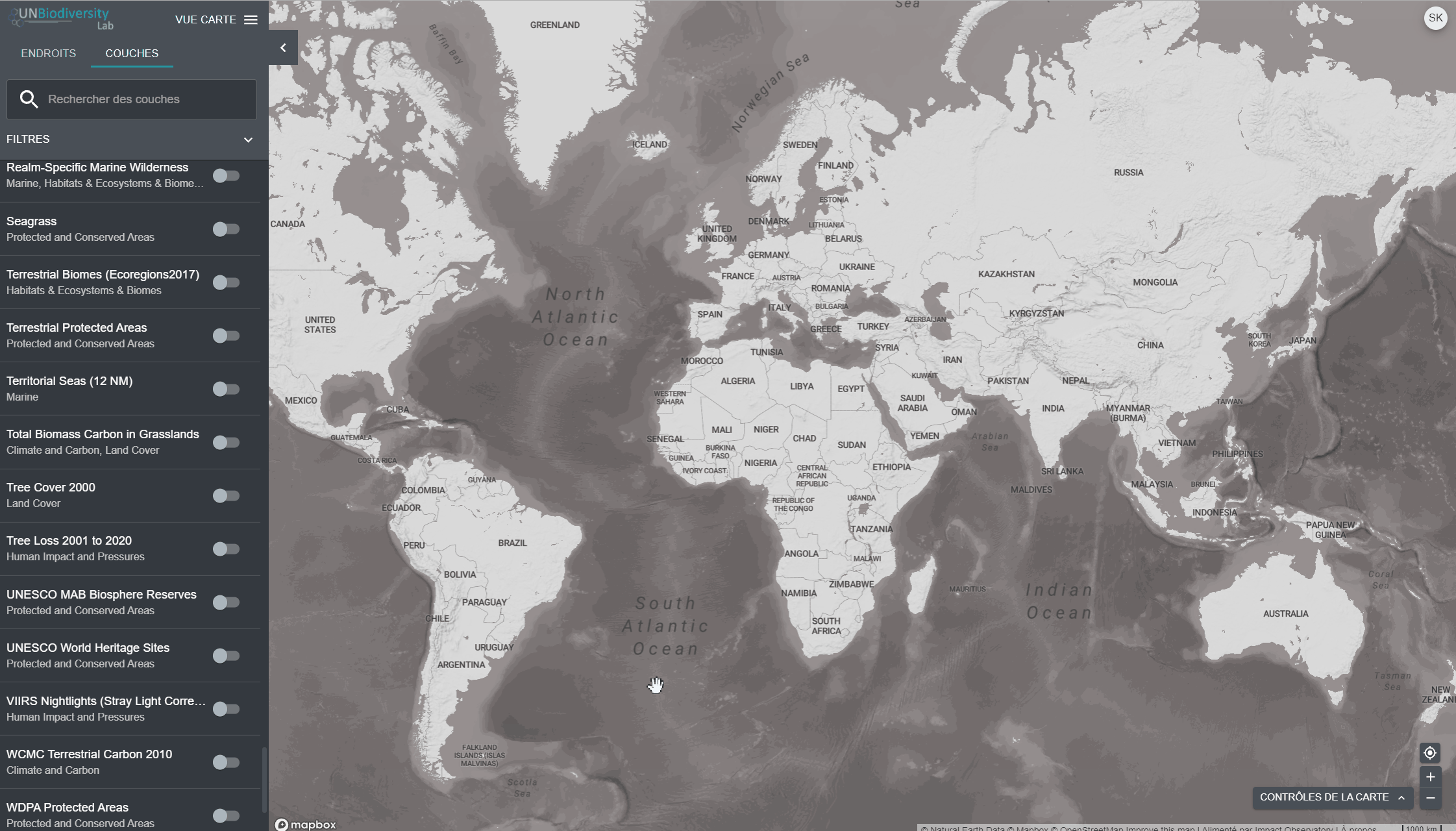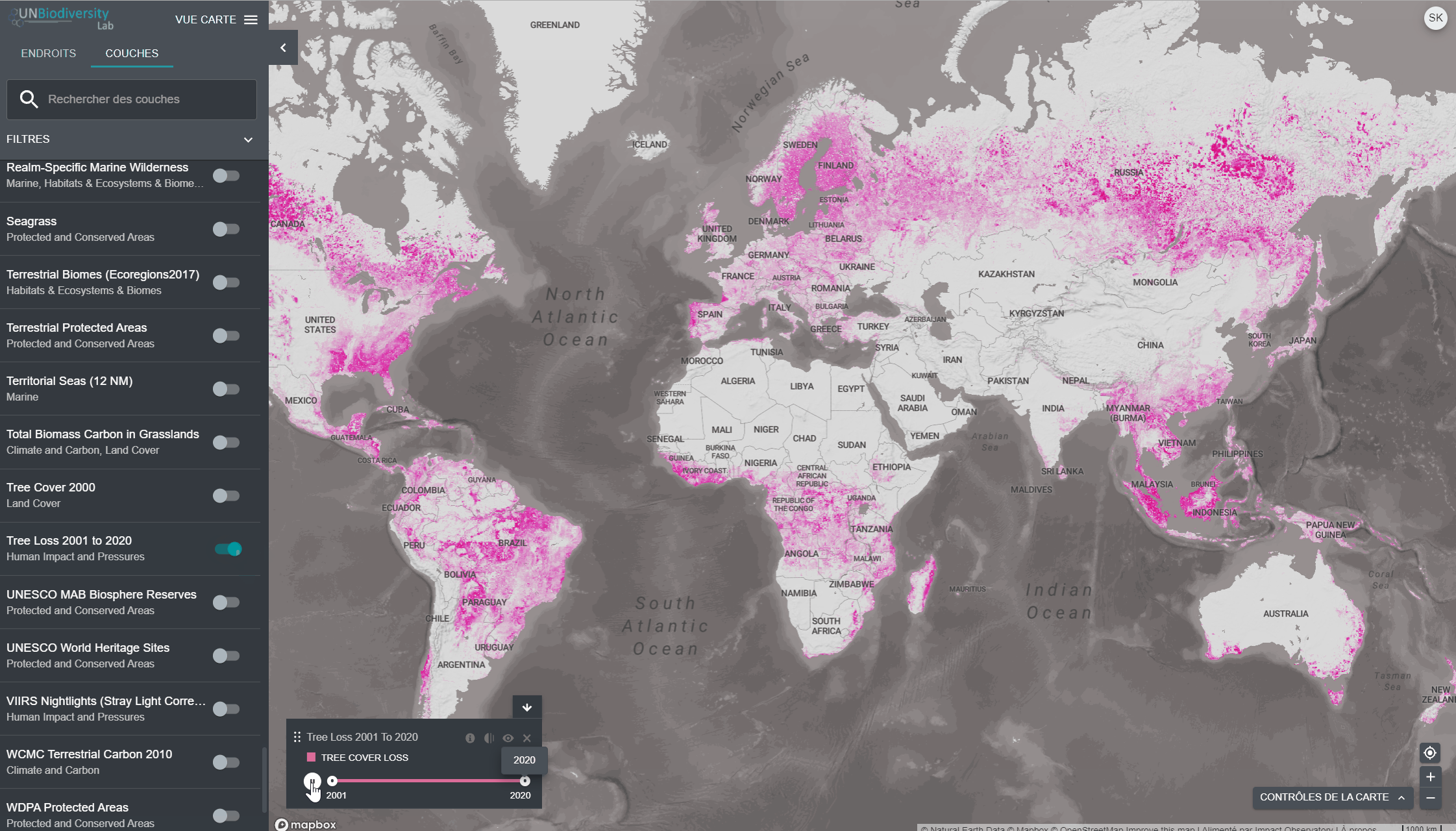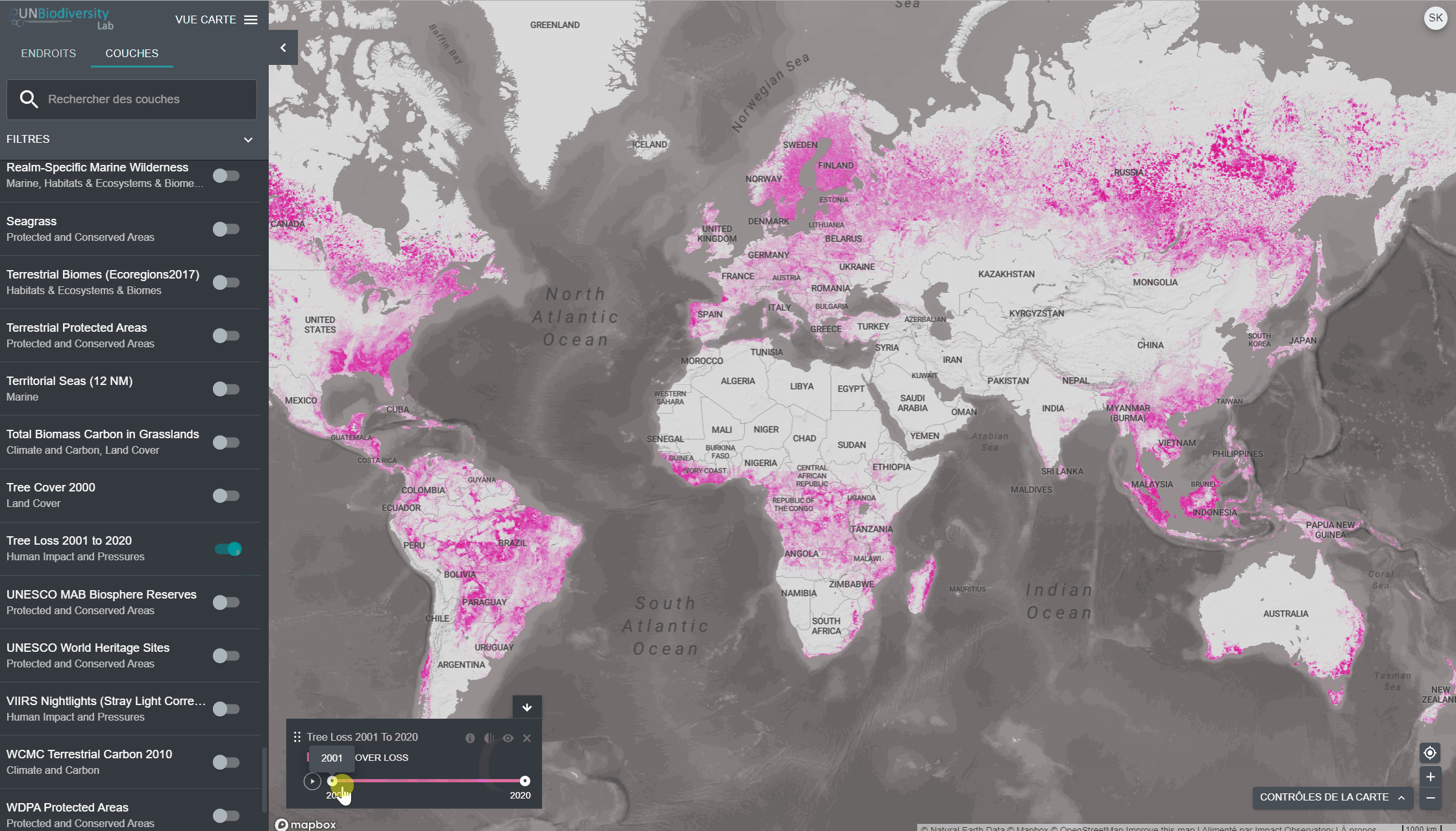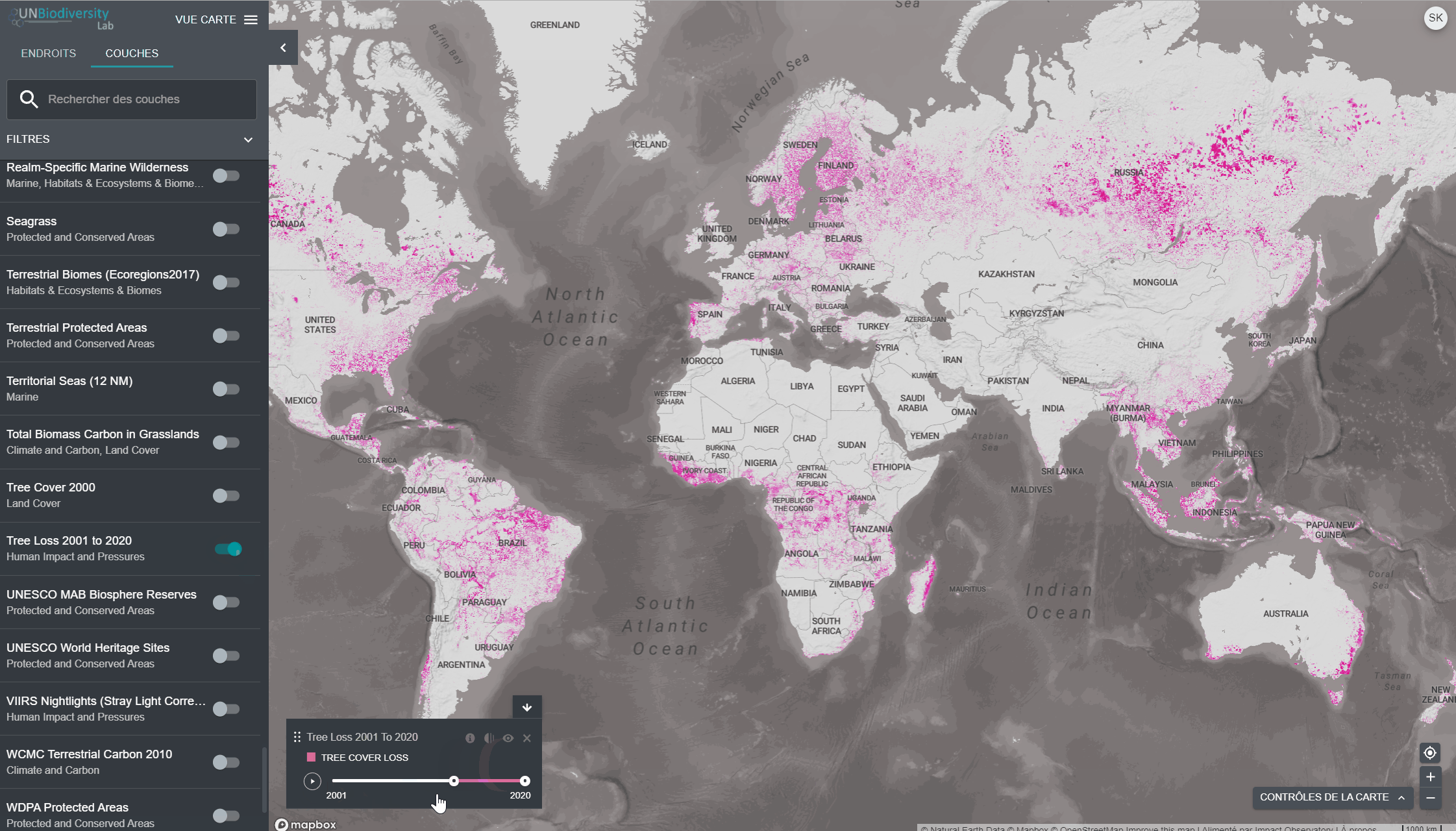
- Naviguez vers votre domaine d’intérêt, si vous le souhaitez. Vous pouvez également rester sur la vue globale.
- Cliquez sur l’icône COUCHES.
- Pour rechercher une couche, vous pouvez soit
- Tapez le nom de la couche que vous souhaitez visualiser dans la boîte de recherche, et sélectionnez le résultat souhaité dans la liste des couches.
OU
- Cliquez pour développer la boîte de filtres et sélectionnez le filtre qui vous intéresse, puis sélectionnez l’endroit souhaité dans la liste des résultats de la recherche.
4. Cliquez sur le bouton à gauche du nom de la couche pour charger cette couche sur la carte. Cliquez à nouveau sur le bouton ou cliquez sur l’icône X sur la couche info pour supprimer cette couche.
5. Cliquez à nouveau sur le bouton ou cliquez sur l’icône X sur la couche info pour supprimer cette couche.
Le partage des couches de données est facile. Pour ce faire, il faut:
- Activez la ou les couches qui vous intéressent dans votre visualiseur de carte.
- Copiez l’URL affichée dans votre navigateur.
- Partagez ! Toutes les couches de données de notre plateforme publique seront accessibles à tous, qu’ils soient ou non des utilisateurs enregistrés.

- Cliquez sur l’icône ENDROITS et sélectionnez vos lieux d’intérêt.
- Cliquez sur l’icône … à droite du nom du pays, puis cliquez sur Couches de clips et d’exportation.
- Tapez le nom ou sélectionnez les données que vous souhaitez télécharger. Si les données contiennent des couches de plusieurs années, sélectionnez l’année que vous souhaitez télécharger.
- Cliquez sur télécharger.
- La source de données sélectionnée sera découpée dans la case limitant le pays.
- Un petit tampon est ajouté à la boîte de délimitation, ce qui permet d’élargir légèrement la zone de la trame coupée. Cela permet de s’assurer que toute incongruité entre la frontière nationale utilisée dans l’UNBL et le fichier officiel de frontière nationale que vous souhaitez utiliser n’entraîne pas de perte de données. Cela suppose que les différences sont potentiellement faibles. Si ce n’est pas le cas, veuillez nous contacter à l’adresse support@unbiodiversitylab.org pour obtenir de l’aide.
- Accédez au fichier compressé .zip téléchargé dans votre dossier de téléchargement une fois le téléchargement terminé.
- Les données téléchargées peuvent être ouvertes dans n’importe quel logiciel SIG pour une analyse plus approfond

- Sélectionnez la couche d’intérêt.
- Cliquez sur l’icône de la couche info.
- Cliquez sur le lien sous EN SAVOIR PLUS pour télécharger les données à partir de leur source originale.
- Si vous rencontrez des problèmes pour accéder aux données, veuillez contacter support@unbiodiversitylab.org pour obtenir une aide supplémentaire.
- Personnalisez la vue des couches que vous avez sélectionnées, comme vous le souhaitez.
- Utilisez la fonction de capture d’écran de votre ordinateur pour saisir la carte.
- Pour l’inclusion dans des rapports ou publications officiels, veuillez vous assurer que vous répondez aux normes de cartographie:
- Les cartes doivent être claires et concises.
- Le texte important sur les cartes doit être clair et lisible (par exemple, les villes, les noms de lieux, les éléments de légende, etc.)
- La carte doit comprendre des éléments cartographiques de base, notamment : une légende des couches de données pertinentes et une barre d’échelle.
- La carte doit fournir la ou les attributions et citations correctes de la ou des sources de données utilisées pour sa création, soit sur la carte elle-même, soit dans une légende décrivant la carte, par exemple :
Exemple (dans la carte)::
Sources : Sanderman, et al, 2018 ; PNUE-WCMC et UICN, 2021.
Sources : Sanderman, et al, 2018 ; PNUE-WCMC et UICN, 2021.
Exemple (dans une légende): /span>
La figure 2 montre l’estimation du carbone organique du sol présent dans les mangroves (d’après Sanderman, et al., 2018) dans les zones protégées au Vietnam (PNUE-WCMC et UICN, 2021).
Veillez également à inclure des citations complètes pour les ensembles de données utilisés dans la section des références du document, par exemple:
Sanderman, J. et al. (2018) “A global map of mangrove forest soil carbon at 30 m spatial resolution”, Environmental Research Letters, 13(5), p. 055002. doi : 10.1088/1748-9326/aabe1c. PNUE-WCMC et UICN (2021), Planète protégée : The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) [en ligne], 02/2021, Cambridge, Royaume-Uni : UNEP-WCMC et UICN Disponible sur : www.protectedplanet.net.
Inclure des informations sur la carte (ou dans la citation décrivant la carte) sur : qui a créé la carte ; la date de production de la carte sur UN Biodiversity Lab ; et une note indiquant que la carte a été créée en utilisa
PNUE-WCMC et UICN (2021), Planète protégée : The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) [en ligne], 02/2021, Cambridge, Royaume-Uni : UNEP-WCMC et UICN Disponible sur : www.protectedplanet.net.
-
- Inclure des informations sur la carte (ou dans la citation décrivant la carte) sur : qui a créé la carte ; la date de production de la carte sur UN Biodiversity Lab ; et une note indiquant que la carte a été créée en utilisant UN Biodiversity Lab.
Exemple:
Créé par James Bond à l'aide du UN Biodiversity Lab (www.unbiodiversitylab.org) le 14 février 2021
-
- Enfin, assurez-vous d'inclure également une citation de la carte dans la section des références du document. Nous recommandons ce format :
Auteur. "Titre de la carte" [format]. Échelle. (Date de production). Carte générée par le laboratoire de biodiversité de l'ONU [web]. Version 2. PNUD et PNUE, 2021.
Exemple:
Bond, James. "Mangrove Forest Soil Organic Carbon within Vietnam's Protected Areas" [carte]. L'échelle n'est pas donnée. (14 février 2021). Carte générée par le laboratoire de biodiversité de l'ONU (www.unbiodiversitylab.org) [web]. Version 2. PNUD et PNUE, 2021.
Nous accueillons volontiers les suggestions de données qui permettraient d’enrichir le UN Biodiversity Lab ! Si vos données concernent la biodiversité, la conservation ou le développement durable au niveau local, national ou international, veuillez remplir ce formulaire.
Notre équipe recevra les suggestions au fur et à mesure de leur réception. Le PNUD, le PNUE et le PNUE-CMSC ont formalisé des critères pour les données publiées sur la plate-forme publique afin d’aider à identifier et à conserver les meilleures couches de données disponibles sur ces thèmes, de manière à permettre des analyses et des rapports plus rationnels et standardisés. Ces critères de sélection placeront les données dans l’un des trois niveaux de données et prendront en compte des aspects tels que la pertinence des données, l’octroi de licences ouvertes et la disponibilité, la transparence et la couverture géographique. Les critères sont disponibles ici.
Pour télécharger des données à l’usage de votre institution dans un espace de travail privé, veuillez consulter la question suivante sur la demande d’un espace de travail privé.
We recognize that national data is often higher quality and better suited to countries’ needs for decision-making, monitoring, and reporting. UNBL offers free workspaces to stakeholders who need a secure area to access and use spatial data. Our workspaces can serve as a common data repository, offer a collaborative work environment, and enable you to calculate dynamic indicators for a subnational or transboundary area of interest. These password-protected spaces enable you to control access to your data, and ensure data security through storage on UN servers.
Nous encourageons les utilisateurs à explorer comment les espaces de travail du UNBL peuvent vous aider à construire des communautés de pratique pour transformer les données en action.
To request a secure UNBL workspace please contact support@unbiodiversitylab.org or click on the UNBL workspaces tab on our support page and fill out the form.
You can access our user guide on UNBL workspaces ici.
Télécharger le guide d'utilisation de la plateforme publique : Anglais | Français | Espagnol | Portugais | Russe
- Connectez-vous à votre compte.
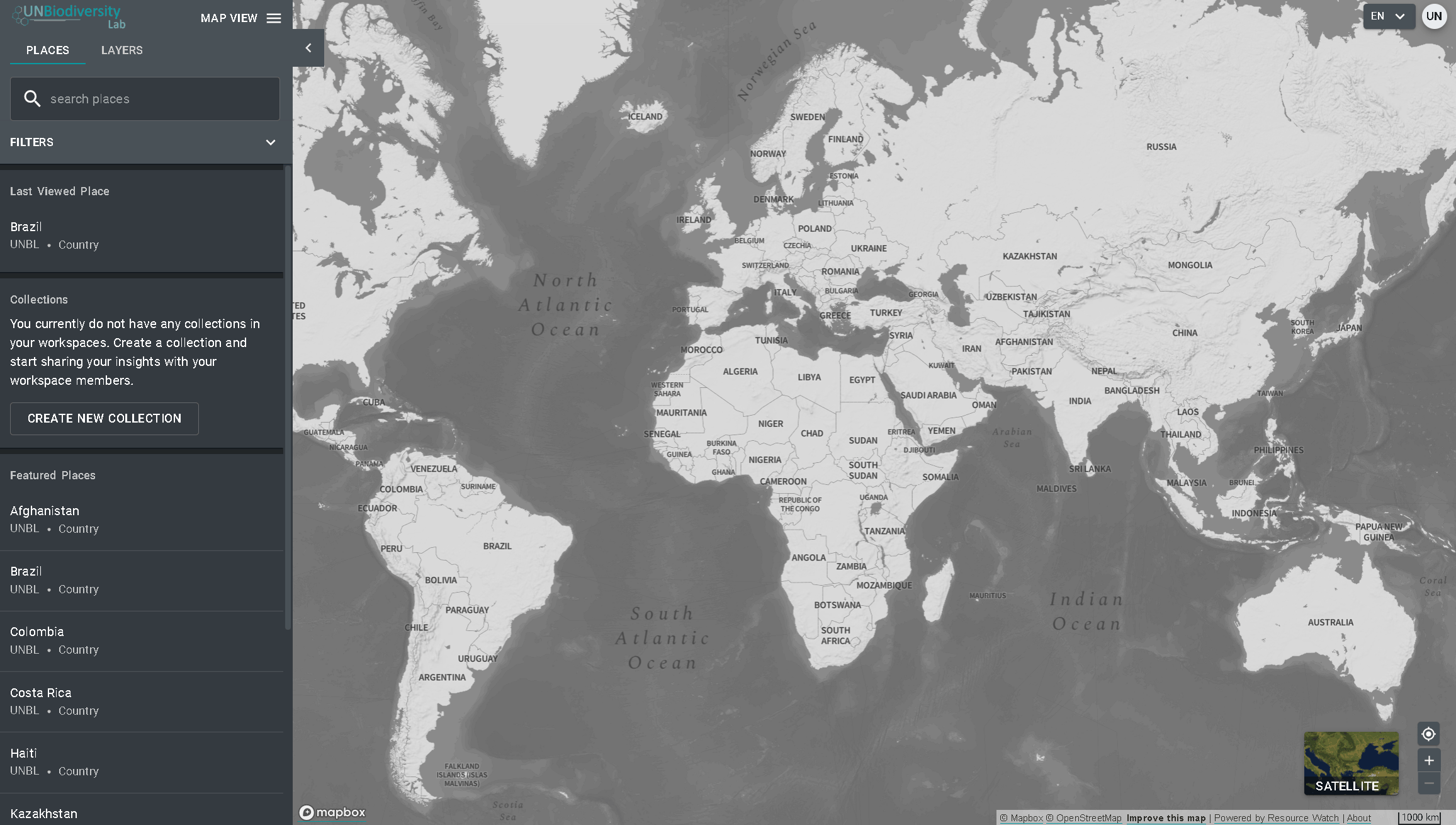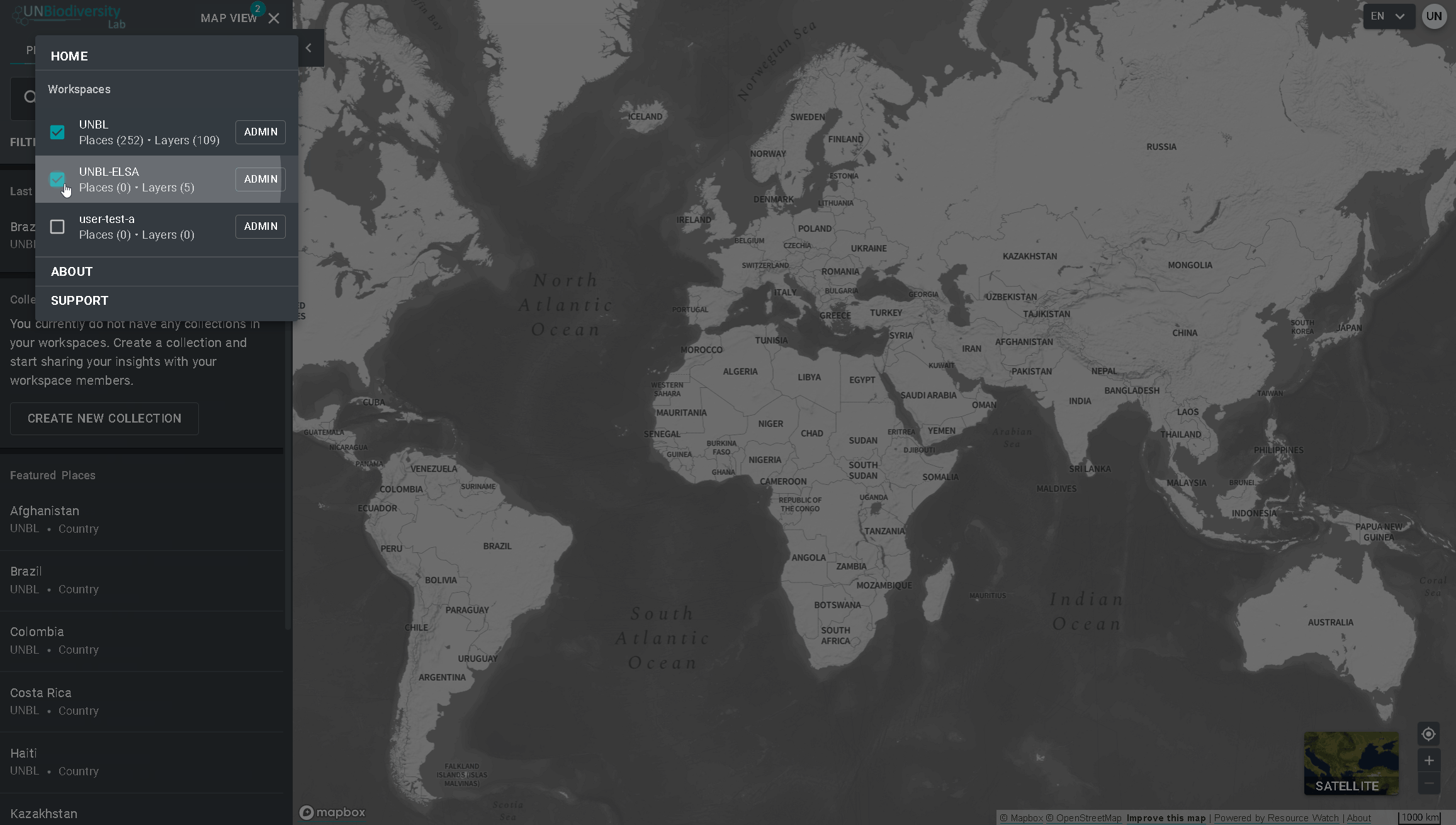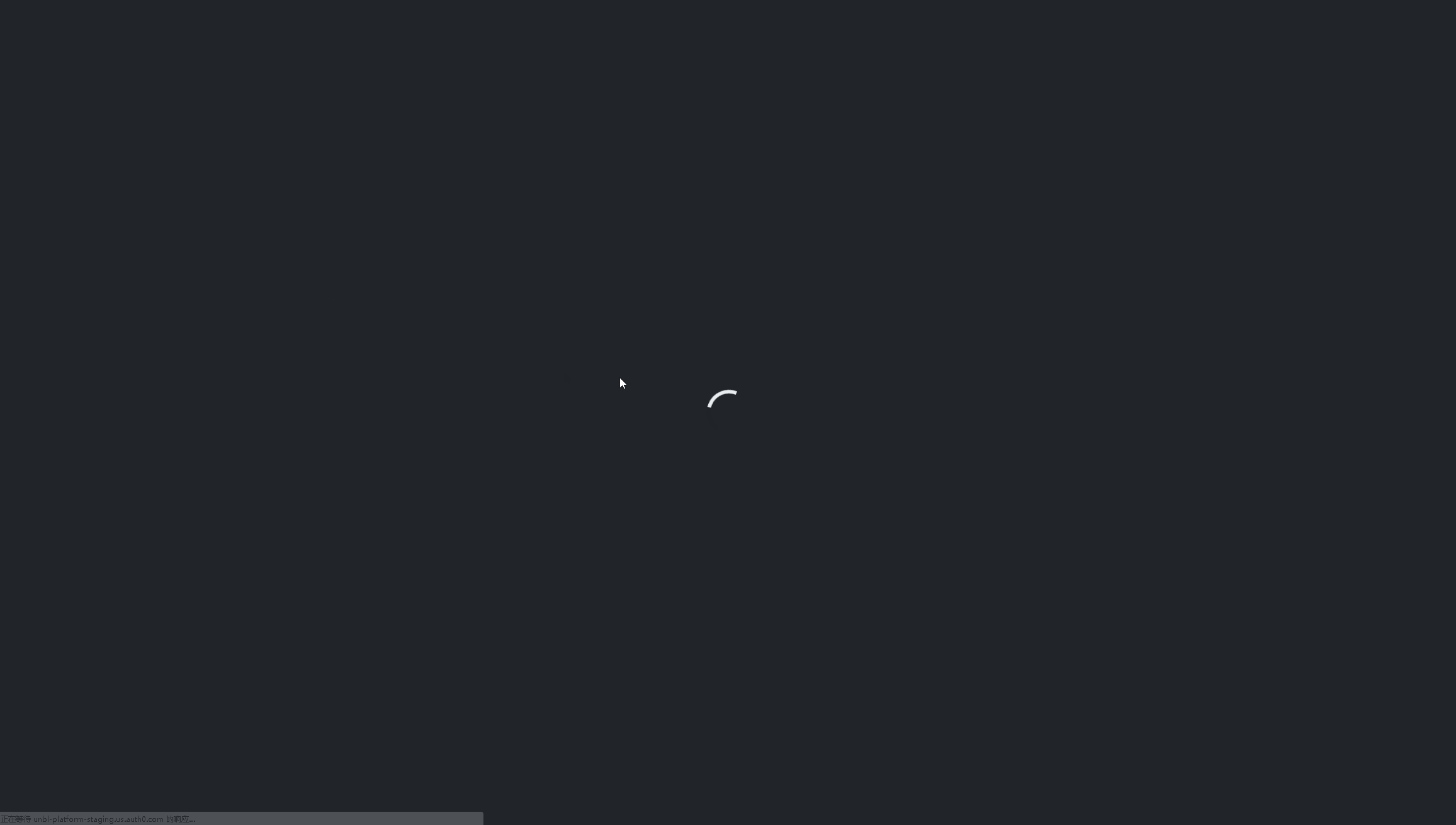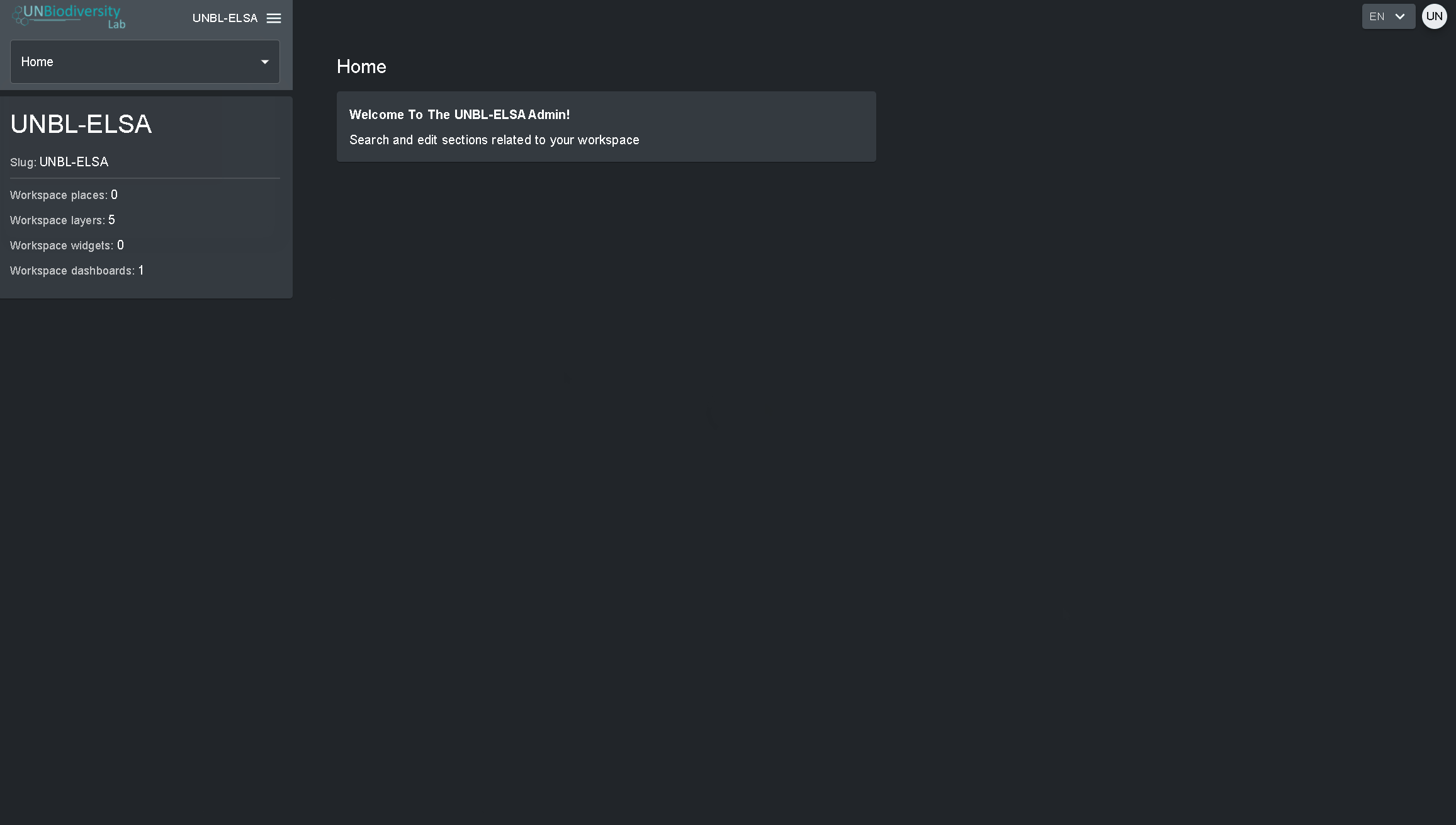
- Cliquez sur le bouton déroulant VUE CARTE. Cela affichera les espaces de travail auxquels vous appartenez.
- Vous pouvez visualiser les actifs (lieux et couches de données) pour chaque espace de travail indépendamment ou tous en même temps. Cochez la case des espaces de travail que vous souhaitez inclure dans votre vue. Note : si aucun espace de travail n’est sélectionné, cela revient à sélectionner tous les espaces de travail.
- Décochez les espaces de travail que vous ne voulez pas voir, ce qui vous permet de ne voir que les lieux téléchargés dans votre espace de travail UNBL et de filtrer les biens indésirables.
Remarque : nous vous recommandons de ne pas décocher la plate-forme publique de l’UNBL, car cela supprimera l’accès aux couches mondiales publiques et aux mesures du tableau de bord pour tous les domaines
Pour rechercher un domaine d’intérêt, vous pouvez soit:
- Cliquez sur l’icône ENDROITS, tapez le nom du pays ou de la juridiction que vous souhaitez consulter dans la boîte de recherche, et sélectionnez le résultat souhaité dans la liste des résultats de la recherche.
OU
2. Cliquez sur l’icône ENDROITS, cliquez pour agrandir la boîte de filtres, et sélectionnez le filtre qui vous intéresse. Vous pouvez ensuite sélectionner l’endroit souhaité dans la liste des résultats de la recherche.
Pour visualiser les mesures dynamiques des lieux de votre espace de travail UNBL :
- Sélectionnez un domaine d’intérêt.
- Examinez les métriques dans le panneau de gauche.
- Cliquez sur l’icône “AFFICHER SUR LA CARTE” si vous souhaitez visualiser cette couche sur la carte. Cliquez sur l’icône SUPPRIMER LA CARTE ou sur l’icône enlever la couche dans la légende pour effacer l’écran.
- Cliquez sur l’icône i pour afficher les informations sur les couches, les pages d’information fournissent une brève description des données, des documents à lire et des liens vers les sources.
- Pour télécharger les données de synthèse de la métrique au format .csv ou .json, cliquez sur l’icône en forme de flèche. Vous pouvez également télécharger les données à partir des liens de source sur les pages d’information des couches.
Pour rechercher les couches disponibles :
- Cliquez sur l’icône COUCHES. Les couches de données des espaces de travail que vous avez sélectionnés rempliront automatiquement cet onglet.
- Pour rechercher une couche, vous pouvez soit
- Tapez le nom de la couche que vous souhaitez visualiser dans la boîte de recherche, et sélectionnez le résultat souhaité dans la liste des couches.
- Cliquez pour développer la boîte de filtres et sélectionnez le filtre qui vous intéresse, puis sélectionnez l’endroit souhaité dans la liste des résultats de la recherche.
- Cliquez sur le bouton à gauche du nom de la couche pour charger cette couche sur la carte.
- Cliquez à nouveau sur le bouton ou cliquez sur l’icône X sur la couche info pour supprimer cette couche.
- Cliquez sur le menu VUE CARTE.
- Sélectionnez le bouton d’administration associé à l’espace de travail de votre choix.
- La page d’administration de votre espace de travail est également accessible à l’URL suivante : https://map.unbiodiversitylab.org/admin//YOURWORKSPACESLUGNAM
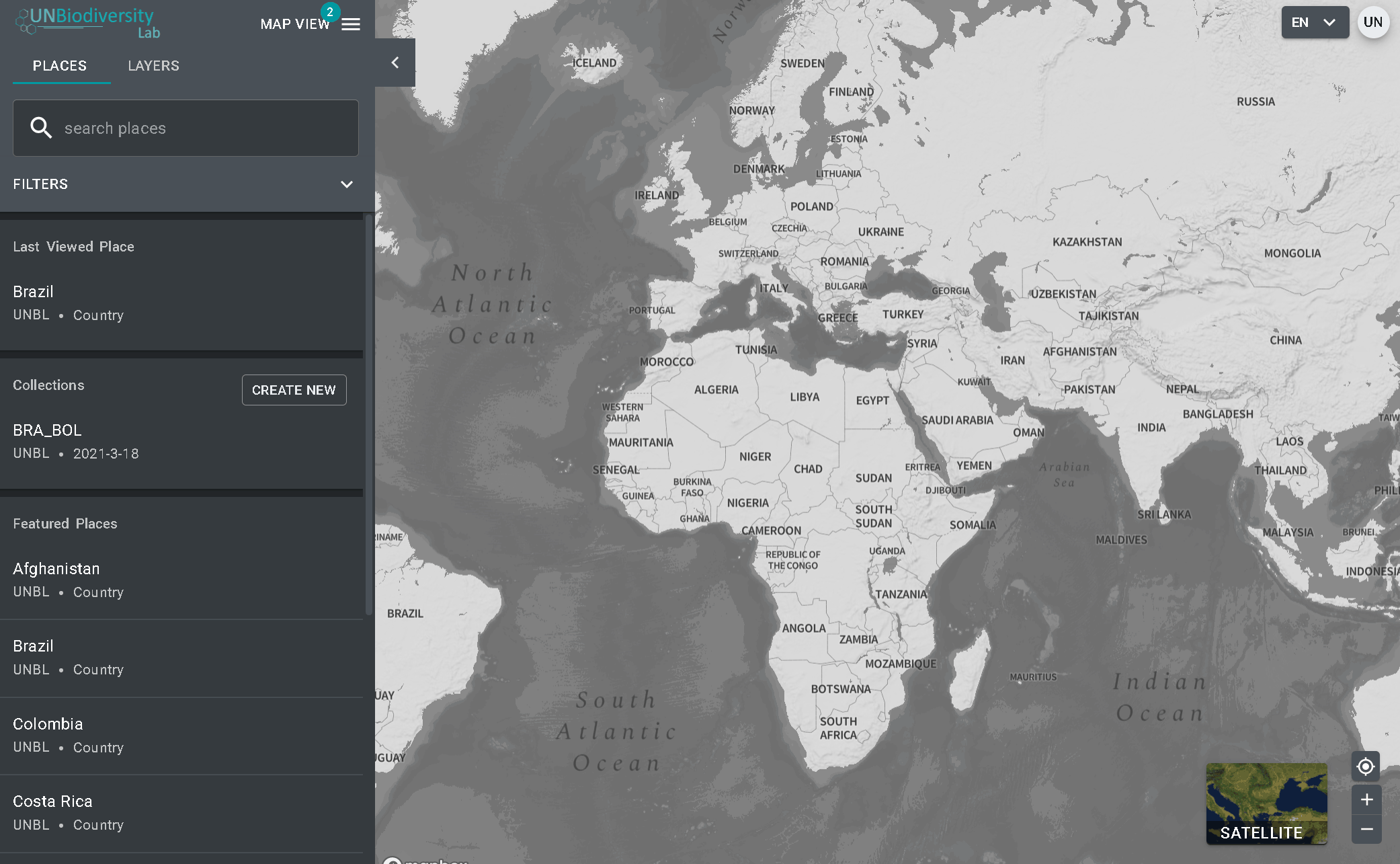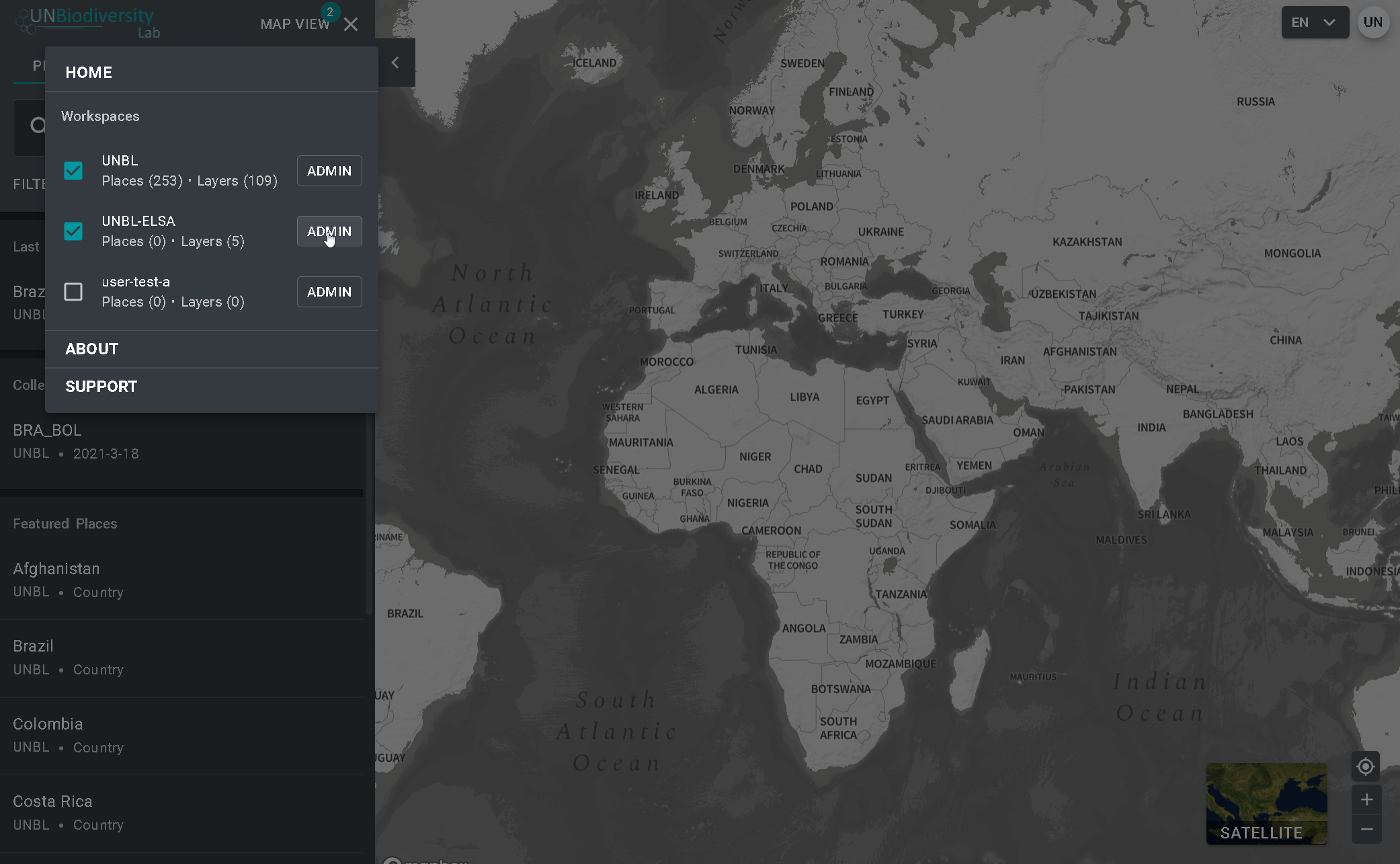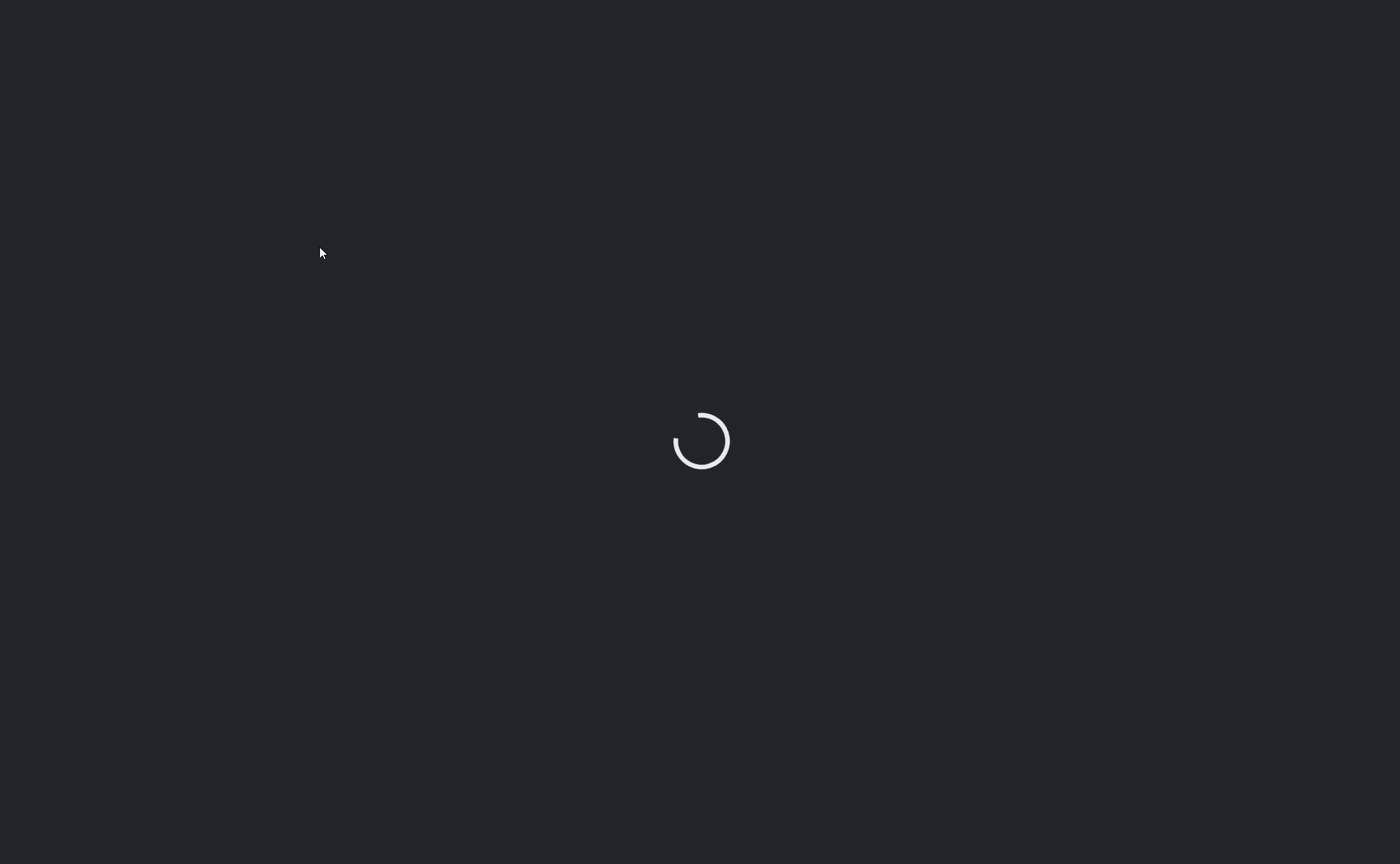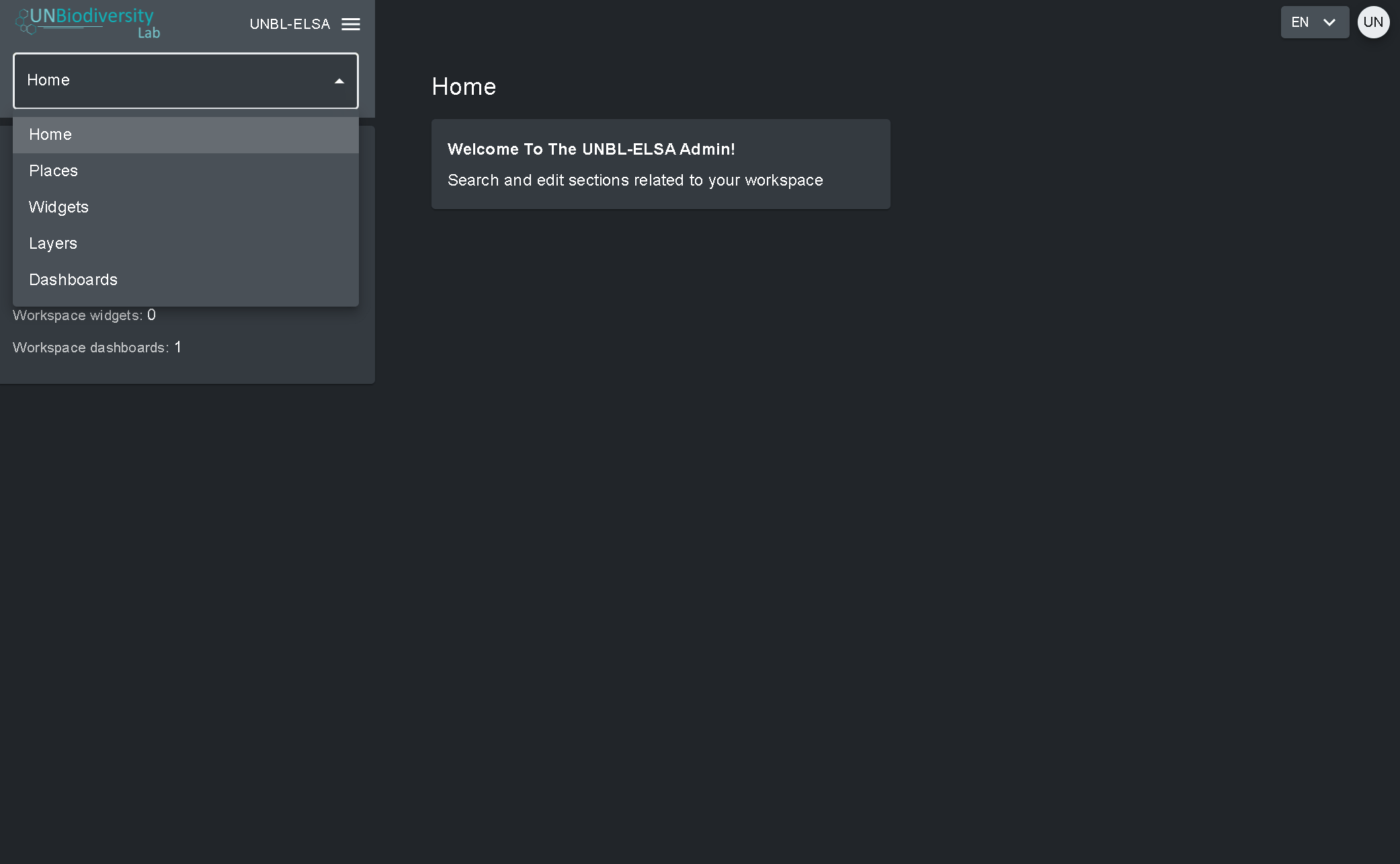
Pour accéder aux différentes composantes :
- Cliquez sur l’onglet à droite du bouton d’accueil pour développer le menu déroulant.
- Sélectionnez le composant que vous souhaitez visualiser. De plus amples informations sur chaque composant sont fournies dans la suite de ce guide de l’utilisateur.
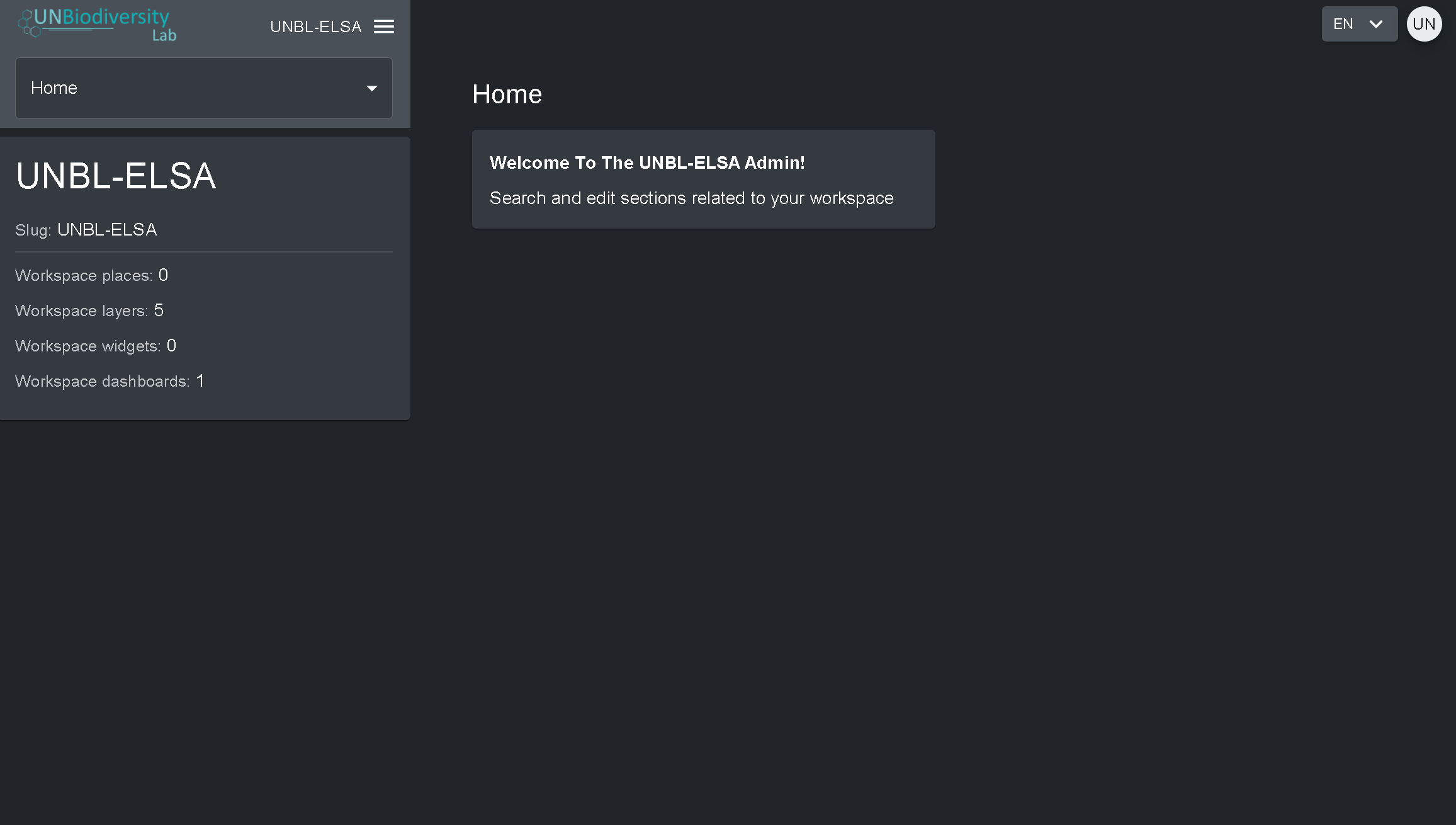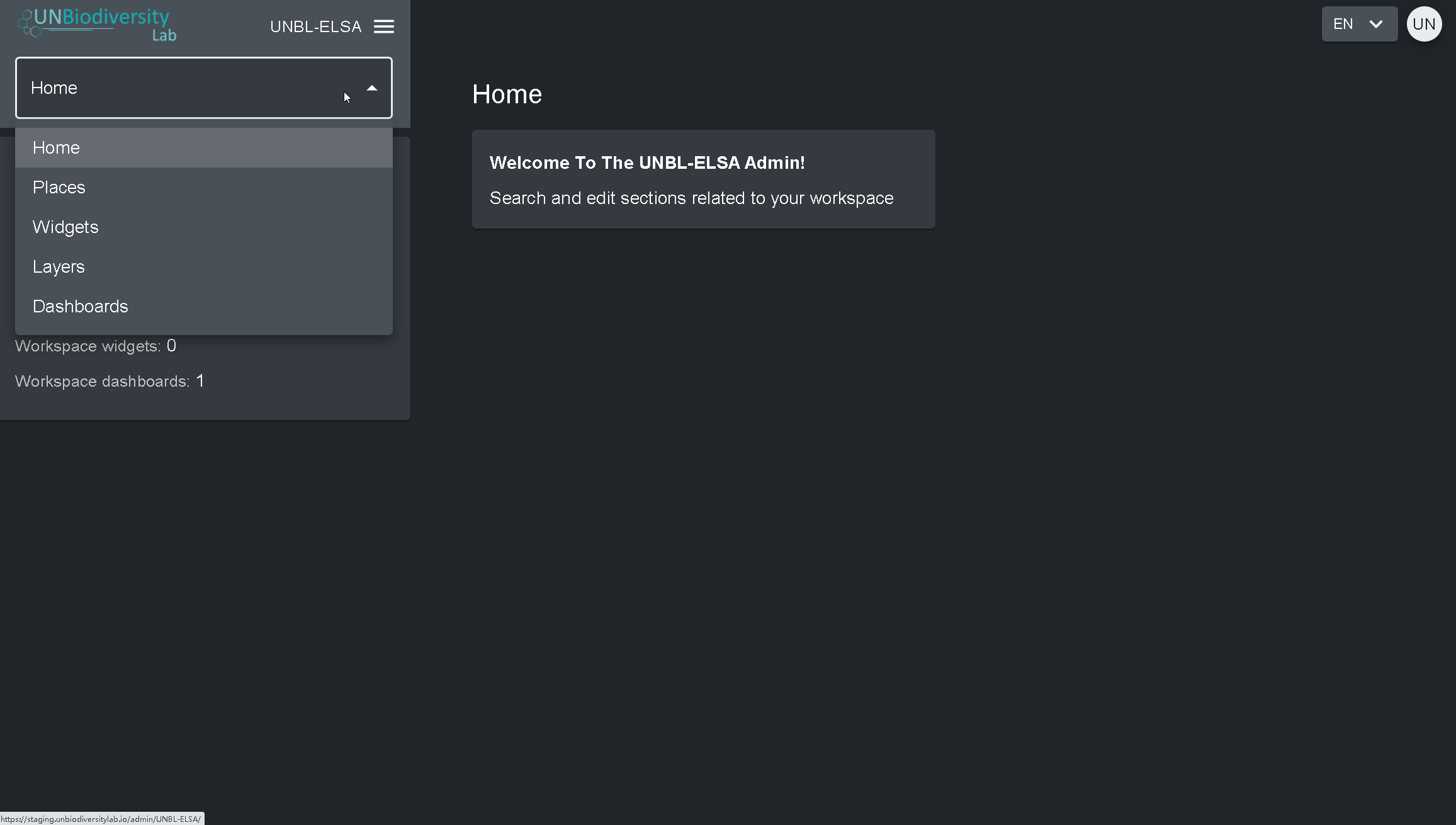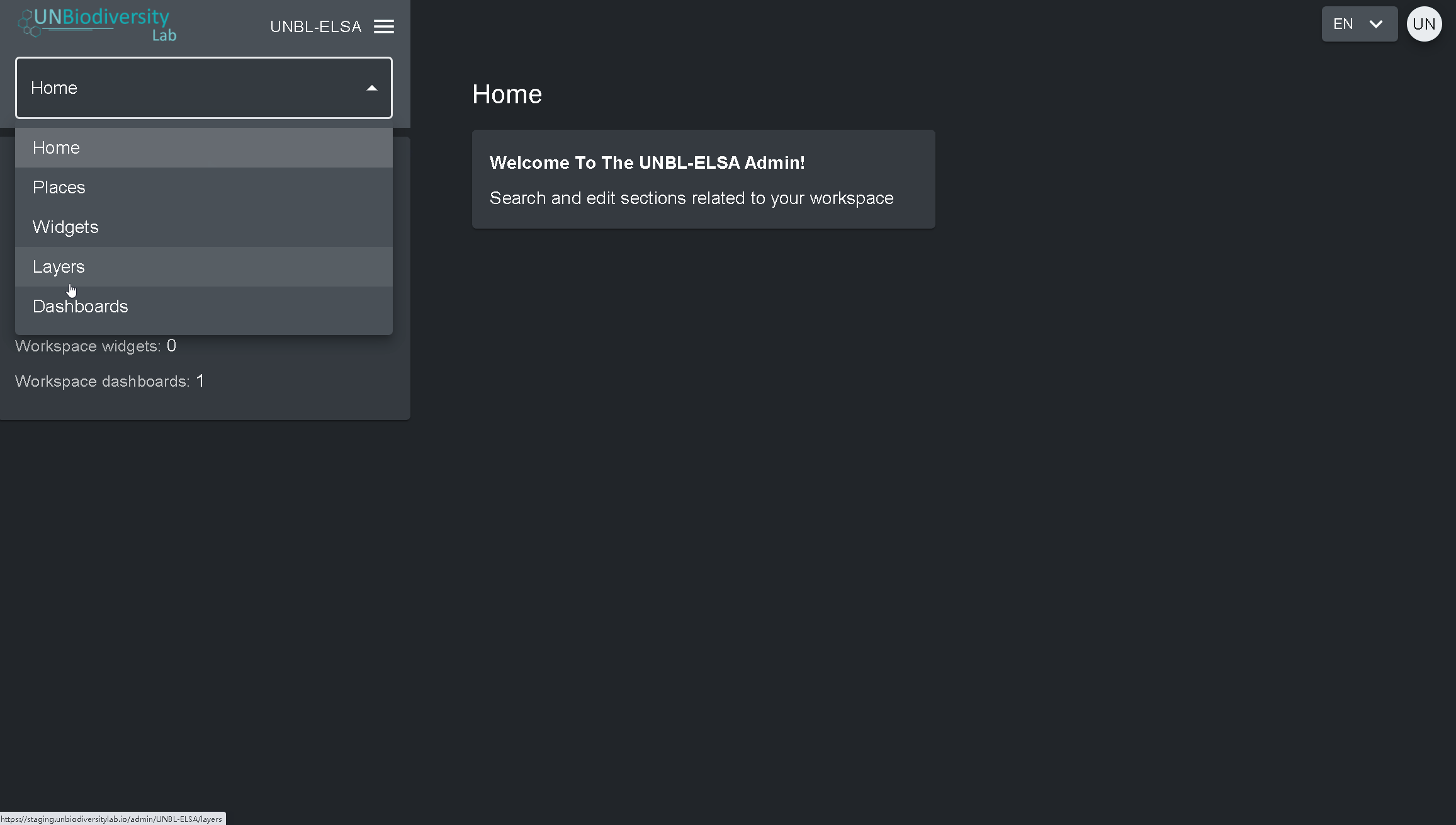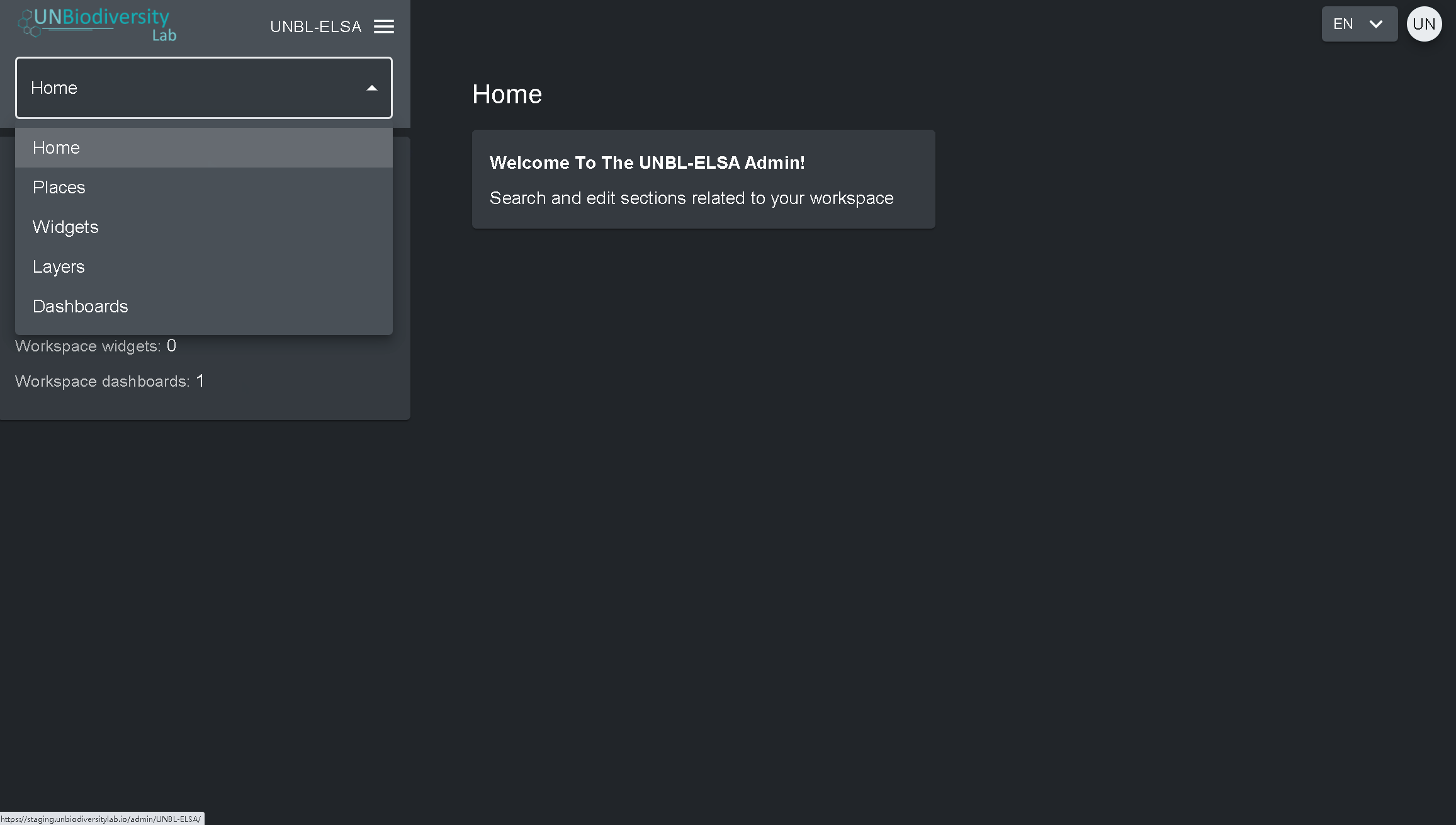
Les propriétaires – le créateur de l’espace de travail. Actuellement, seuls les administrateurs de la plate-forme UNBL peuvent créer des espaces de travail UNBL et attribuer un propriétaire. Les propriétaires ont la possibilité d’ajouter tous les types d’utilisateurs, de gérer les actifs de l’espace de travail (lieux et couches) via l’outil d’administration, et de visualiser tous les actifs de l’espace de travail sur la carte.
Les administrateurs – peuvent ajouter et gérer des utilisateurs, attribuer des rôles aux utilisateurs en tant qu’éditeurs et visionneurs, gérer les ressources de l’espace de travail via l’outil d’administration, et afficher toutes les ressources de l’espace de travail sur la carte.
Les éditeurs – peuvent gérer les ressources de l’espace de travail via l’outil d’administration, et visualiser toutes les ressources de l’espace de travail sur la carte. Les éditeurs doivent avoir une expérience de travail avec les logiciels SIG pour pouvoir télécharger et modifier les couches de données.
Visualiseurs – permettent de visualiser tous les actifs de l’espace de travail sur la carte. Les visualiseurs n’ont pas accès à l’outil d’administration.
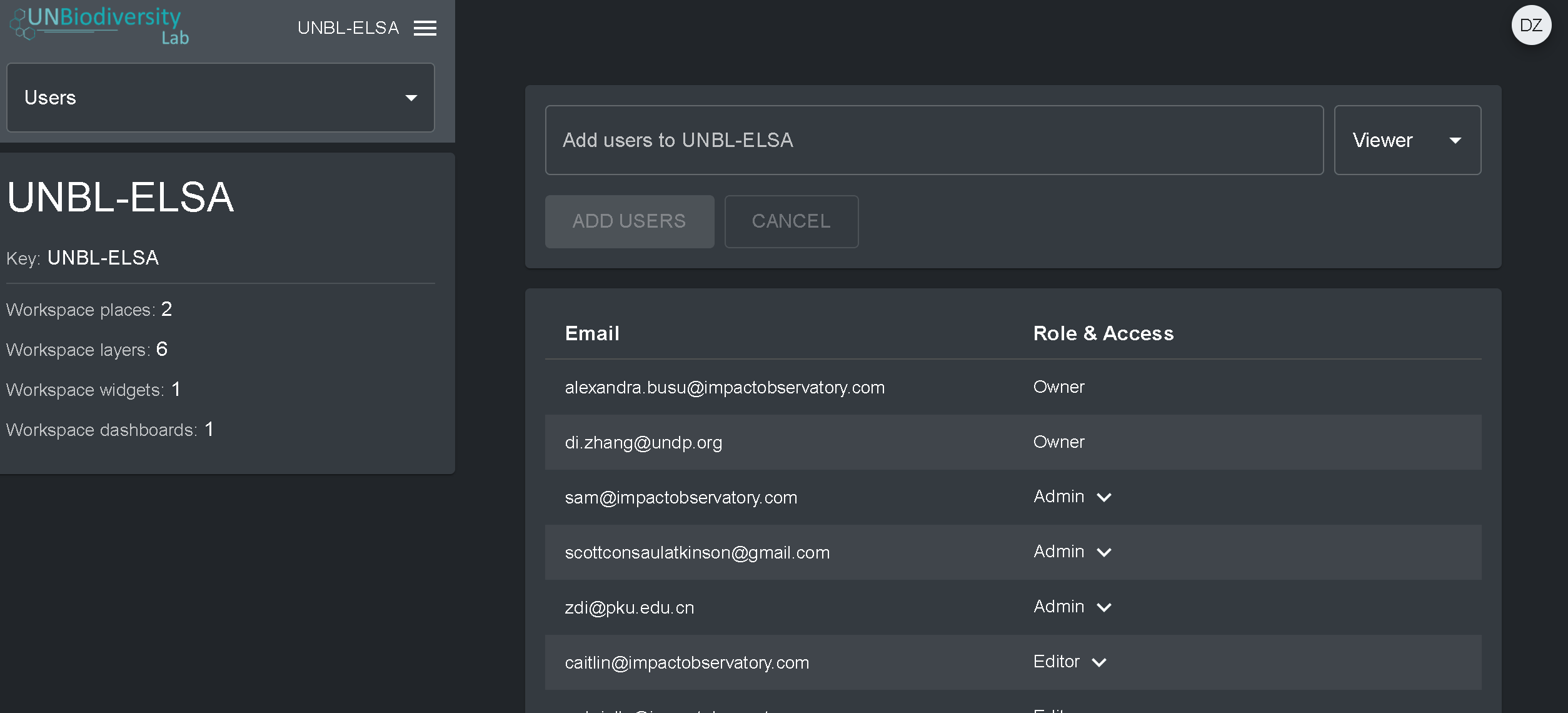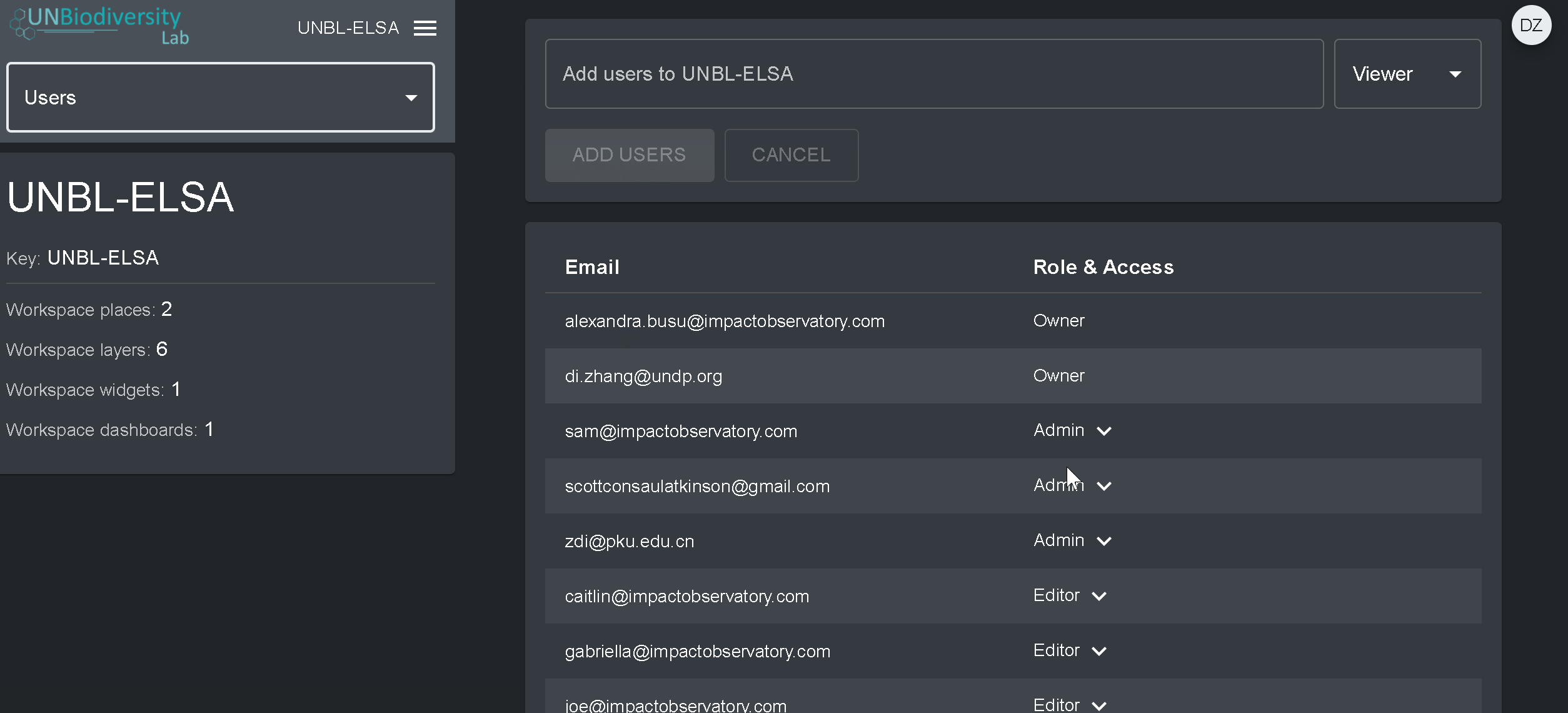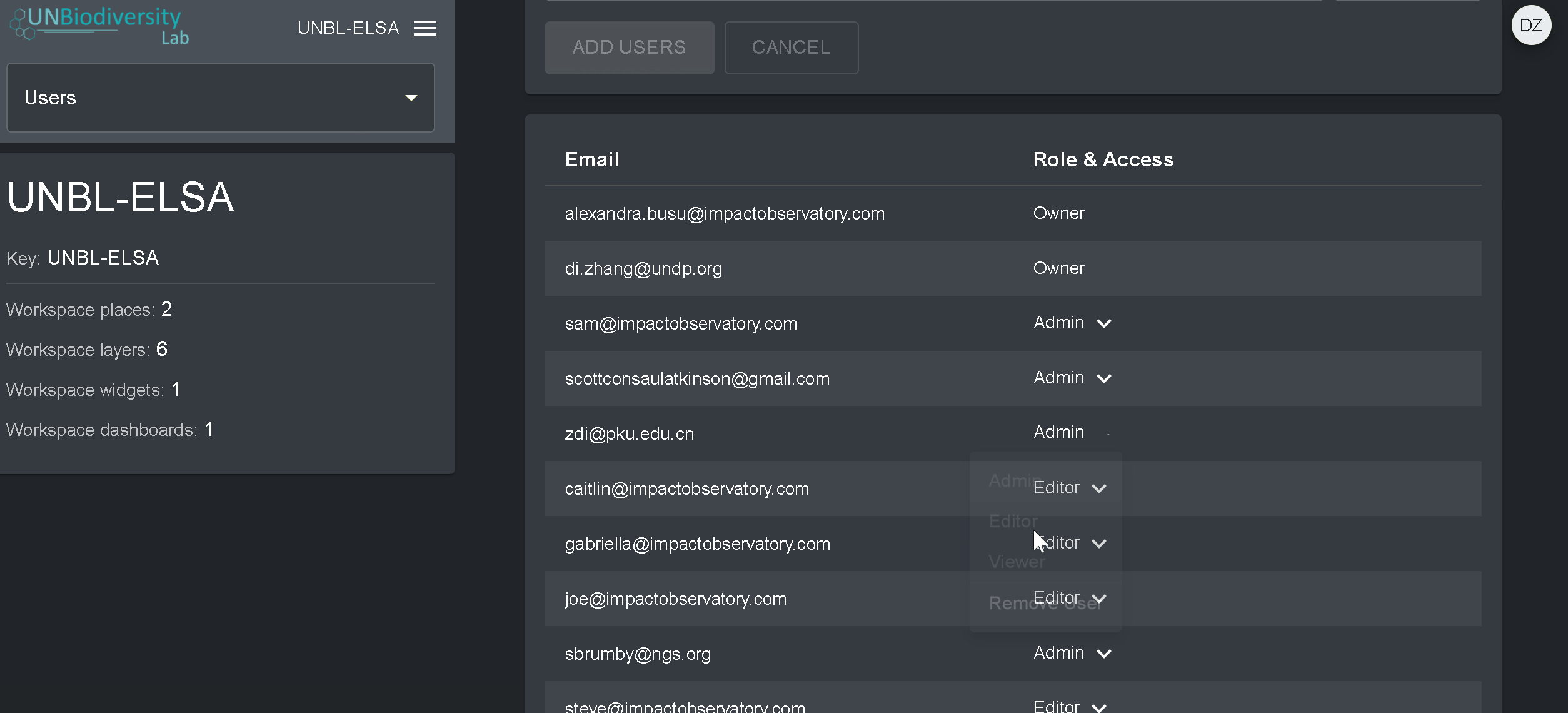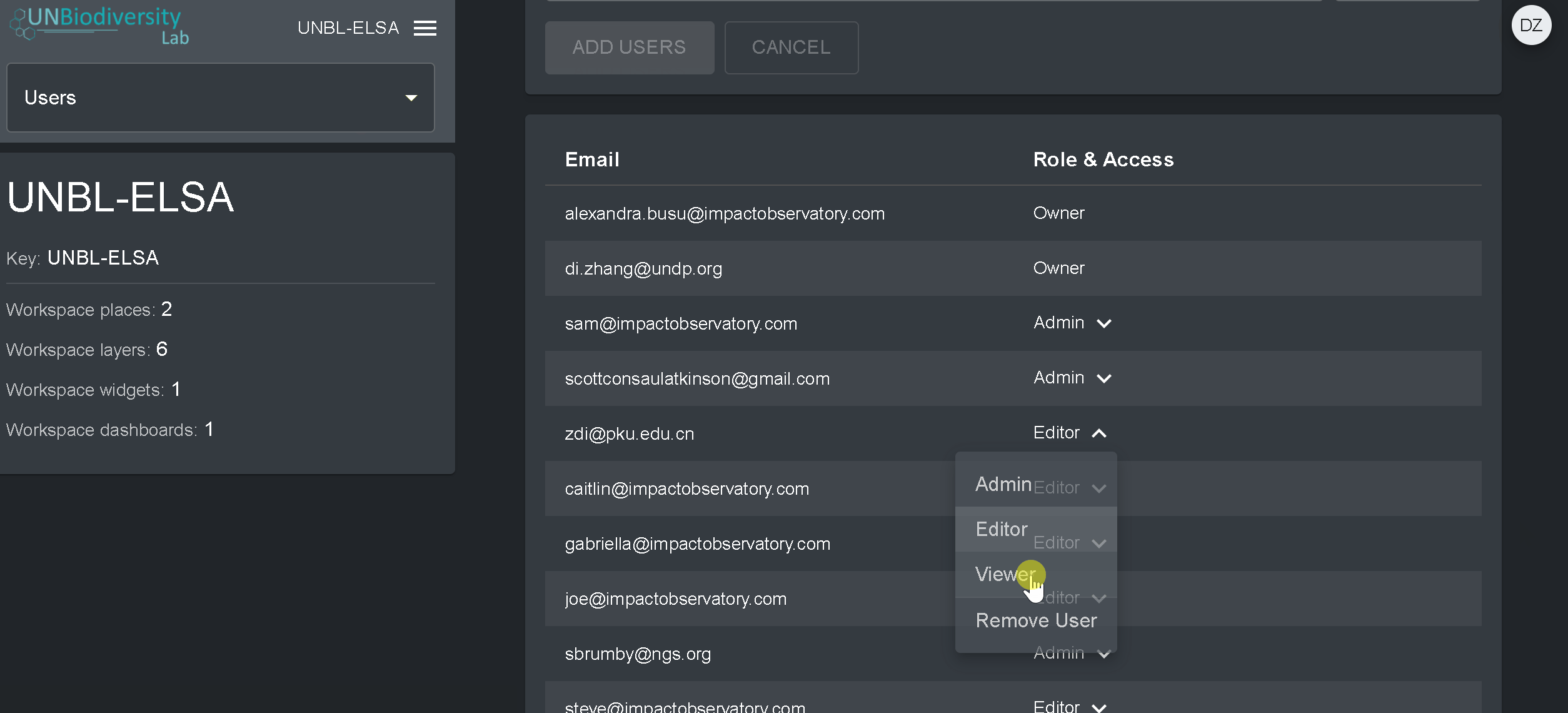
Pour ajouter des utilisateurs à votre espace de travail :
- Demandez à l’utilisateur souhaité de s’inscrire pour obtenir un compte sur l’UNBL (voir notre guide de l’utilisateur de la plateforme publique de l’UNBL pour plus de détails).
- Accédez à la page Utilisateurs à partir du menu déroulant situé à gauche de l’écran des outils d’administration.
- Sélectionnez le bouton “AJOUTER DES UTILISATEURS”. Saisissez l’adresse électronique de l’utilisateur dans la barre “Courriel de l’utilisateur” et attribuez-les à un ou plusieurs groupes d’utilisateurs dans la barre “Groupes d’utilisateurs”. Les noms sont automatiquement générés à partir de l’adresse électronique de l’utilisateur.
- Note : l’utilisateur doit déjà être un utilisateur enregistré dans la plate-forme principale de l’UNBL pour pouvoir être ajouté à votre espace de travail. S’il n’est pas déjà un utilisateur enregistré de la plate-forme, vous obtiendrez un message d’erreur.
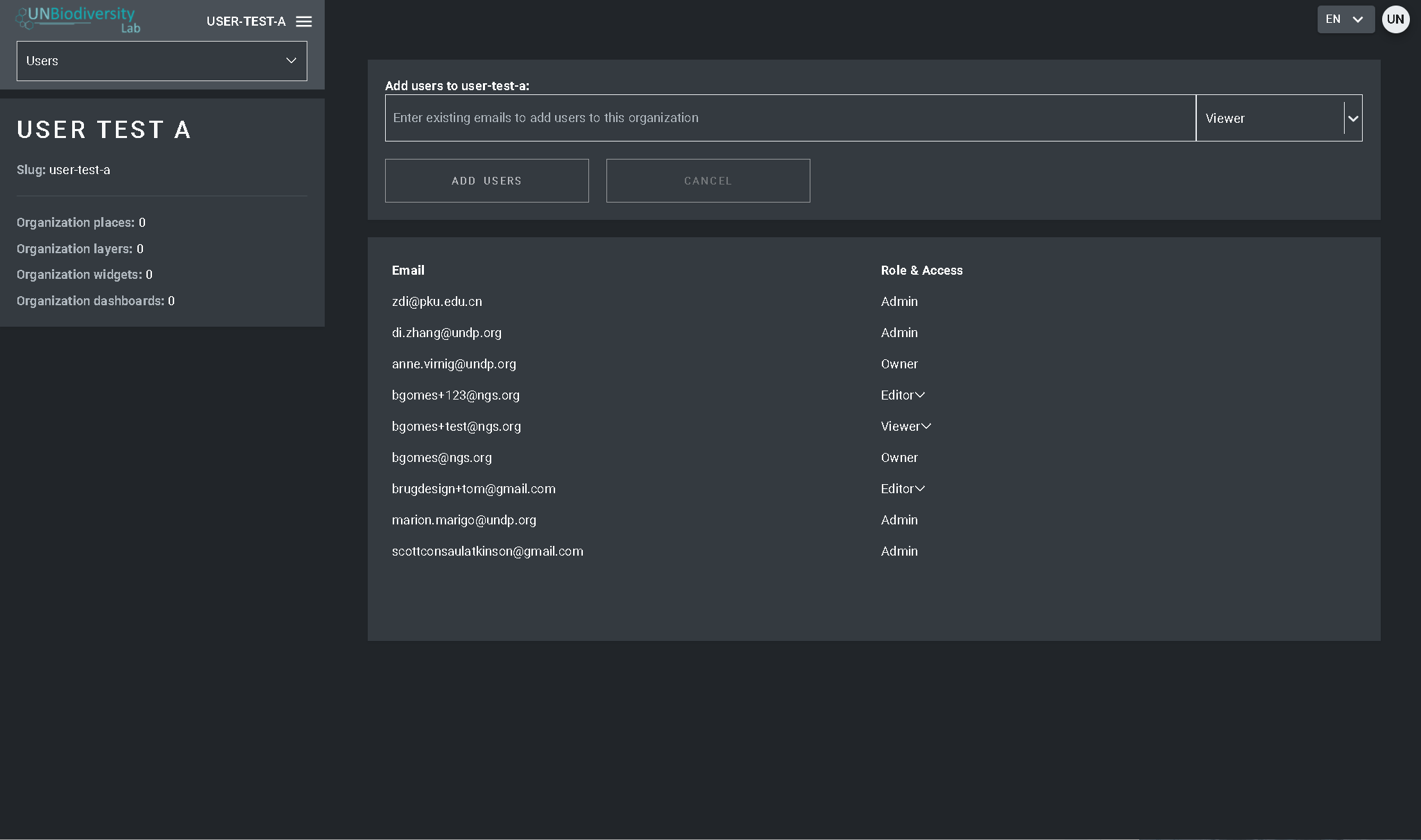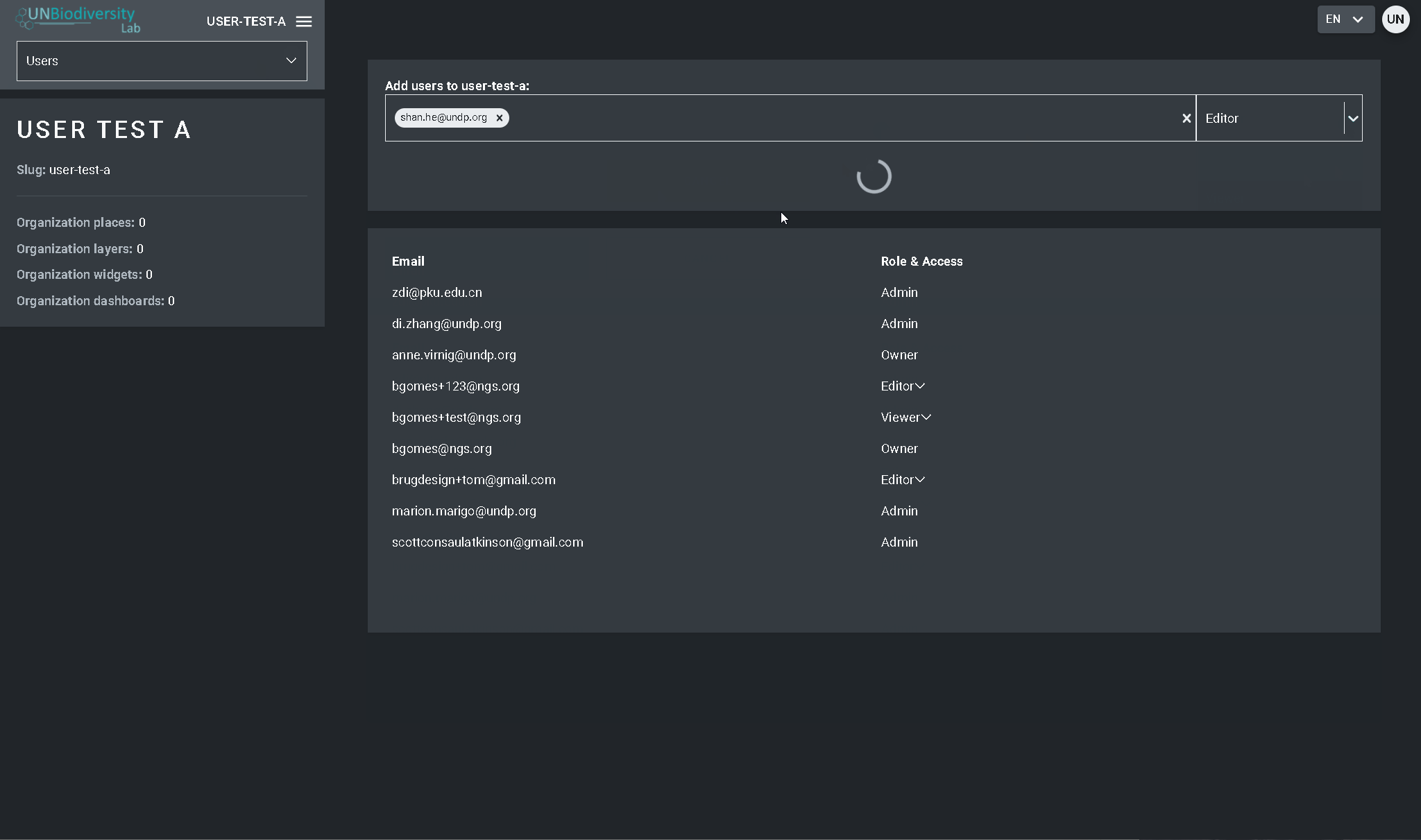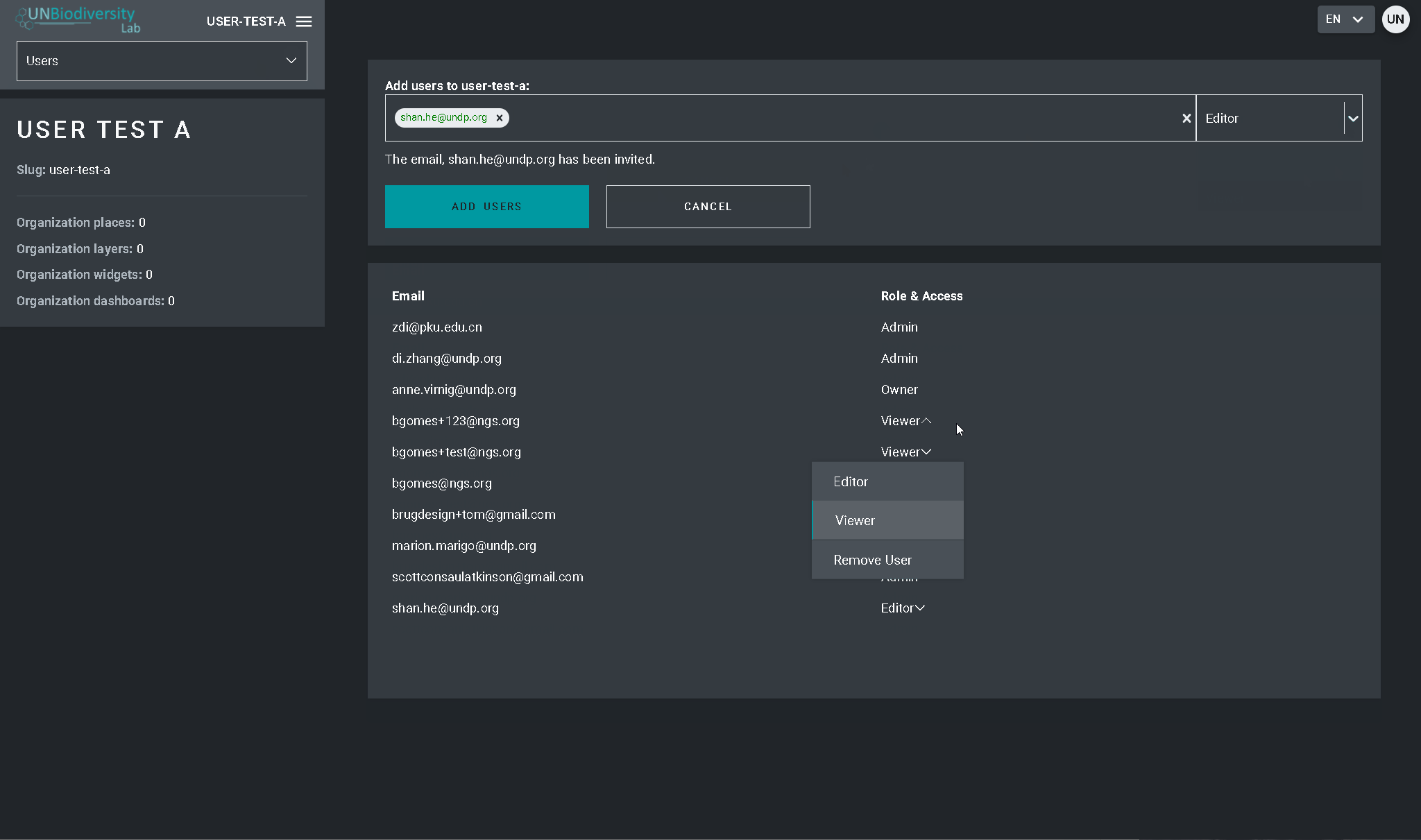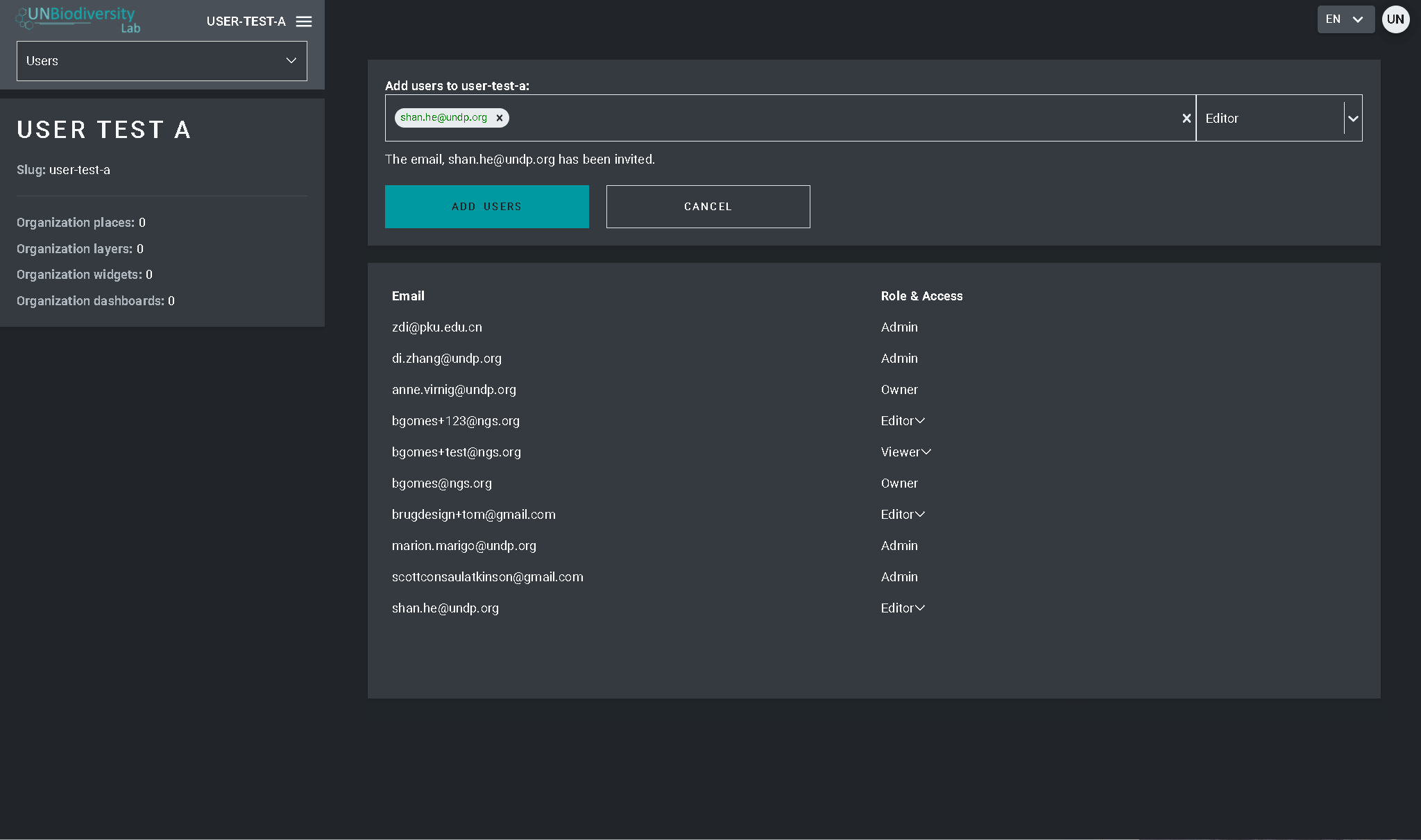
Pour supprimer ou modifier des utilisateurs existants :
- Accédez à la page Utilisateurs à partir du menu déroulant situé à gauche de l’outil d’administration. Lorsque vous entrez dans la page Utilisateurs, tous les utilisateurs de votre espace de travail seront répertoriés dans le panneau de gauche.
- Sélectionnez un nom d’utilisateur dans le panel.
- Pour modifier le rôle et les autorisations de l’utilisateur dans votre espace de travail, choisissez EDITER UTILISATEUR et attribuez-lui le rôle souhaité dans la barre de recherche Rôles de l’utilisateur. Veillez à supprimer toute autorisation inutile en cliquant sur le [x].
- Pour supprimer l’utilisateur, cliquez sur la case SUPPRIMER L’UTILISATEUR.
- des mesures dynamiques seront automatiquement calculées pour ce lieu ; et
- découper n’importe quelle couche matricielle (accessible au public) de ce lieu et la télécharger pour un travail ultérieur dans un logiciel SIG de bureau.
- Accédez à la page Endroit à partir du menu déroulant situé à gauche de l’outil d’administration.
- Cliquez sur le bouton CREER UN NOUVEAU LIEU.
- Sur la page Nouveau lieu, remplissez les informations suivantes :
-
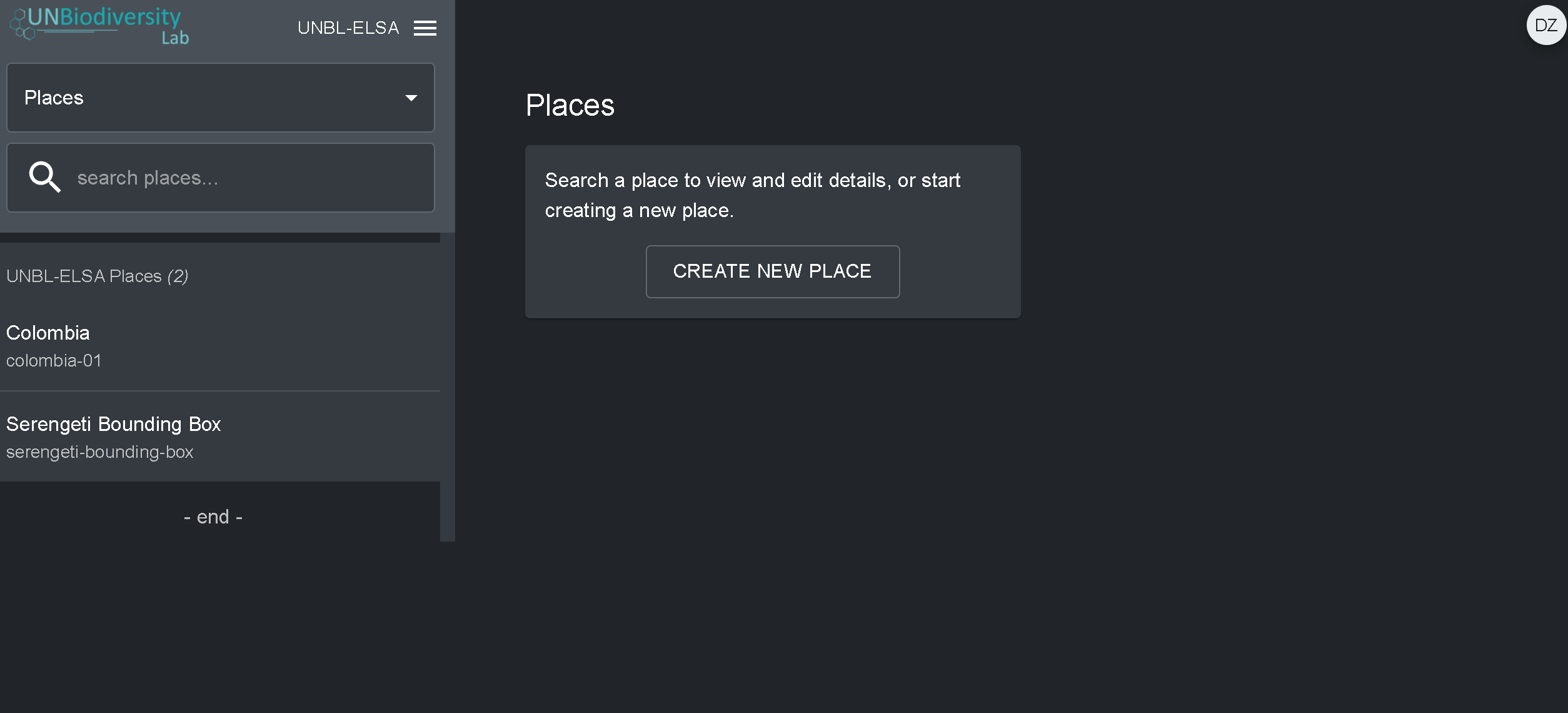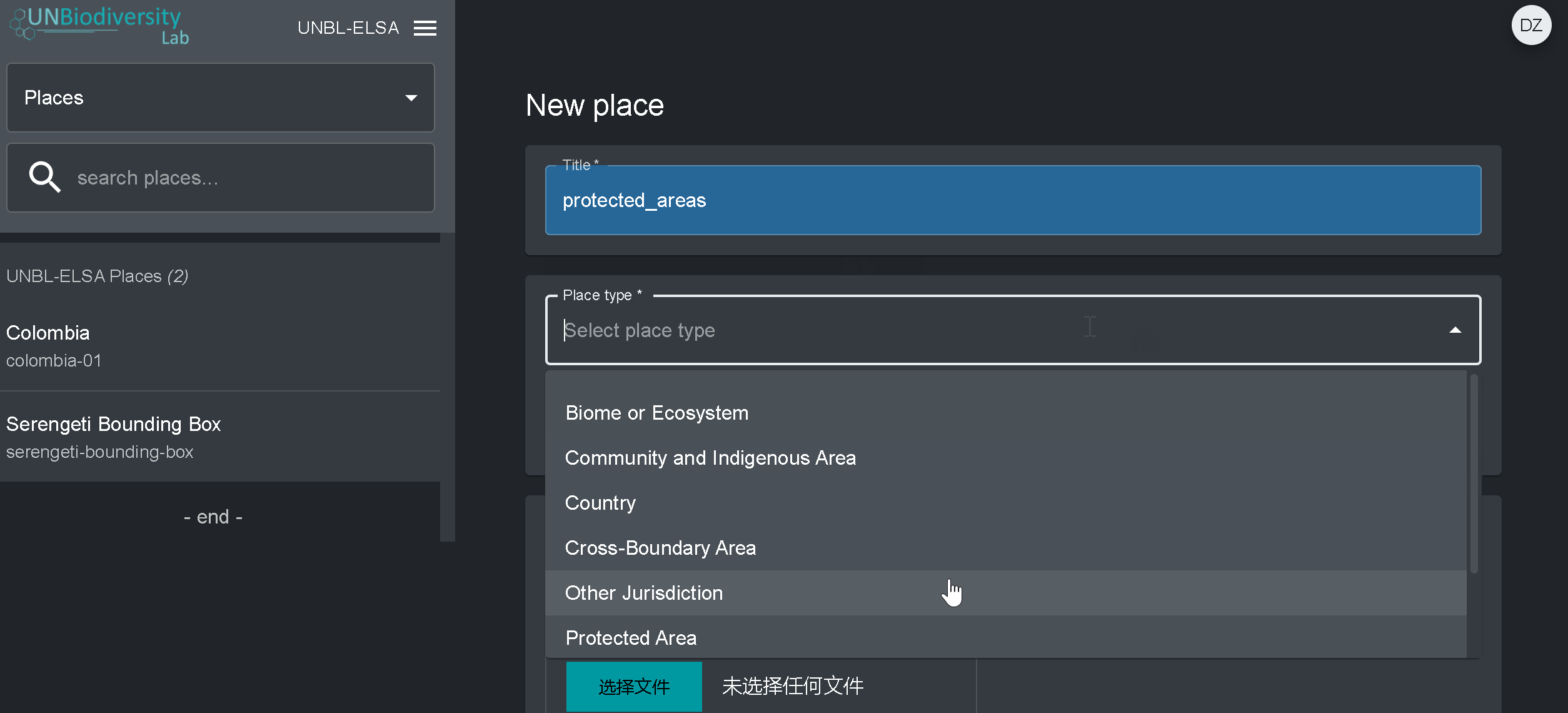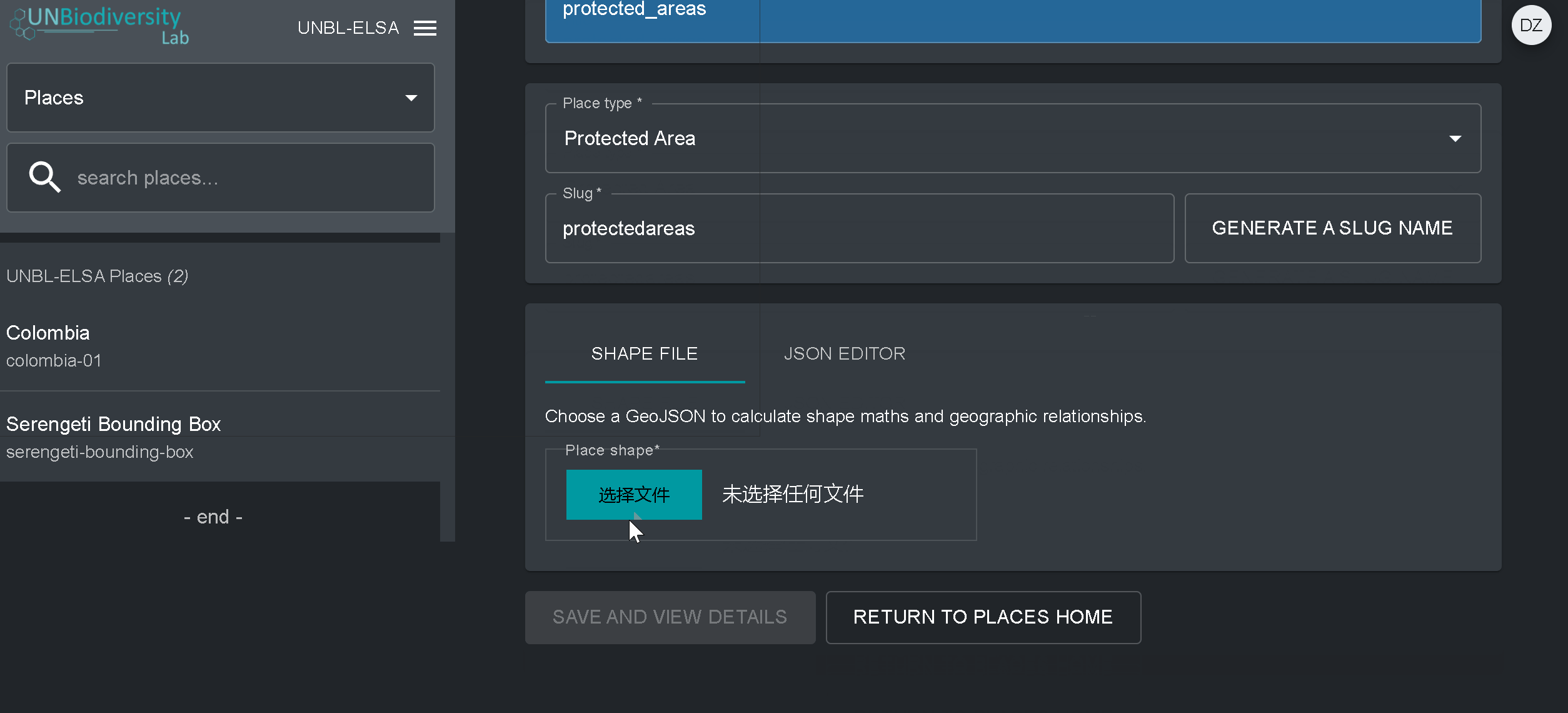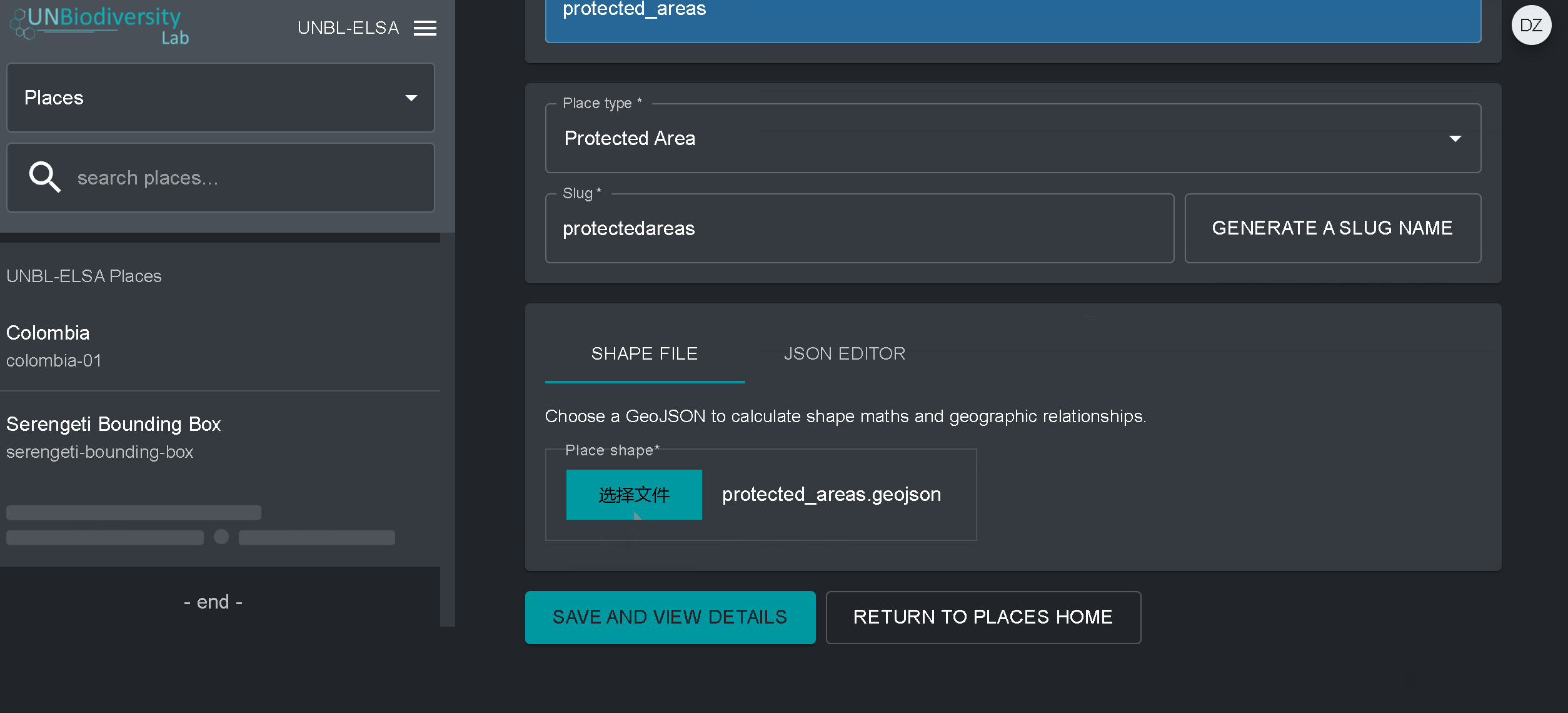
- Titre : Insérer le nom du lieu. Nous recommandons de les garder courts et clairs. Actuellement, aucun caractère spécial n’est autorisé.
- Type de lieu : Sélectionnez la classe appropriée dans le menu déroulant. Cela vous sera utile pour filtrer vos recherches plus tard. Vous pouvez choisir entre Pays, Juridiction, Biome, Zone protégée ou Zone d’espèces.
- Slug : Insérez un identifiant unique pour le lieu qui ne contient que des lettres minuscules, des chiffres et des traits d’union. Aucun espace ne peut être utilisé. Nous vous recommandons d’utiliser le bouton GENERER UN NOM DE SLUG pour vous aider à générer une slug approprié.
- Forme du lieu : Téléchargez le fichier GeoJSON représentant votre lieu à l’aide du bouton CHOISIR FICHIER. Le fichier doit être un GeoJSON de moins de 6 Mo et ne doit pas comporter plus d’un million de sommets. Bien que le système autorise les téléchargements jusqu’à 6 Mo, nous recommandons fortement d’utiliser des fichiers ne dépassant pas 2 Mo pour un rendu et des calculs de métriques optimaux. Il peut s’agir d’un seul ou de plusieurs polygones, mais notre système ne lira pas les sous-caractéristiques d’un polygone. Voici un guide plus complet sur les exigences en matière de format.
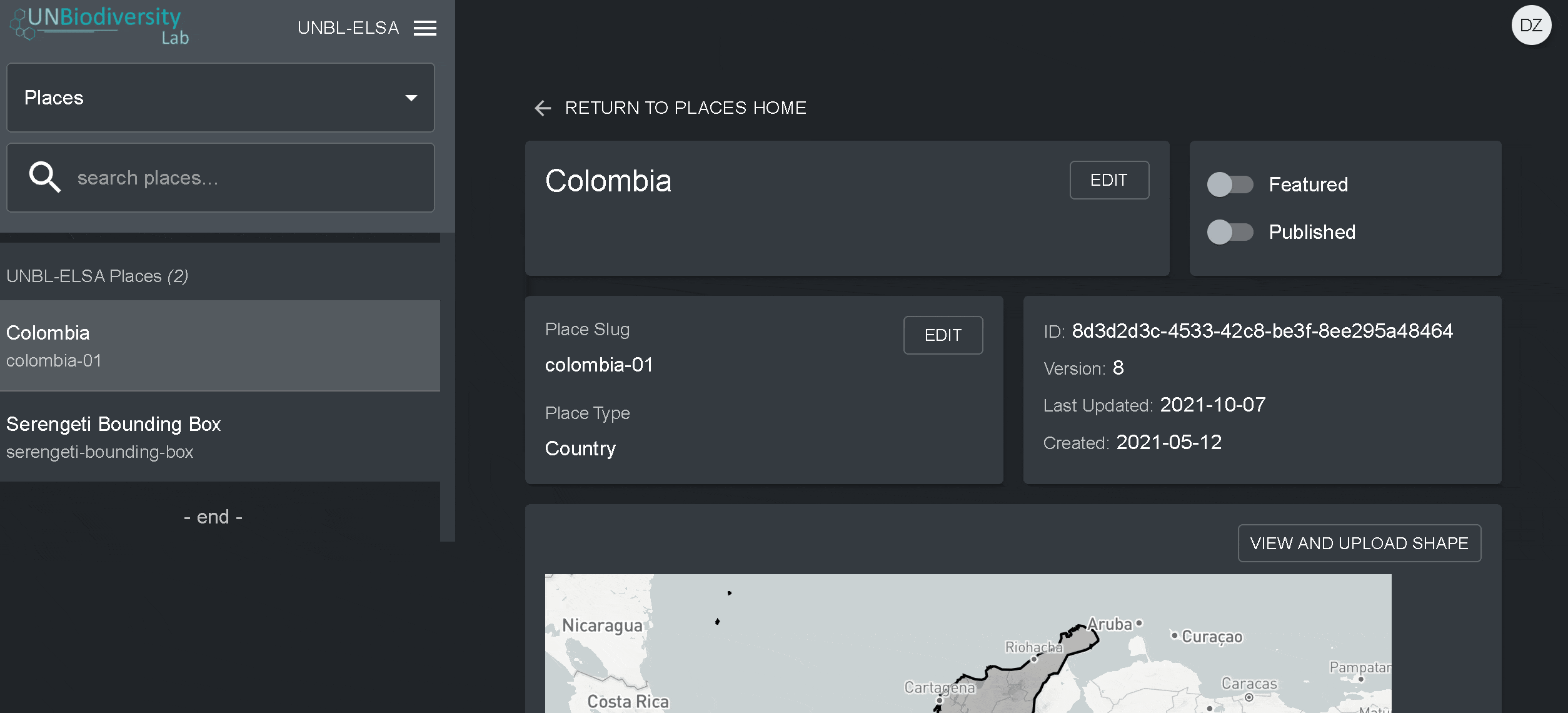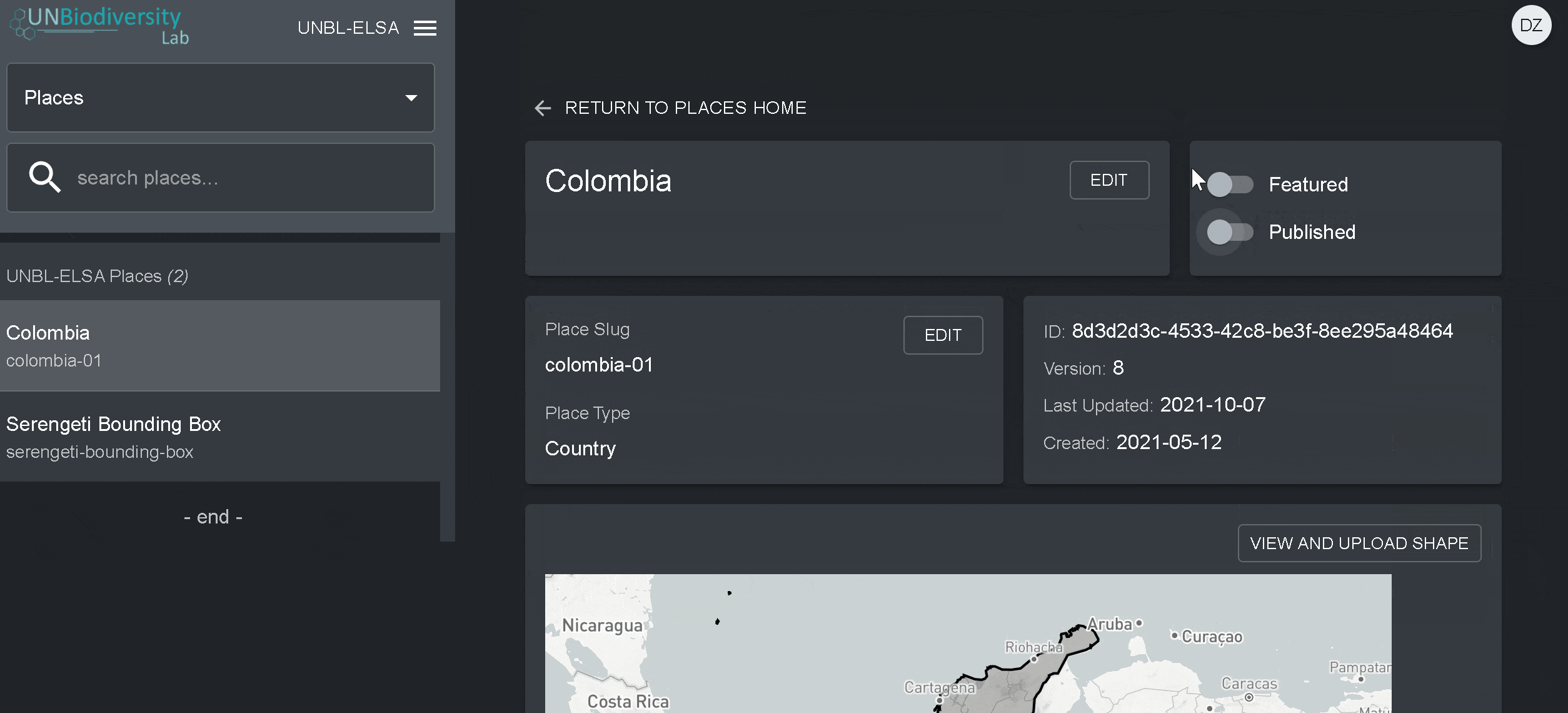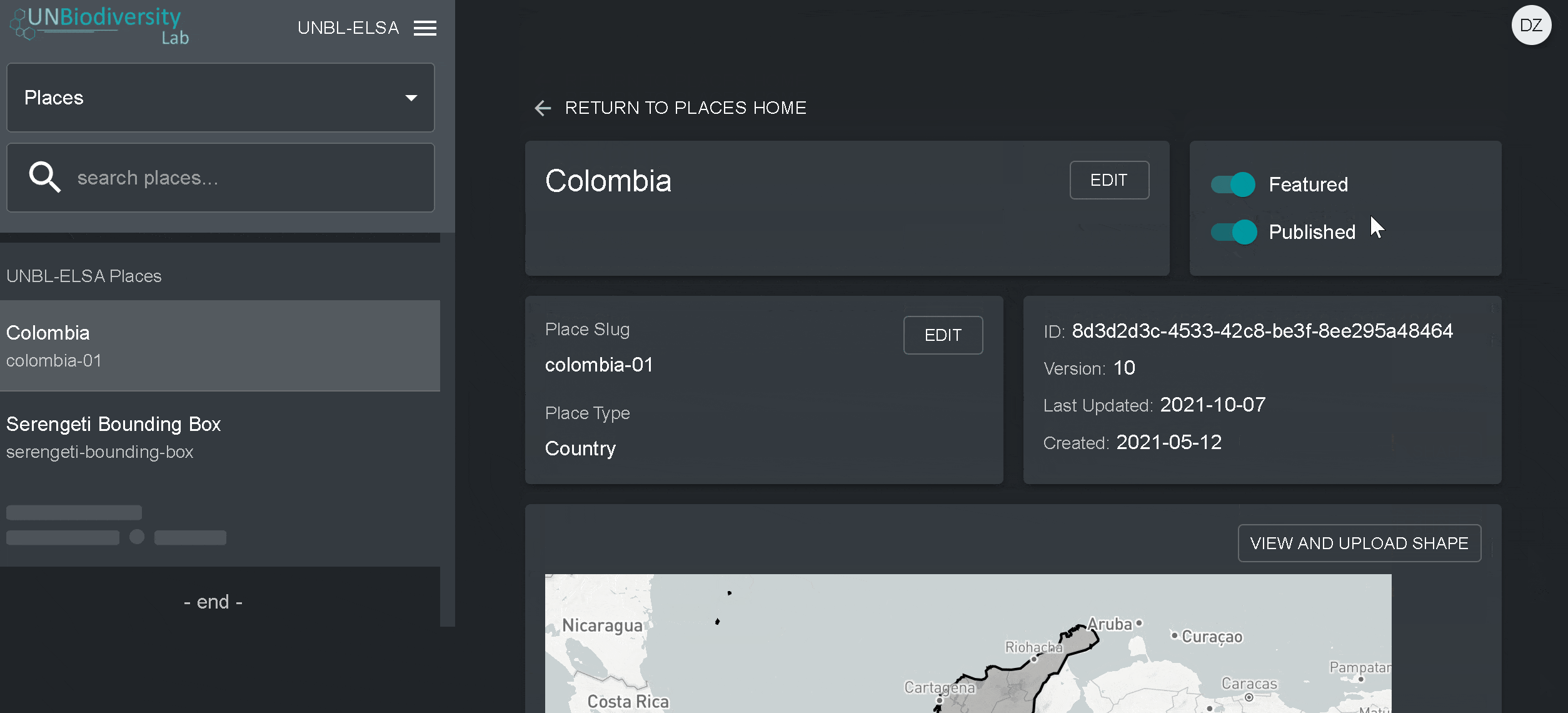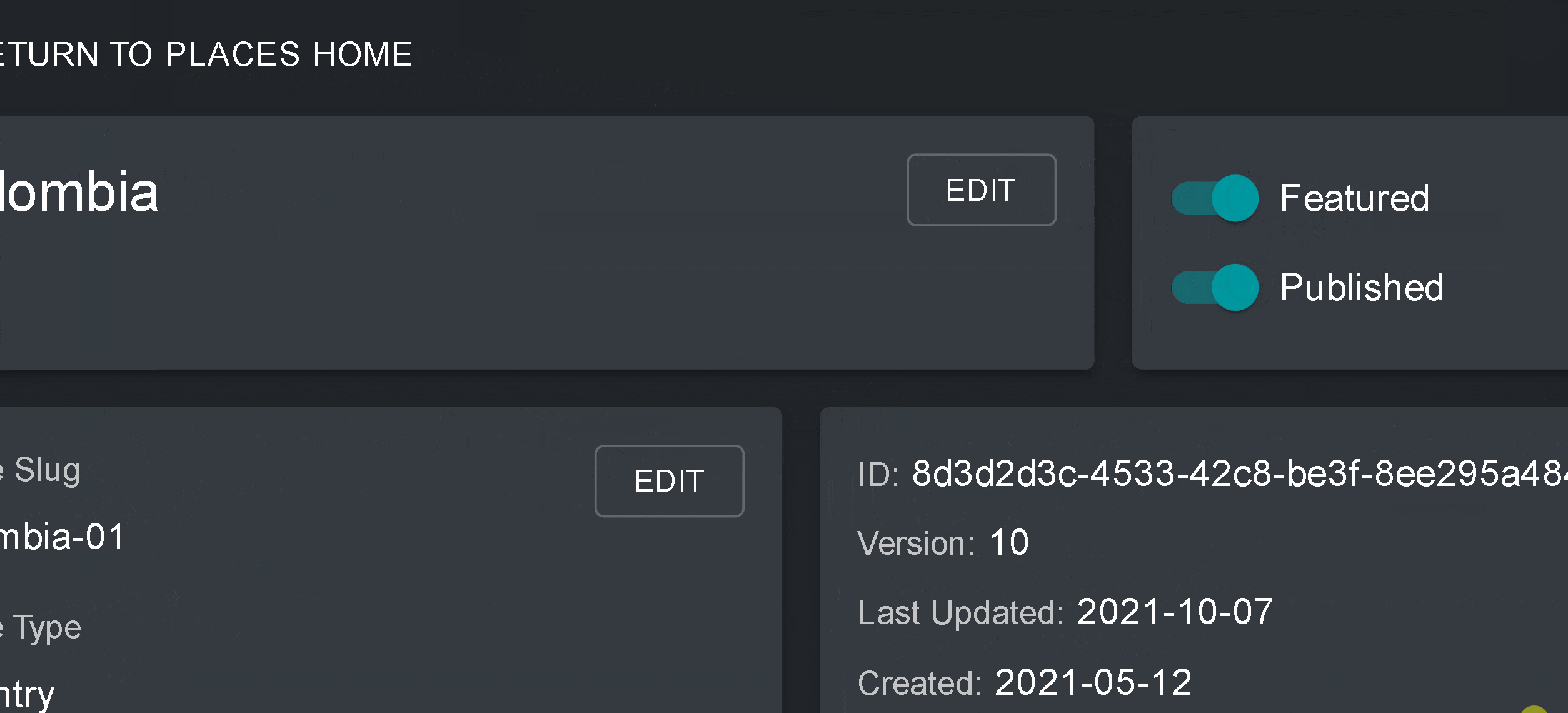
- Une fois que vous aurez enregistré votre nouveau lieu, vous serez amené à l’écran d’accueil du lieu. Pour que votre lieu soit accessible en vue cartographique, vous devez le publier en cliquant sur le bouton Publié. Les lieux non publiés restent dans l’outil d’administration jusqu’à ce que vous soyez prêt à les publier dans la vue cartographique de l’espace de travail.
- Pour faire de ce lieu un lieu vedette de votre espace de travail, activez le bouton “En vedette”. Cela fera office de signet pour que le lieu apparaisse en haut de la liste dans l’onglet Lieux chaque fois qu’un lieu n’est pas sélectionné.
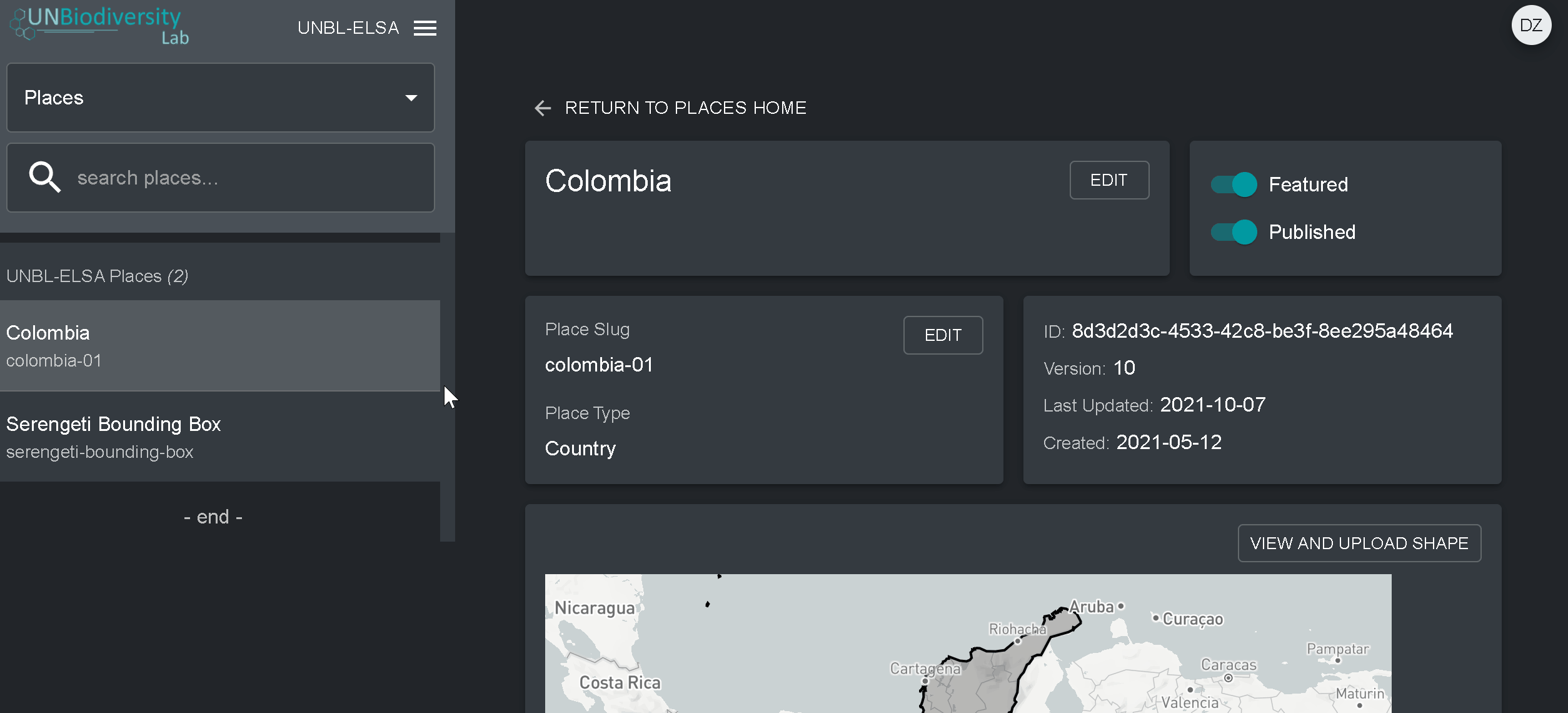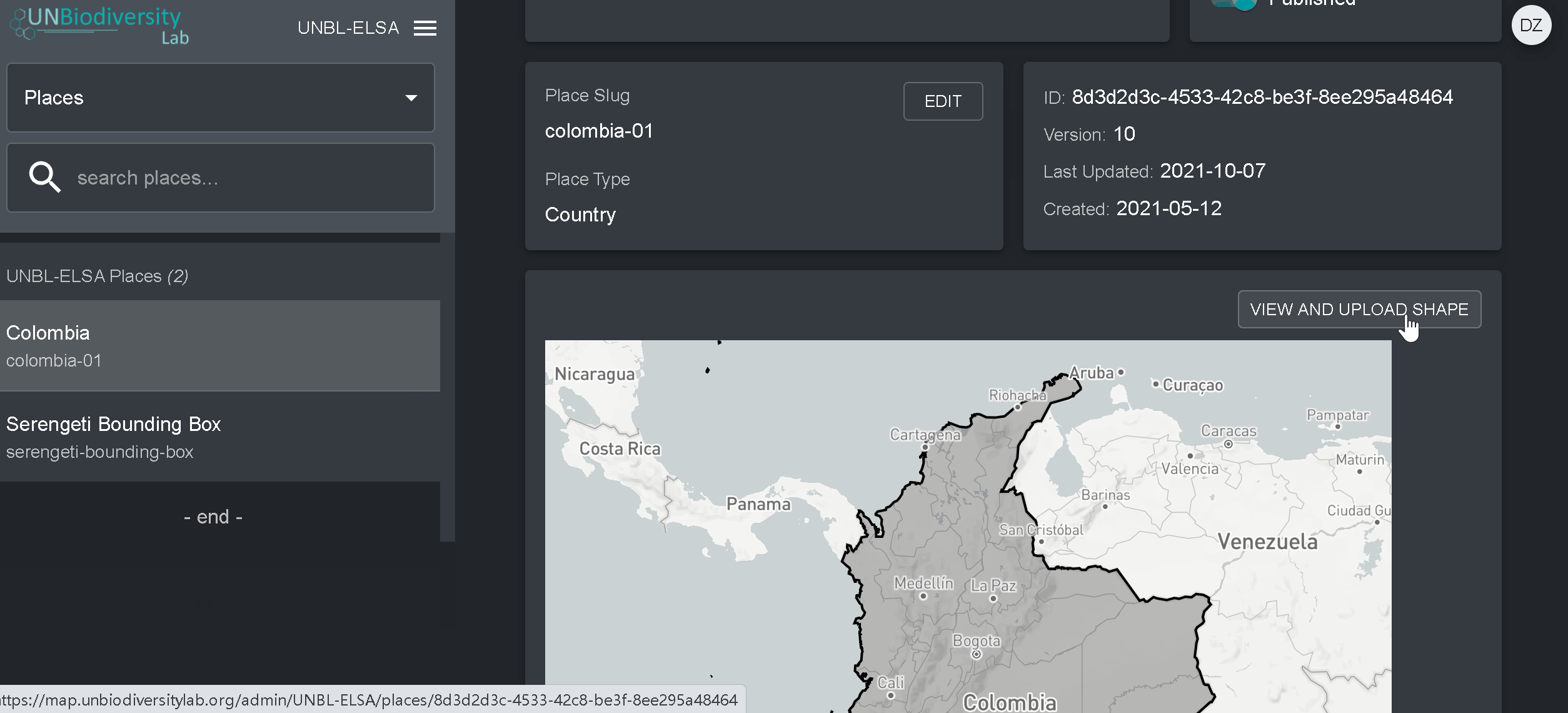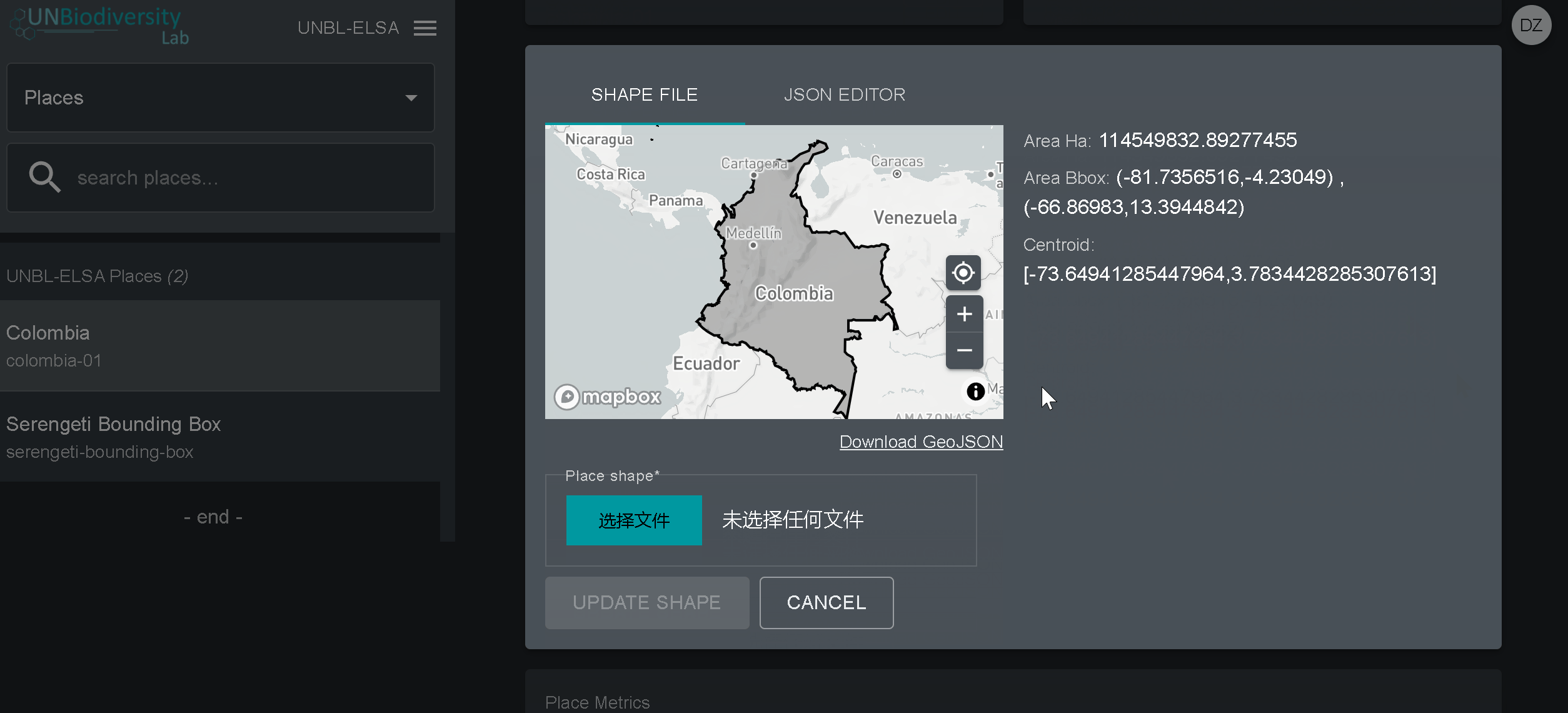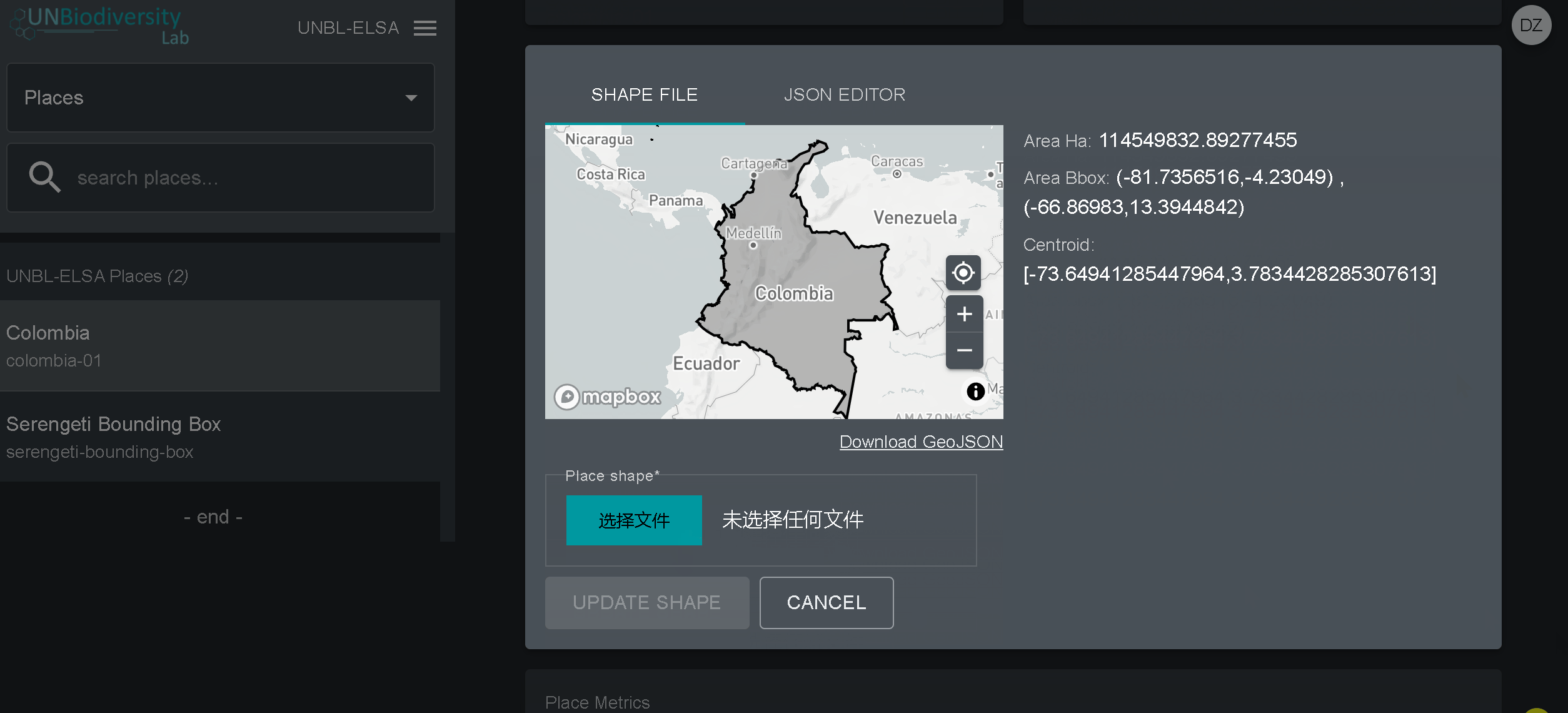
- Accédez à la page Endroits à partir du menu déroulant situé à gauche de l’outil d’administration.
- Sélectionnez le lieu qui vous intéresse dans la liste des lieux située dans la barre de menu de gauche. Une fois que vous aurez cliqué sur le lieu, ses détails apparaîtront dans le panneau de droite.
- Cliquez sur le bouton « Voir et charger la forme » au-dessus de la fenêtre du plan de base pour voir quelques informations géospatiales de base sur votre forme et pour télécharger toute nouvelle version de la forme que vous pourriez avoir à l’avenir.
- Naviguez vers la page “Couches” à partir du menu déroulant à gauche de l’outil d’administration.
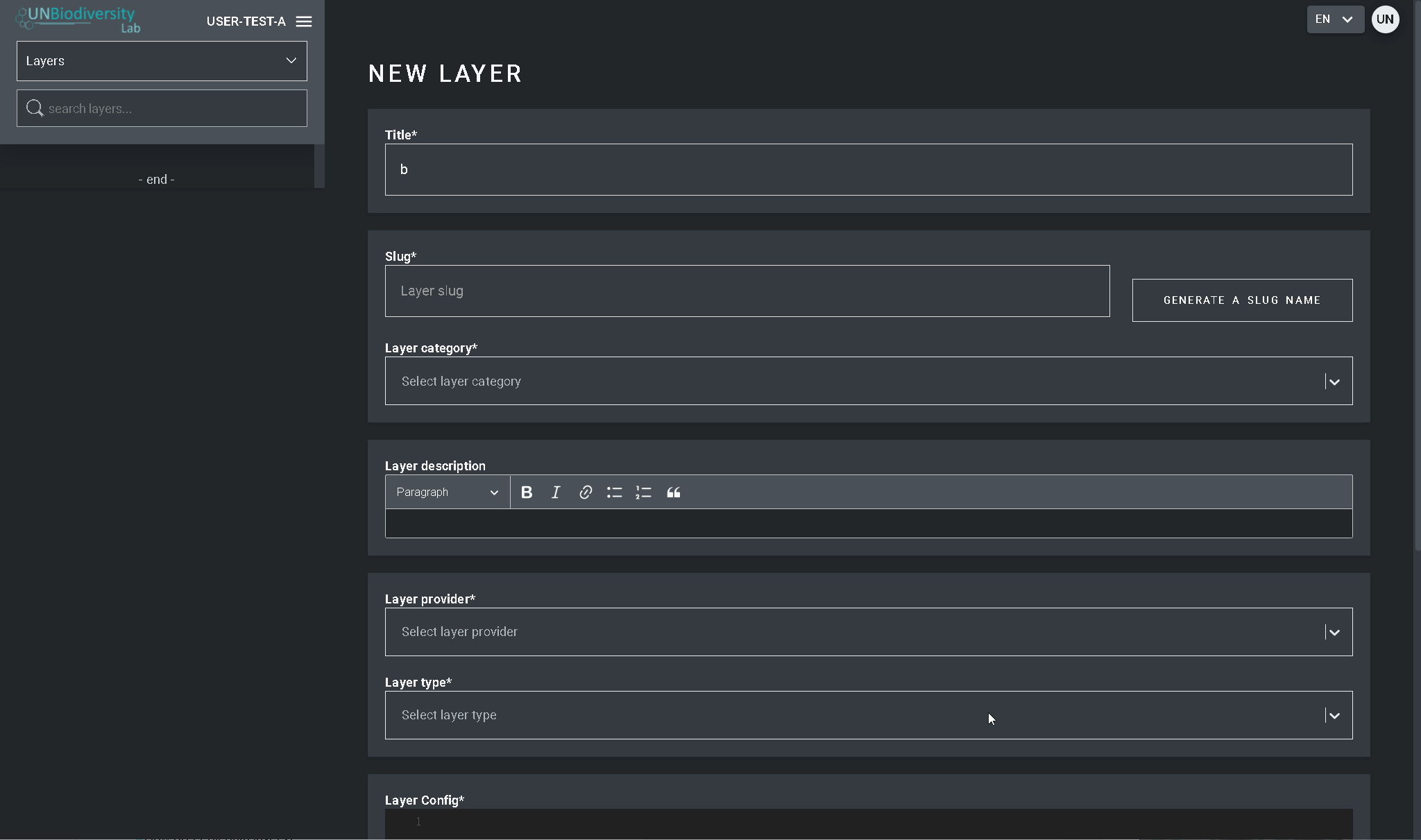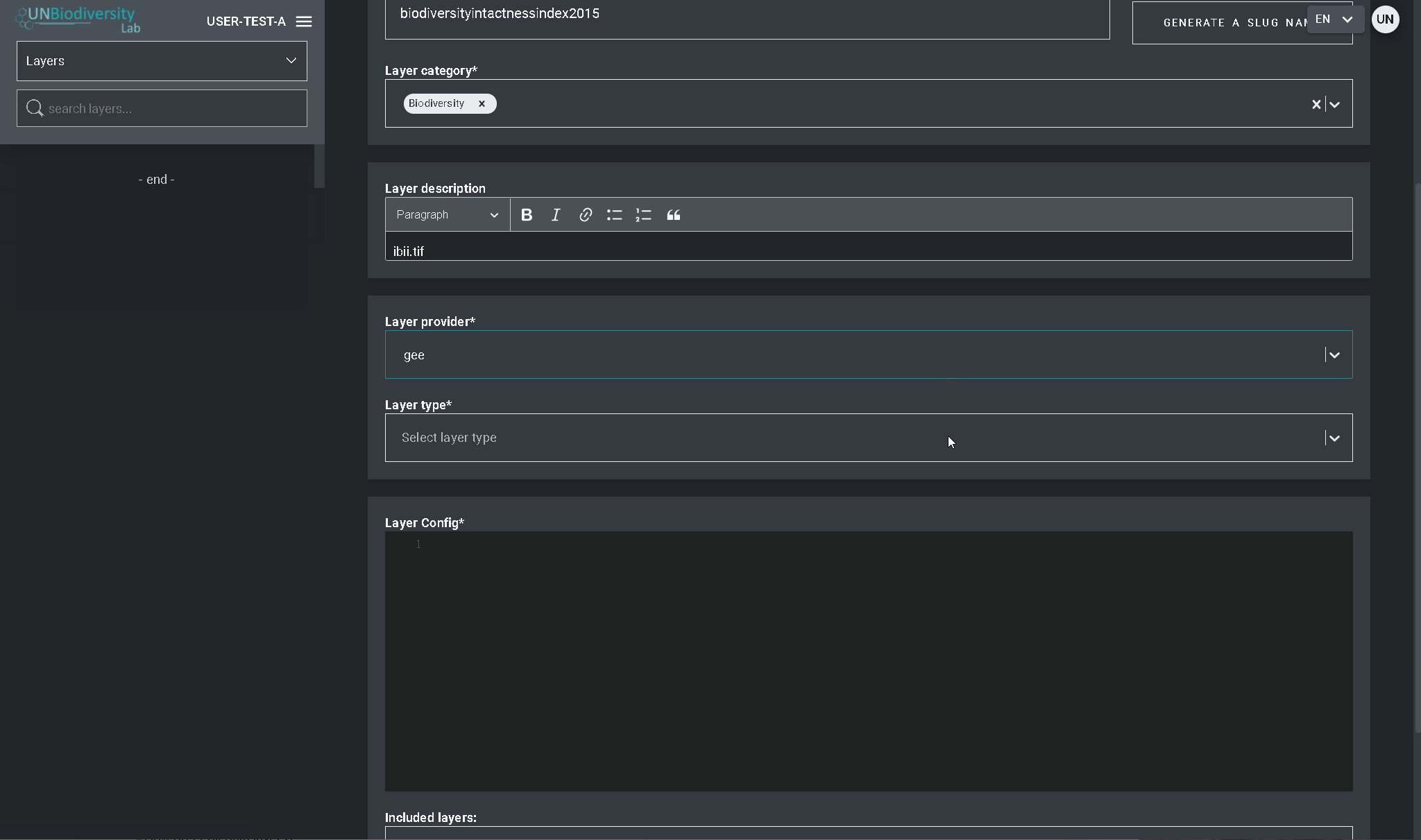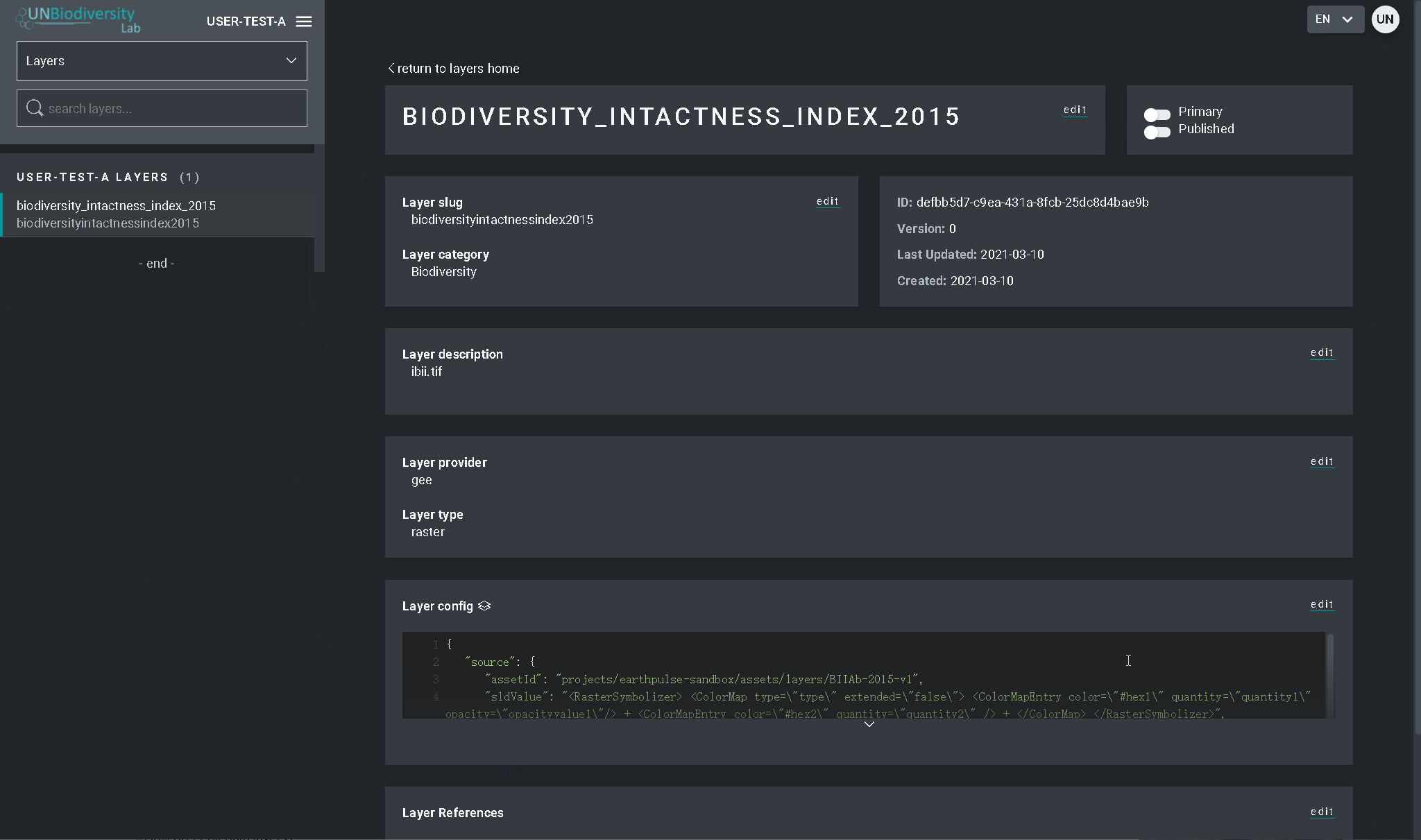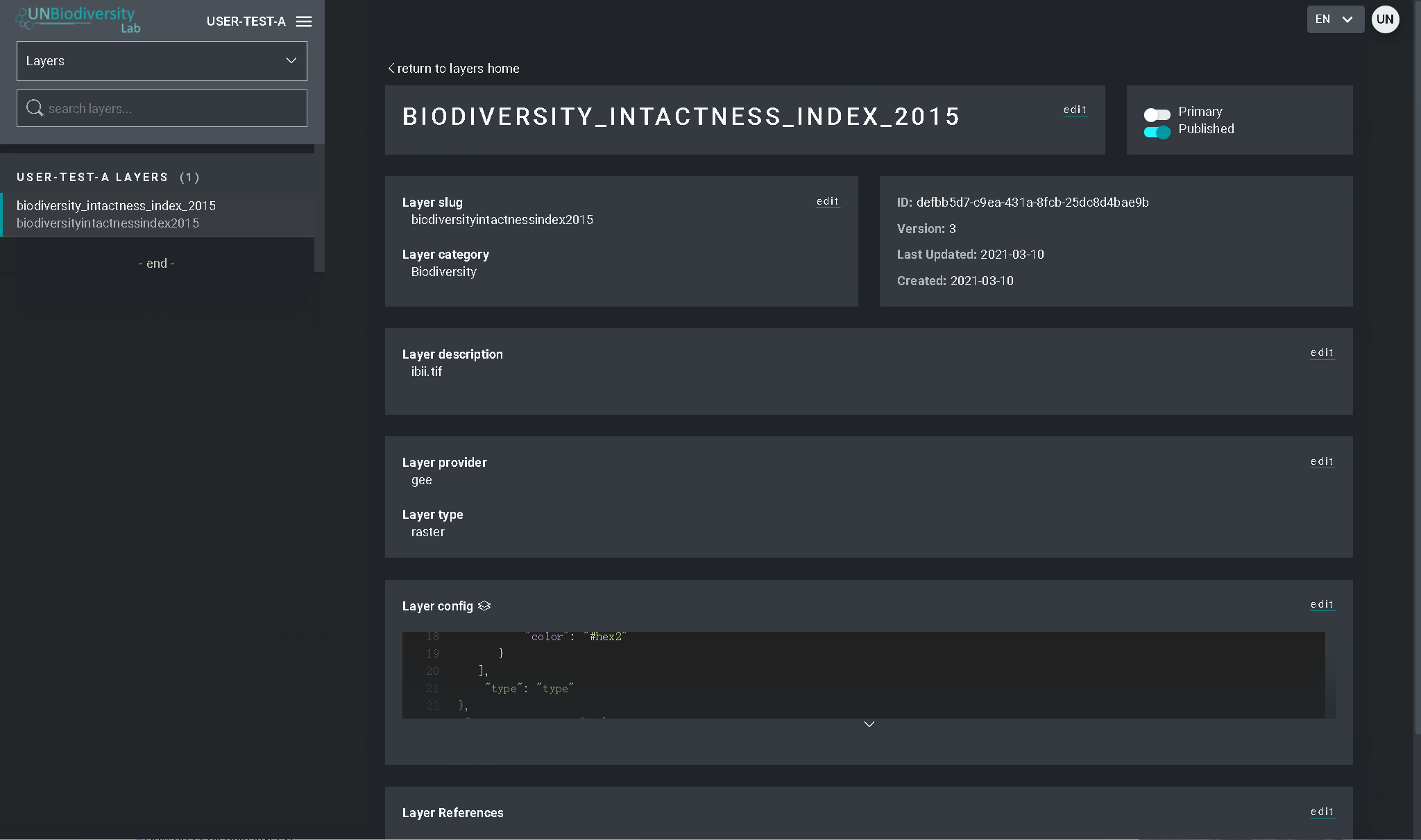
- Sélectionnez le bouton CREER UNE NOUVELLE COUCHE.
- Sur la page Nouvelle couche, remplissez les informations suivantes : Nombre de la capa: recomendamos que sea corto y claro. Actualmente, no se permiten caracteres especiales.
- Titre de la couche : Nous vous recommandons de faire en sorte qu’elles soient courtes et claires. Actuellement, aucun caractère spécial n’est autorisé.
- Slug : insérez un identifiant unique pour la couche qui ne contient que des lettres minuscules, des chiffres et des traits d’union. Aucun espace ne peut être utilisé. Nous vous recommandons d’utiliser le bouton GENERER UN NOM DE SLUG pour vous aider à générer une lopin approprié.
- Catégorie de couche : Sélectionnez la classe thématique appropriée dans le menu déroulant. Cela vous sera utile pour filtrer vos recherches plus tard. Vous pouvez choisir parmi les domaines administratifs ; la biodiversité ; le climat et le carbone ; les services écosystémiques ; les habitats, les écosystèmes et les biomes ; l’impact et les pressions de l’homme ; l’occupation des sols ; le milieu marin ; les risques naturels ; les zones protégées et conservées ; la restauration ; les aspects socio-économiques et le développement durable.
- Fournisseur de couche : Choisissez de quelle source vous dérivez la couche.
- Type de couche : Attribuez un type de couche ; actuellement, les espaces de travail UNBL ne peuvent prendre en charge que les couches matricielles.
- Accédez à la page Couches à partir du menu déroulant situé à gauche de l’outil d’administration (vous devrez peut-être actualiser la page pour que la nouvelle couche apparaisse dans la liste).
- Cliquez sur le bouton ÉDITER dans la section Configuration des couches.
- Dans l’écran de l’éditeur de couche, modifiez uniquement les sections en surbrillance du code de configuration, comme indiqué ci-dessus. Tout le reste doit rester inchangé, sinon vous obtiendrez une erreur.
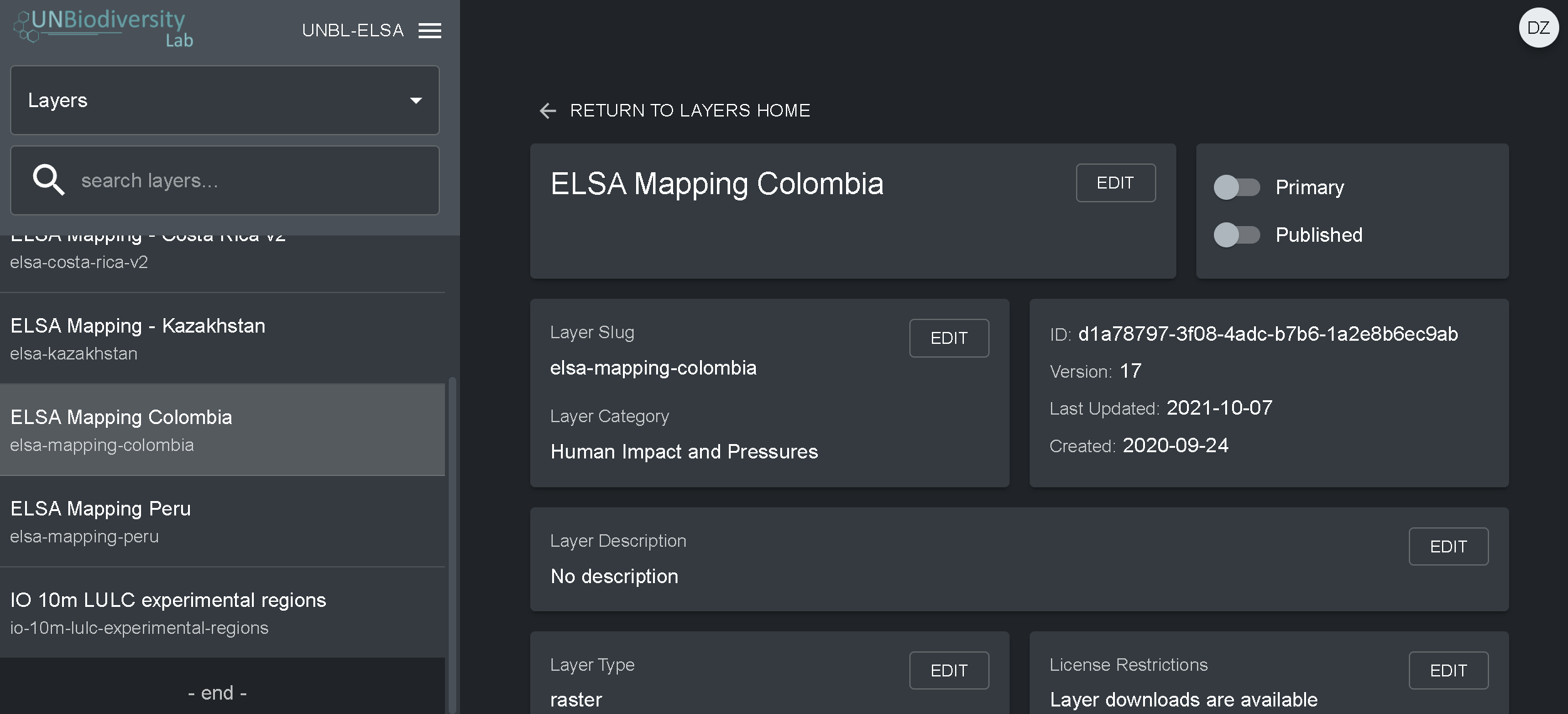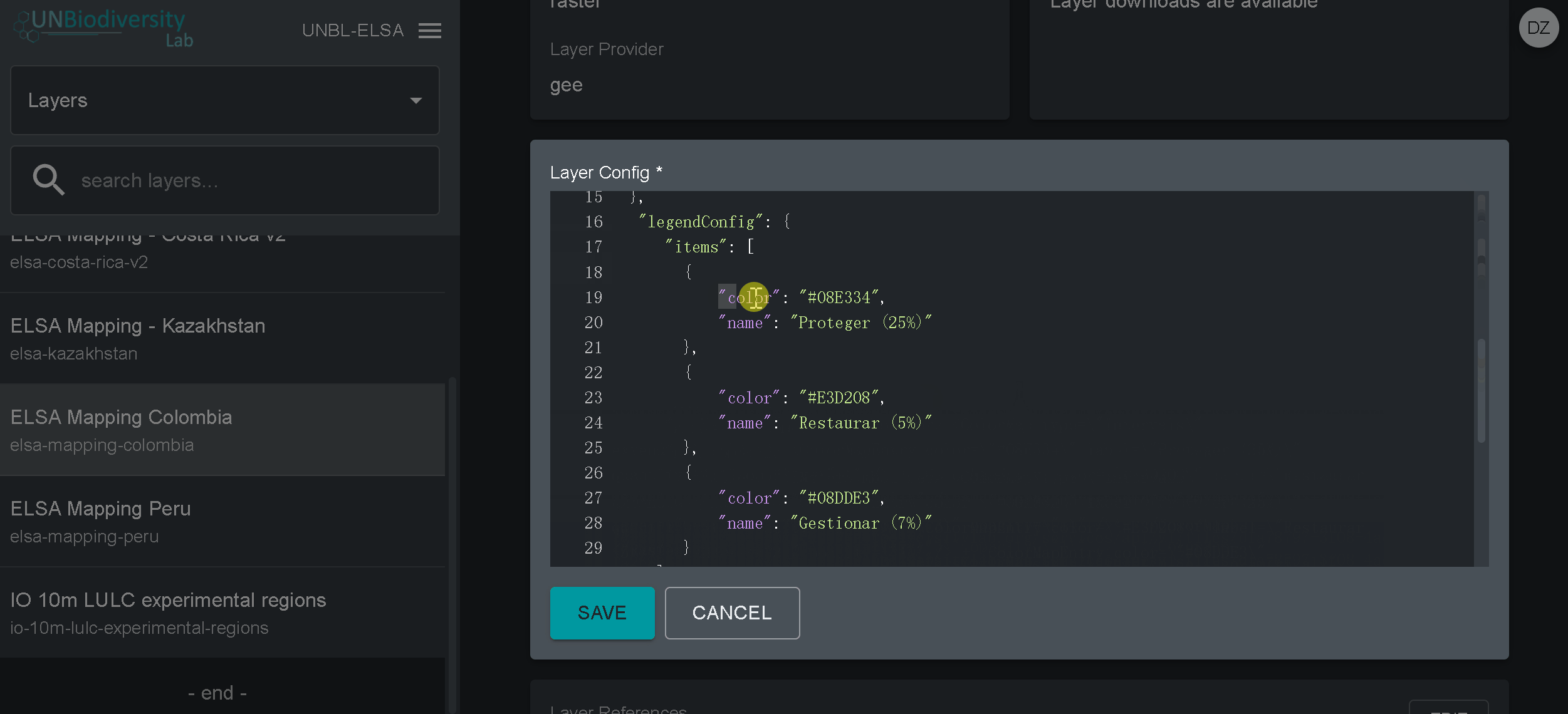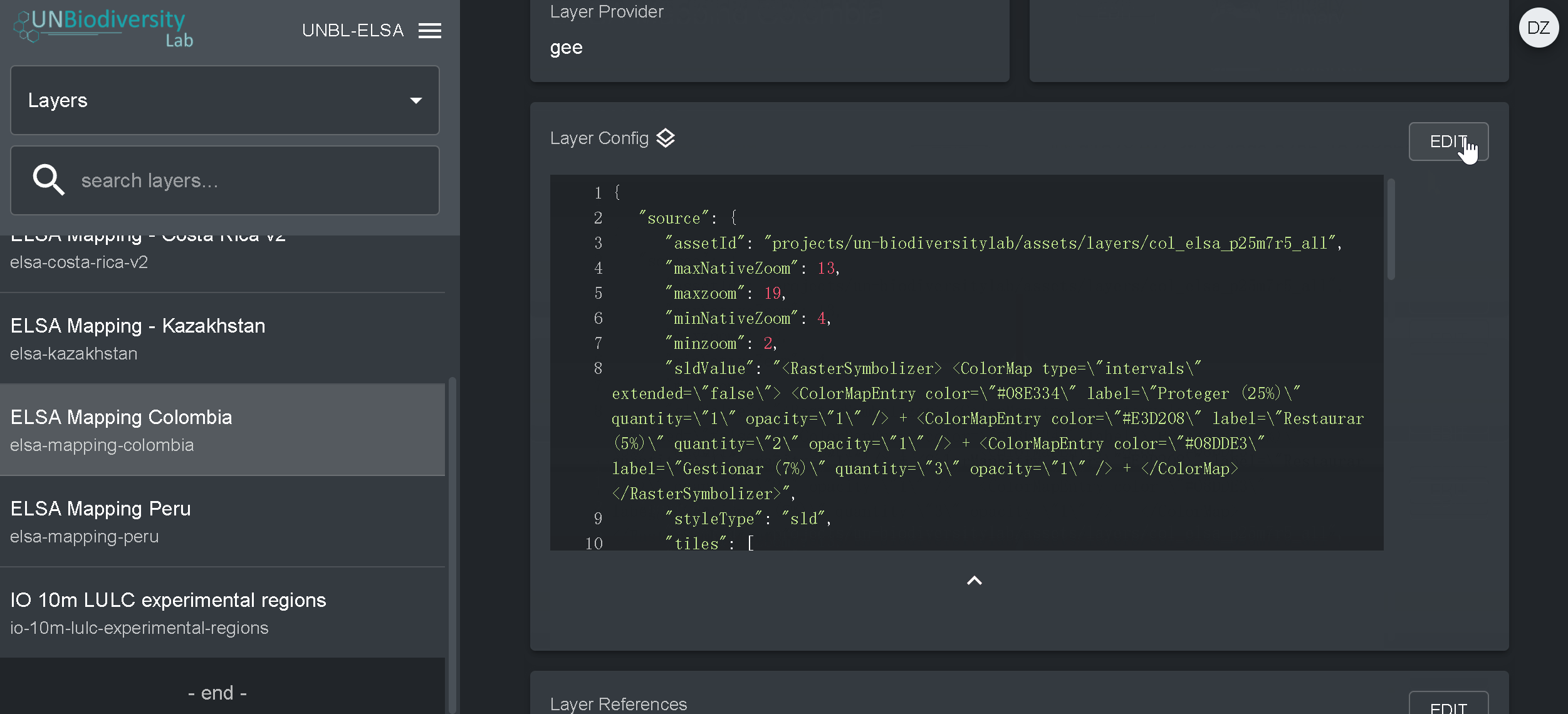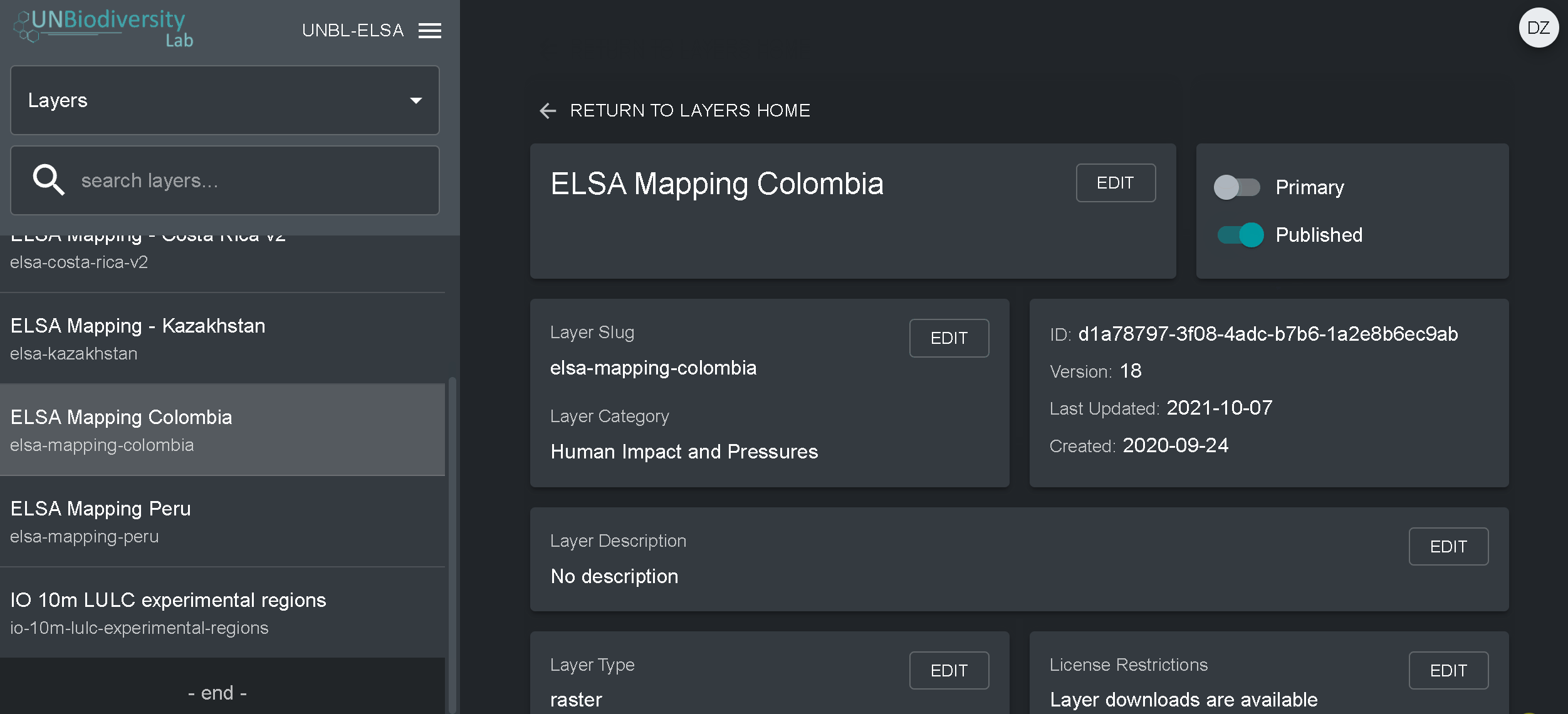
- Copiez et collez l’ID de l’actif Google Earth Engine ici, entre guillemets (” “).
- Saisissez le style de la couche. Le style des couches suit le format SLD (Styled Layer Descriptor). Ce format vous permet de modifier la coloration, la transparence et la plage de valeurs de votre couche. Nous vous recommandons de suivre les étapes suivantes pour remplir cette partie de la configuration sur le guide de l’utilisateur.
- Entrez le style de légende indiqué sur le guide de l’utilisateur.
- Cliquez sur SAVE LAYER une fois que vous avez le style souhaité pour créer une URL unique pour la couche. Cette URL sera ajoutée à la configuration de la couche pour compléter le processus.
- Modifiez l’URL. Après la sauvegarde, une valeur d’identification apparaîtra (entourée ci-dessous). Les tuiles matricielles sont stockées sur la base d’un identifiant unique trouvé dans l’URL de la couche. Collez cette URL dans la configuration de la couche pour charger la couche dans la vue cartographique.
- Sélectionnez Groupe dans le menu déroulant Type de couche.
- Ajoutez chacune des couches composantes à l’aide de la boîte de sélection Couches incluses.
- Ajoutez l’un des deux scripts de configuration spéciaux ci-dessous en fonction de la manière dont vous souhaitez présenter les données dans la légende des couches de la vue cartographique. Remarque : aucune information sur le style, l’url ou la légende n’est nécessaire. Lorsque la couche est marquée comme une couche “groupe”, toute la visualisation est tirée des couches composantes.
-
- Boutons radio : Recommandé pour les couches de groupe contenant deux ou trois années/catégories. Collez le code du guide de l’utilisateur dans le champ de configuration sans le modifier.
- Barre déroulante : Recommandé pour les couches contenant plus de trois années/catégories. Collez le code du guide de l’utilisateur dans la boîte de configuration sans le modifier.
Pour le moment, si vous souhaitez créer une couche animée, veuillez contacter support@unbiodiversitylab.org pour obtenir de l’aide.
Télécharger le guide d'utilisation des espaces de travail sécurisés : Anglais | Français | Espagnol | Portugais | Russe
Espaces de travail du UNBL
Espaces de travail privés
Vous travaillez à la conservation de la nature et au développement durable ? Vous disposez de données nationales que vous aimeriez visualiser et analyser en combinaison avec nos couches de données mondiales ? Nous proposons des espaces de travail permettant à diverses parties prenantes d'utiliser les outils UNBL dans un espace sécurisé.
Contribuer
Contribuer

Avez-vous des données qui pourraient enrichir la plateforme publique du UNBL ? Êtes-vous prêt(e) à faire partie d'une communauté scientifique engagée dans le partage ouvert des données spatiales ? Si vous avez des données mondiales qui concernent la biodiversité, le changement climatique ou le développement durable, nous voulons vous entendre.
Veuillez consulter les critères de sélection des données de l'UNBL ici.

Comment utilisez-vous les données spatiales pour comprendre et agir dans votre travail ? Le UNBL s'efforce de mettre en évidence divers cas d'utilisation dans le monde entier. Notre équipe travaillera avec vous pour créer un reportage photo ou une histoire sur Google Earth afin de mettre en valeur vos réalisations. Les exemples de réussite seront partagés dans notre section Histoires en vedette.
Nous contacter
Nous contacter
Veuillez laisser votre message et vos coordonnées ci-dessous et nous vous répondrons dès que possible. Vous pouvez également nous envoyer un courriel à support@unbiodiversitylab.org.
Programme des Nations Unies pour le Développement
304 East 45th Street
New York, NY 10017
