Apoio
FAQs
Perguntas mais freqüentes
1. Como Começar
2. Dados
PNUD, PNUMA e UNEP-WCMC adotaram critérios para ajudar a identificar e fazer a curadoria das melhores camadas de dados disponíveis sobre estes temas, a fim de permitir análises e relatórios mais simplificados e padronizados. Estes critérios de seleção colocarão os dados em uma das três camadas e considerarão aspectos como relevância dos dados, licenciamento aberto e disponibilidade, transparência e cobertura geográfica. Este sistema por níveis destina-se exclusivamente a auxiliar no desenvolvimento e implementação de conjuntos de dados globais que são adequados para apoiar o progresso em direção à Agenda de Desenvolvimento Sustentável de 2030, as metas emergentes da estrutura global de biodiversidade pós-2020, além de metas globais relacionadas.
Os critérios podem ser vistos aqui.
Aviso legal: Os conjuntos de dados sobre UNBL e outras plataformas a nível da ONU ainda não foram formalmente avaliados em relação a estes critérios. Uma avaliação piloto inicial está em andamento.
- Totalmente documentado usando a especificação Open API 3.0 (formalmente, Swagger)
- Tudo está disponível através de uma API HTTP RESTful
- Todas as interfaces de segurança são criadas com as fichas oAuth 2.0 e JWT
Observe que para quaisquer mapas que você criar na plataforma, você precisa citar os fornecedores de dados seguindo o formato indicado na seção FAQ sobre mapas. Esta é uma exigência para o uso de muitos conjuntos de dados, e é uma boa prática padrão.
3. Ferramentas e funções
4. Espaços de trabalho UNBL
5. Exportação de mapas
- Os mapas devem ser claros e concisos.
- Os textos importantes nos mapas devem ser claros e legíveis (por exemplo, cidades, nomes de lugares, itens de lendas, etc.).
- O mapa deve incluir elementos básicos de mapeamento: legenda (das camadas de dados relevantes) e barra de escala.
- O mapa deve ser exibido com a citação correta (ver abaixo).
Exemplo: Carbono Orgânico do Solo Florestal de Mangue [PDF] Sanderman et al. 2018. 1:25,000. Gerado por James Bond. Mapa Gerado pelo UN Biodiversity Lab. https://map.unbiodiversitylab.org/earth?basemap=grayscale&coordinates=20,0,2&layers=global-mangrove-soil-carbon-01 . (19 de junho de 2021).
6. Solução de problemas
Não consegue ver uma resposta à sua pergunta em nosso FAQ? Sinta-se à vontade para contatar nossa equipe de suporte em support@unbiodiversitylab.org. Você também pode acessar o guia do usuário interativo clicando na aba do guia do usuário acima. Para obter uma versão para download, clique aqui. Inglês | Francês | Espanhol | Português | Russo
Guia do usuário
Guia do usuário
Este guia do usuário foi desenvolvido para guiá-lo através das principais ferramentas e funções do UN Biodiversity Lab. Use as abas abaixo para encontrar guias visuais para nossa plataforma pública e espaços de trabalho seguros.
Se você tiver qualquer outra dúvida, por favor entre em contato conosco em support@unbiodiversitylab.org.
Antes de começar a explorar os dados, inscreva-se no UN Biodiversity Lab
- Clique na página ‘dados’ do site do UN Biodiversity Lab, depois selecione o botão de lançamento para acessar o aplicativo de dados.
- Uma vez carregado, selecione o ícone da conta no canto superior direito e escolha ‘Sign-up’. Digite seu e-mail, nome, país e instituição (opcional), e defina sua senha para se inscrever.
- Você receberá um e-mail dentro de alguns minutos. Siga as instruções neste e-mail para depois seguir o e-mail para verificar a sua conta.
- Uma vez verificada a sua conta, você pode fazer login usando o seu endereço de e-mail e senha cada vez que acessar a plataforma.
- Você pode sair a qualquer momento clicando no seu ícone de usuário e selecionando Sair.
Uma vez inscrito no UN Biodiversity Lab, você poderá gerenciar sua conta, incluindo a edição de seu nome de usuário, e-mail, senha, país e instituição. Você também será capaz de visualizar e editar as áreas de trabalho privadas às quais você pertence.
Para gerir a sua conta:
- Clique no ícone da conta com suas iniciais no canto superior direito e, em seguida, clique em perfil.
- Clique no ícone editar para editar o seu nome de usuário, e-mail, país e instituição.
- Para redefinir sua senha, clique em ENVIAR UM E-MAIL DE REDEFINIÇÃO, depois siga as instruções no e-mail.
- Para deixar qualquer uma das áreas de trabalho privadas a que pertence, clique em editar e depois em sair da áreas de trabalho. Salve as suas alterações.
- Se esta conta não estiver mais em uso, você pode clicar em DELETAR SUA CONTA e na parte inferior desta página. Após excluir a conta, você precisará se inscrever novamente para obter privilégios de usuário registrado no UN Biodiversity Lab.
- Após salvar suas alterações, clique em VOLTAR PARA A VISUALIZAÇÃO DO MAPA.

A navegação entre as duas páginas é simples:
- Para retornar ao site do UN Biodiversity Lab a partir do aplicativo de dados, clique na opção de visualização do mapa e escolha a opção home no canto superior direito do painel.
- Para navegar para o aplicativo de dados do site do UN Biodiversity Lab, clique em Data.
O UN Biodiversity Lab está atualmente disponível em inglês, francês, espanhol, português e russo. O idioma padrão é o inglês.
Para mudar o idioma, clique no ícone de conta no canto direito do mapa e clique novamente para selecionar o idioma de sua preferência no menu suspenso.
Você pode mudar seu idioma no site do UN Biodiversity Lab ou no aplicativo de dados.
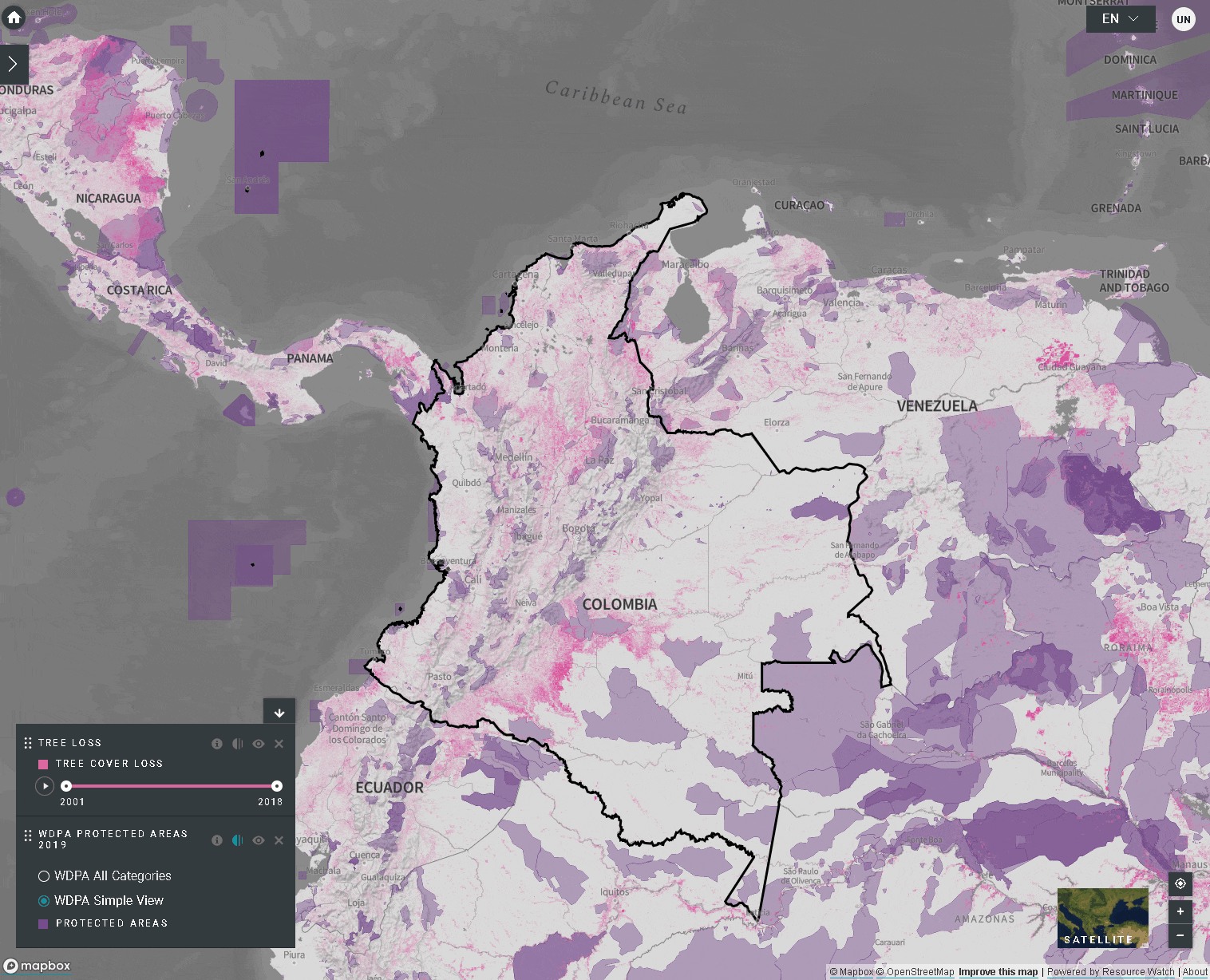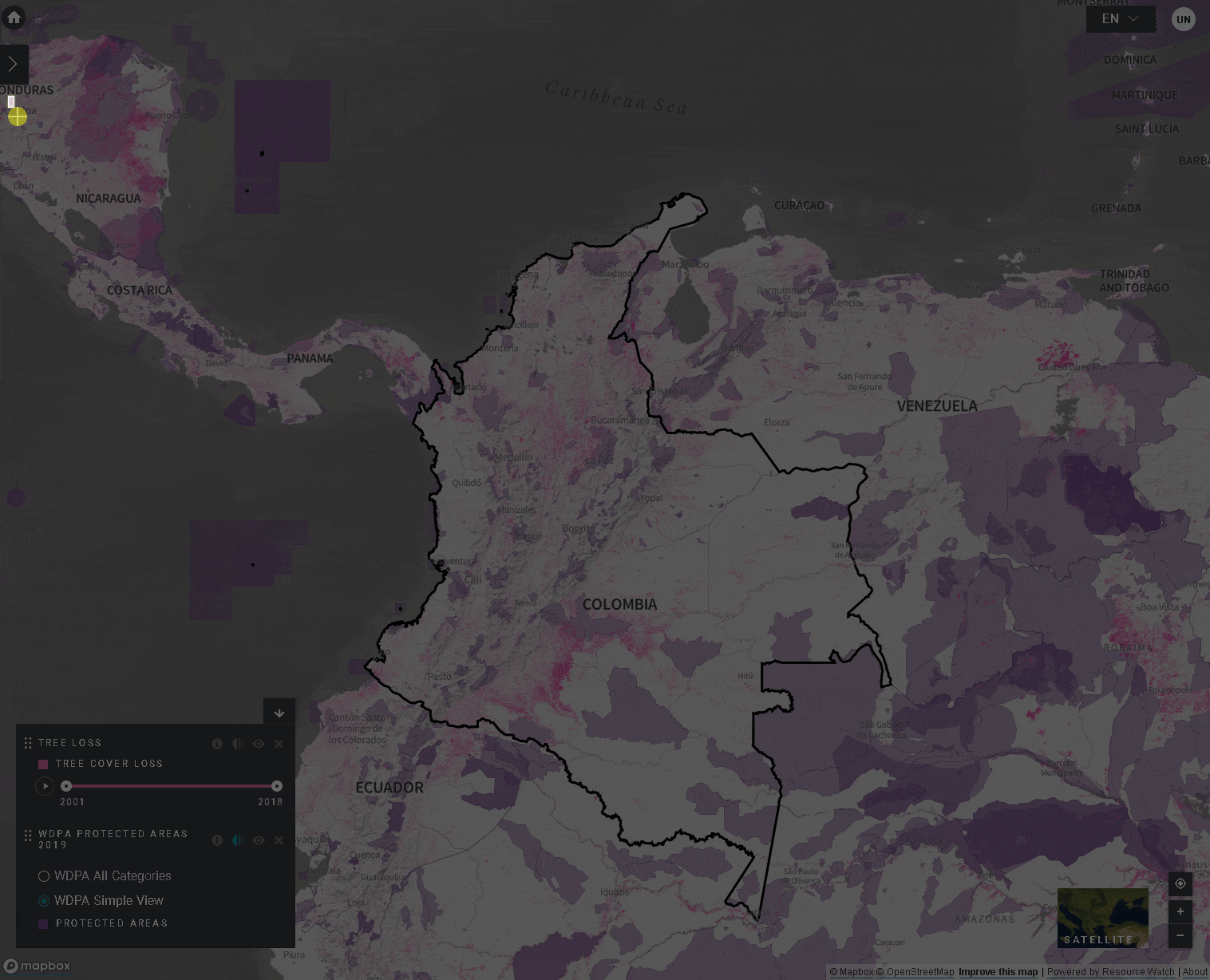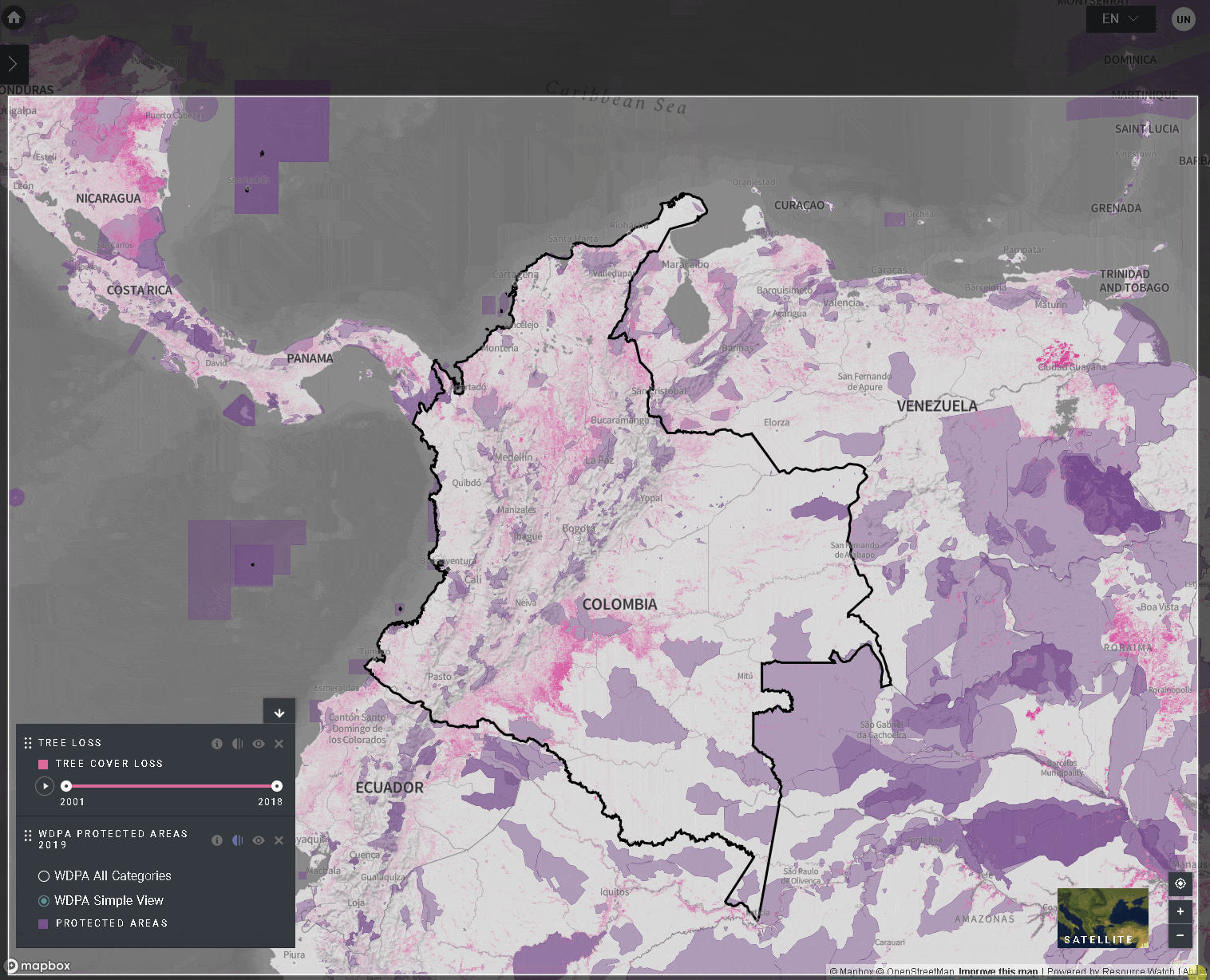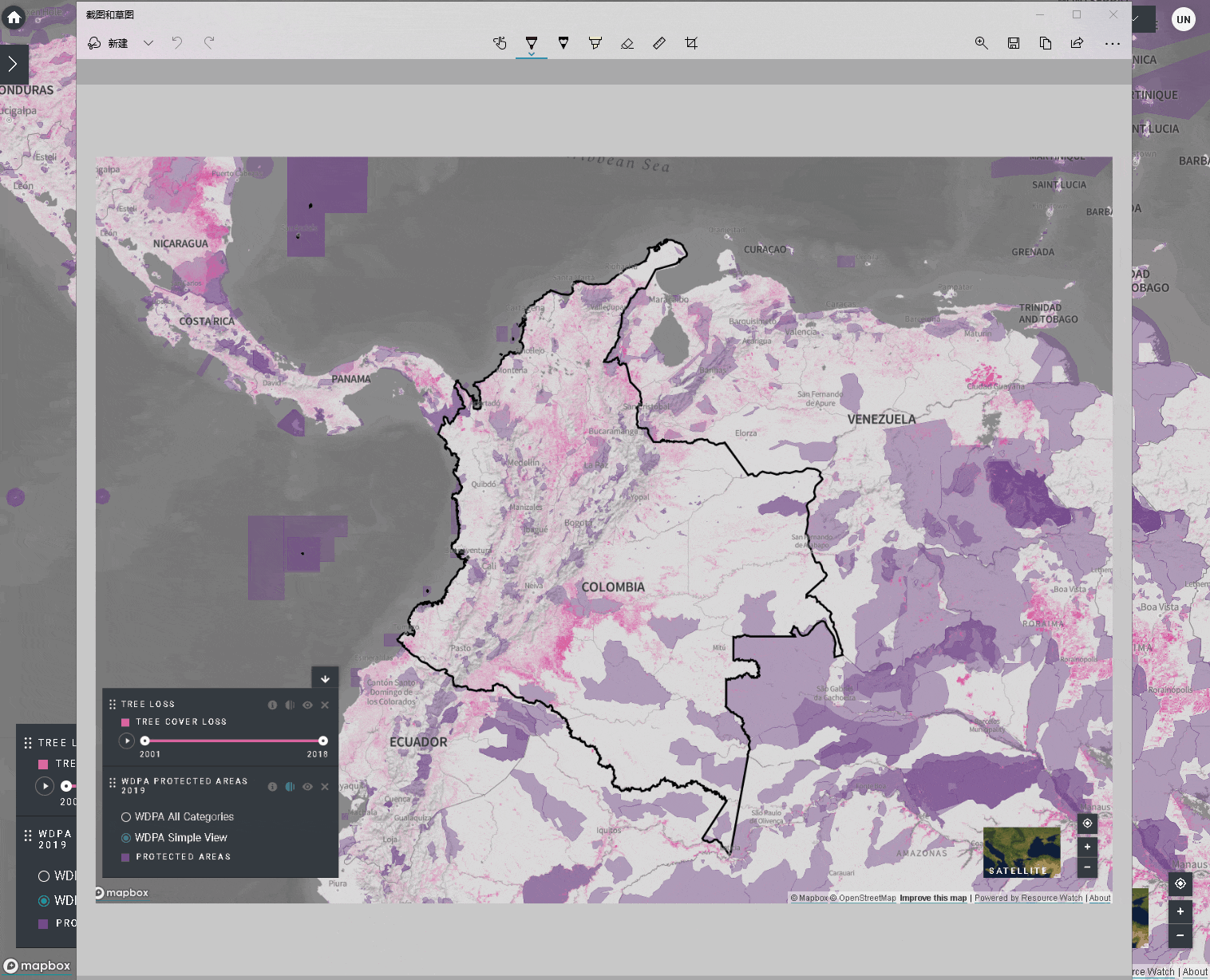
Existem várias características que podem te ajudar a navegar na tela do mapa. Estas incluem:
- Mover mapa: Use o mouse para arrastar a parte do mapa que você gostaria de ver para o meio da tela.
- Ampliar/reduzir o zoom: Clique nos ícones +/- no canto inferior direito do mapa.
- Centralizar: Clique no botão de centralizar acima +/-. Isto irá centralizar o mapa no local selecionado.
- Esconder a barra do menu lateral: Clique na seta no topo do menu da esquerda para colapsar o painel de camadas para uma vista maior do mapa. Clique novamente para expandir o painel.

Há várias opções para você personalizar o mapa base. Estas incluem:
- Etiquetas: As etiquetas mostram o nome dos lugares, incluindo países, estados, cidades e marcos representativos. Clique no botão para ativar as etiquetas e clique novamente para esconder.
- Estradas: Clique no botão para mostrar as estradas; clique novamente para esconder as estradas.
- Fundo do mapa: Oferecemos opções de escala de cinza e satélite para o plano de fundo do mapa. Para alternar entre estas opções, clique na pequena janela na parte inferior direita da tela..
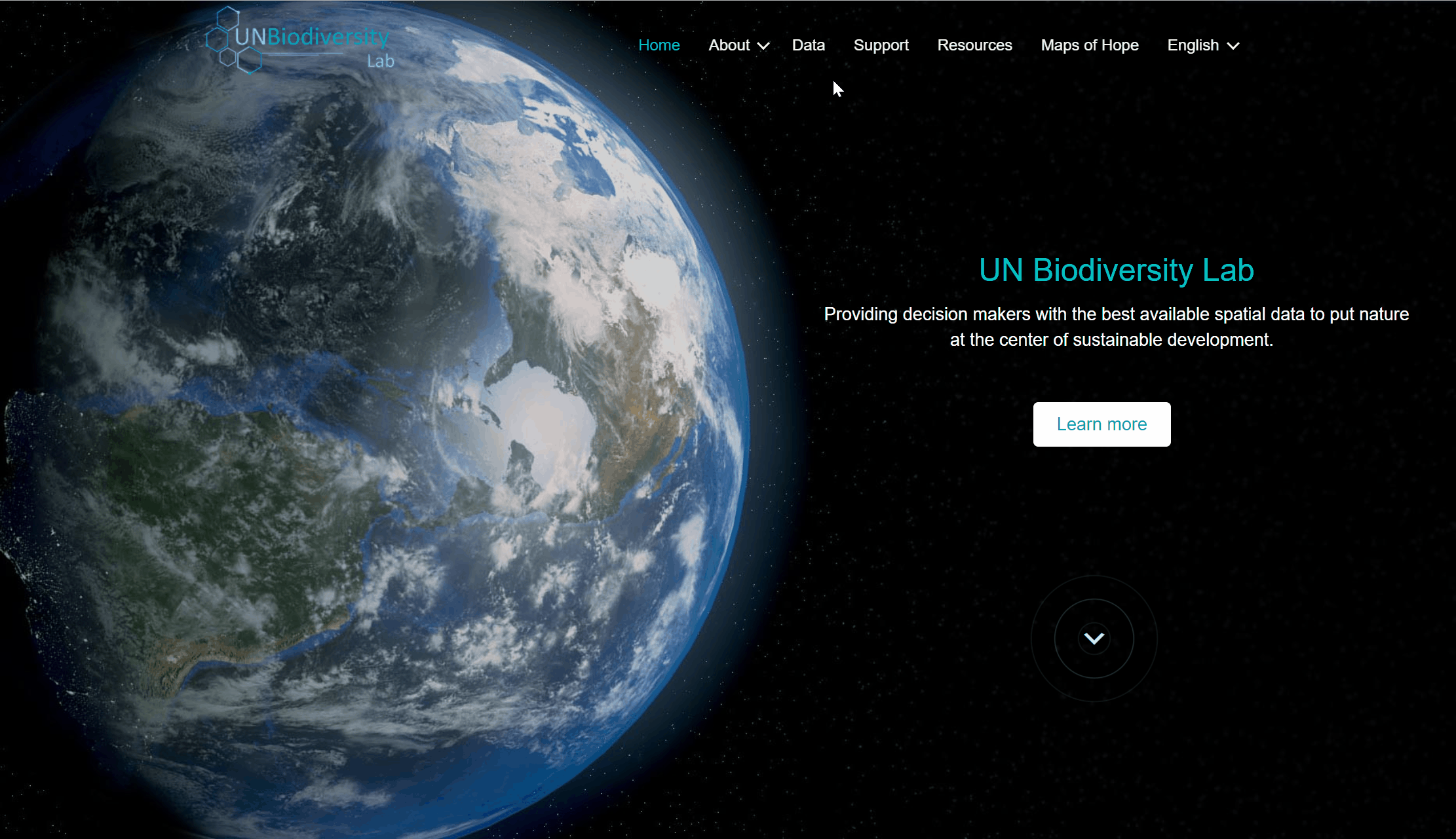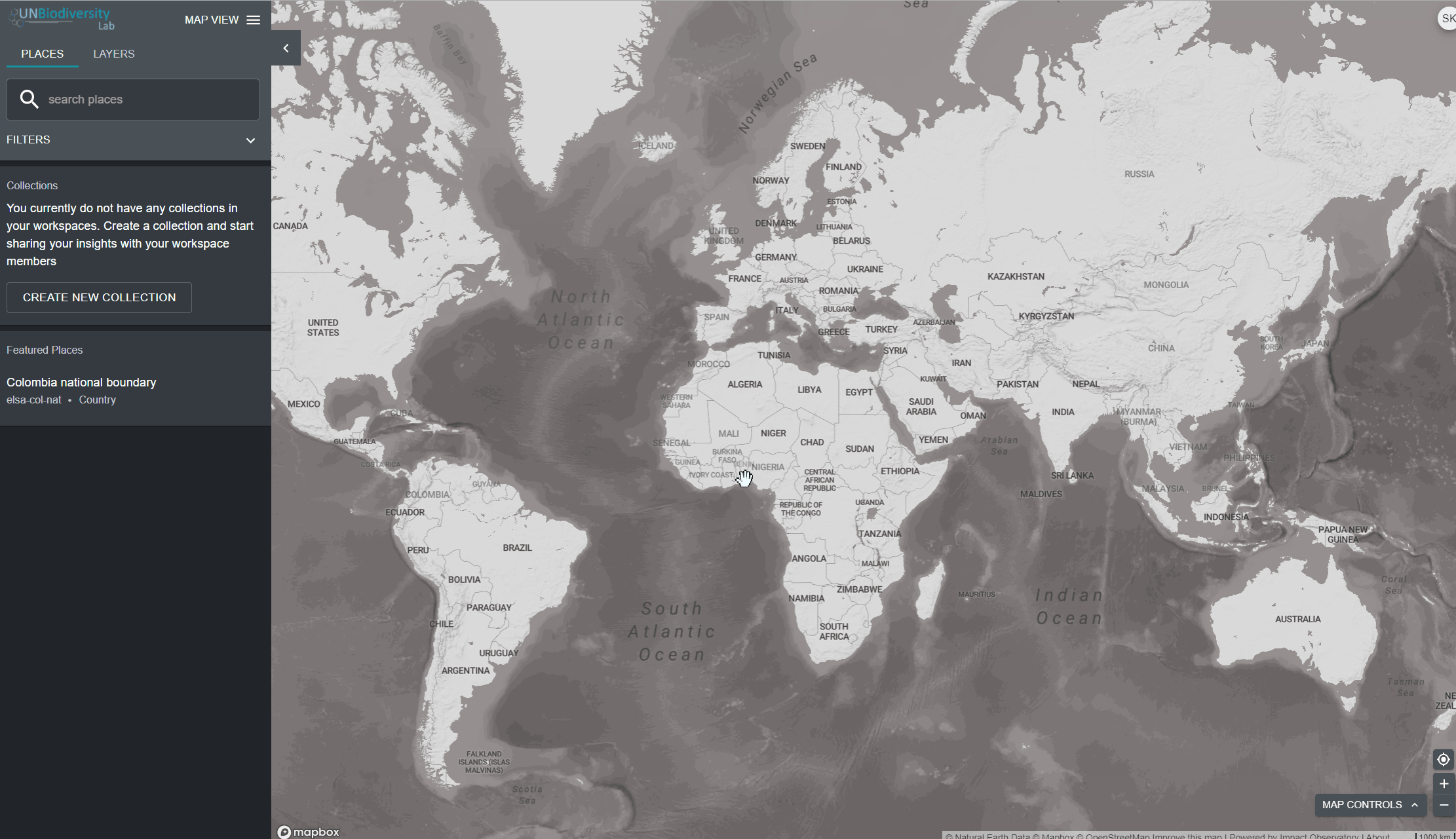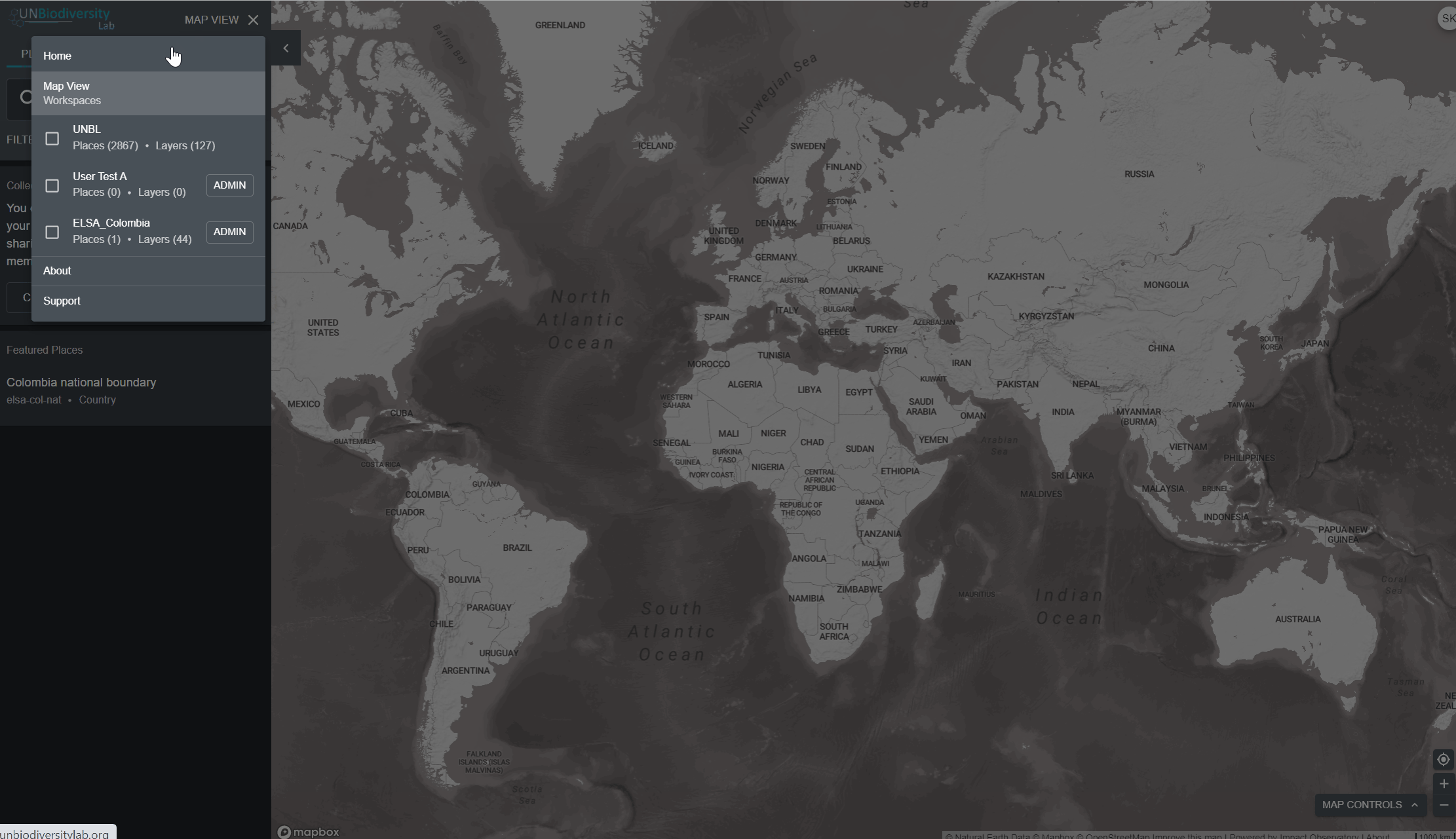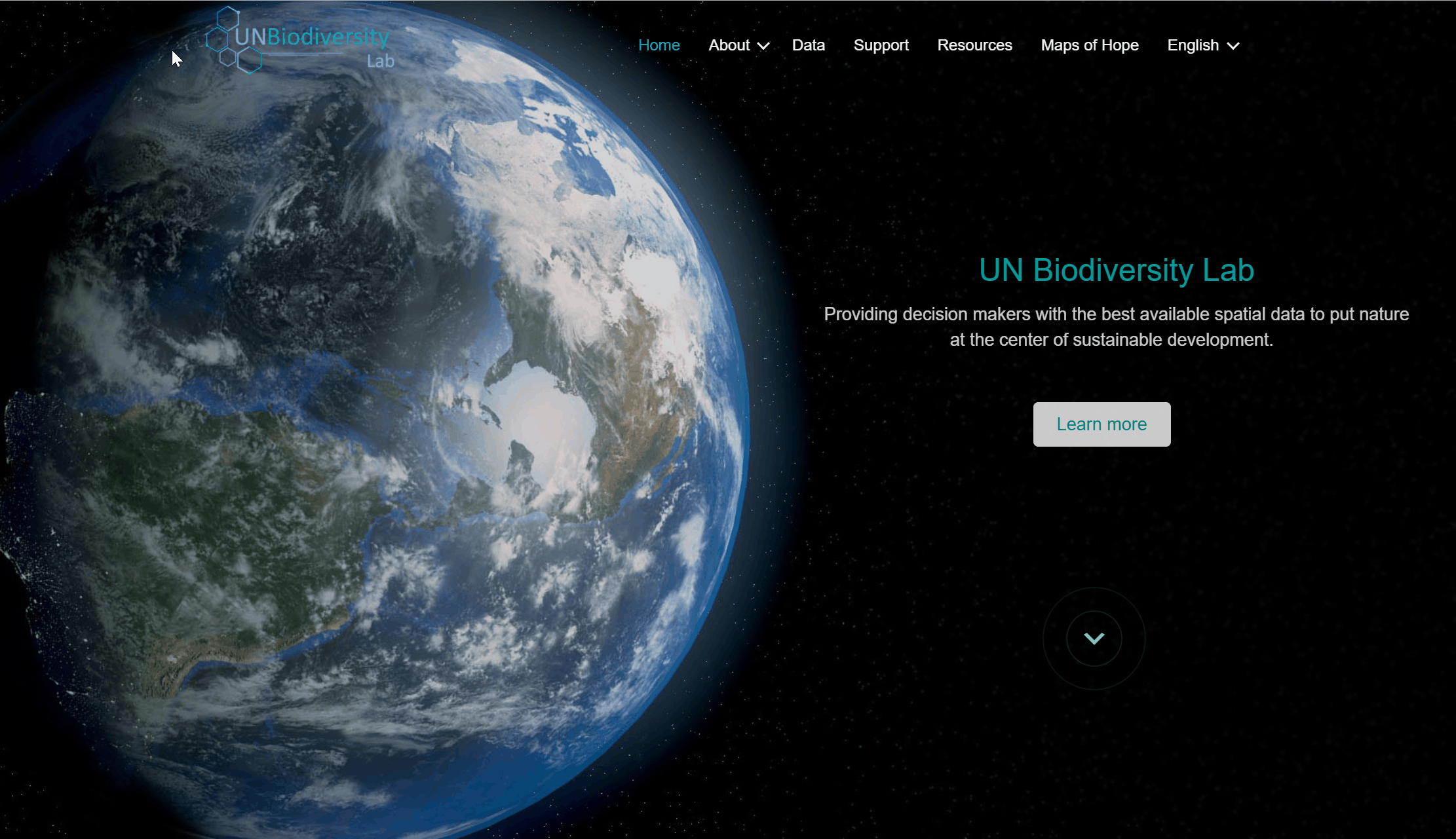
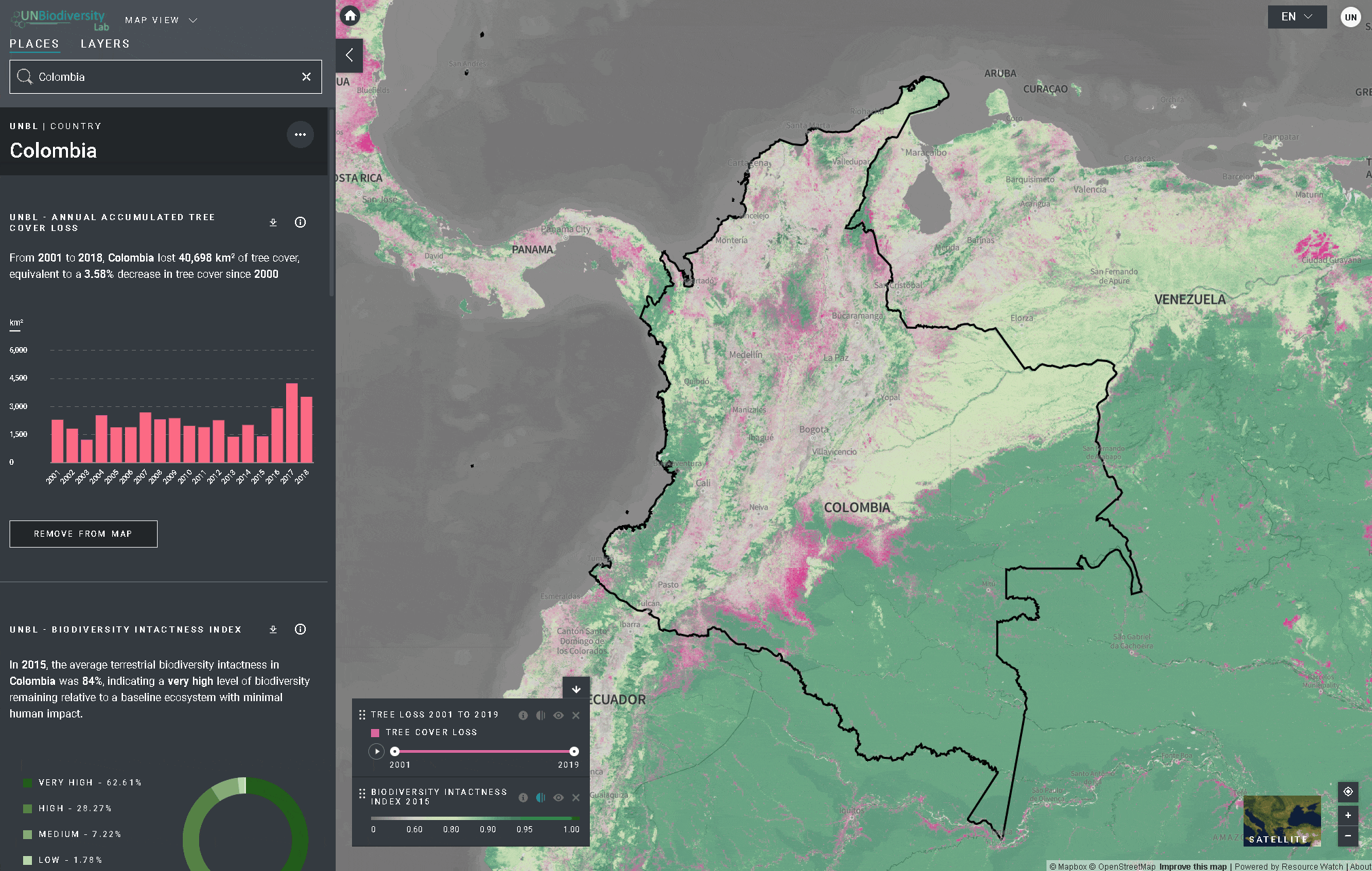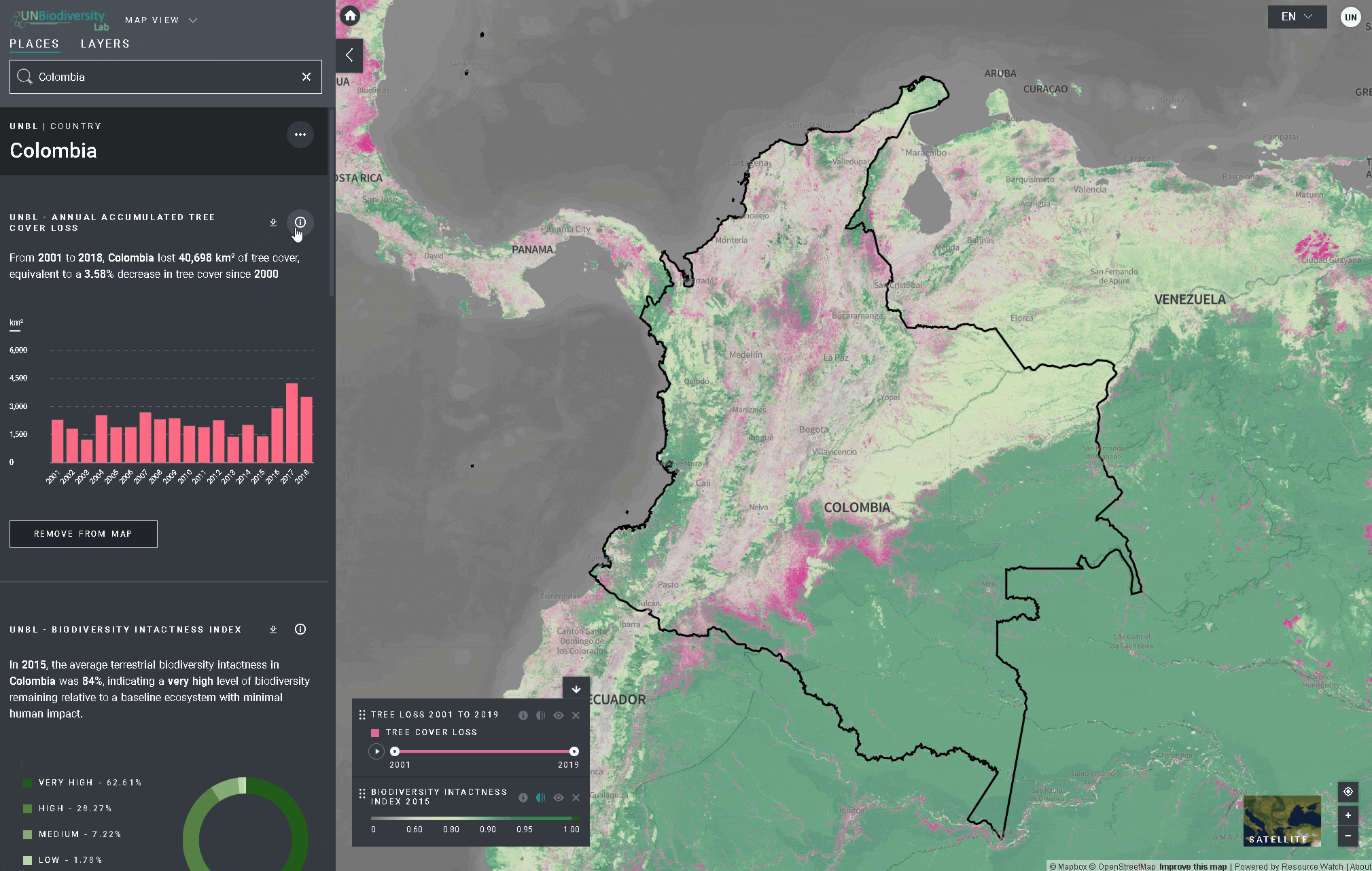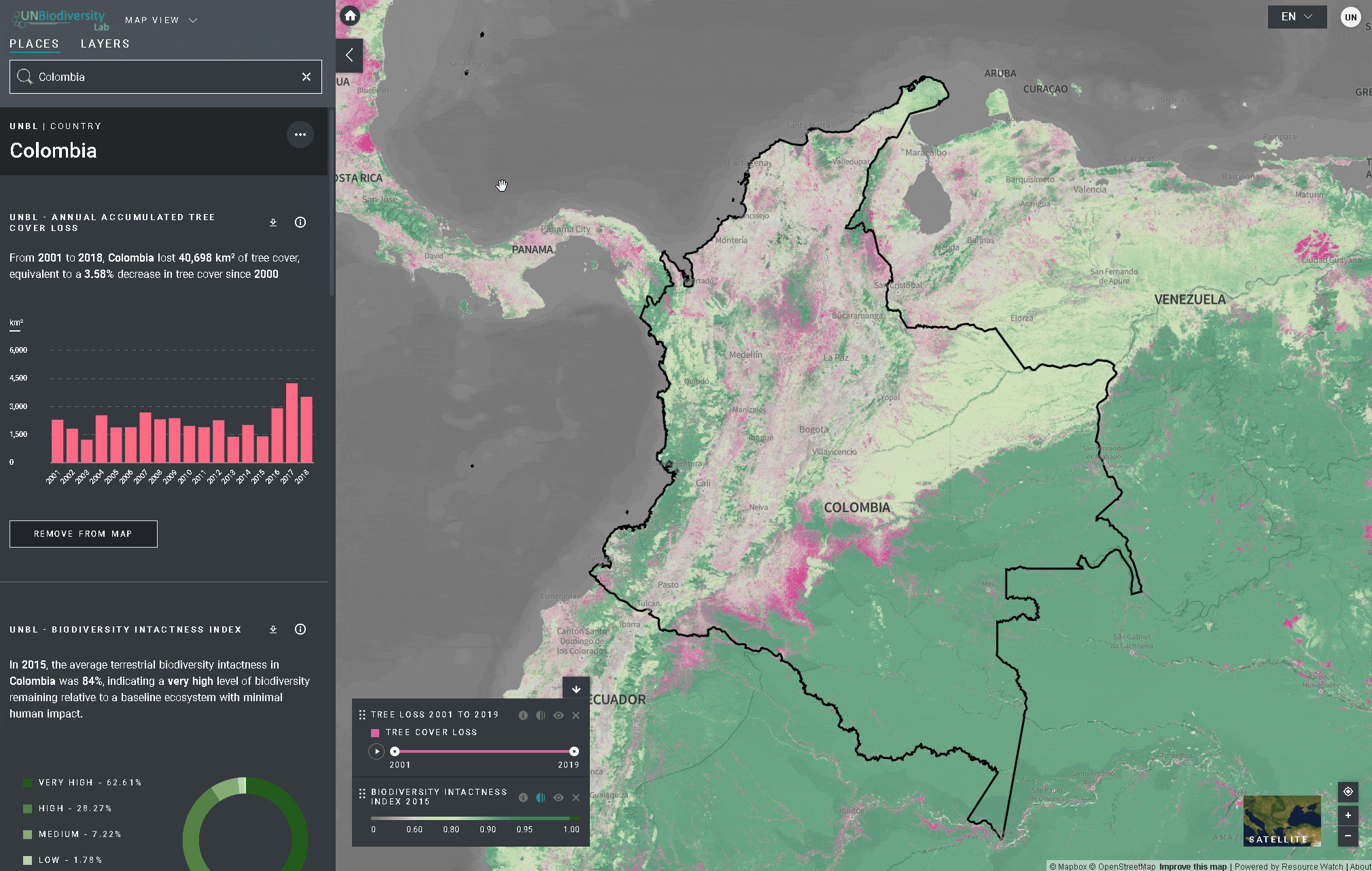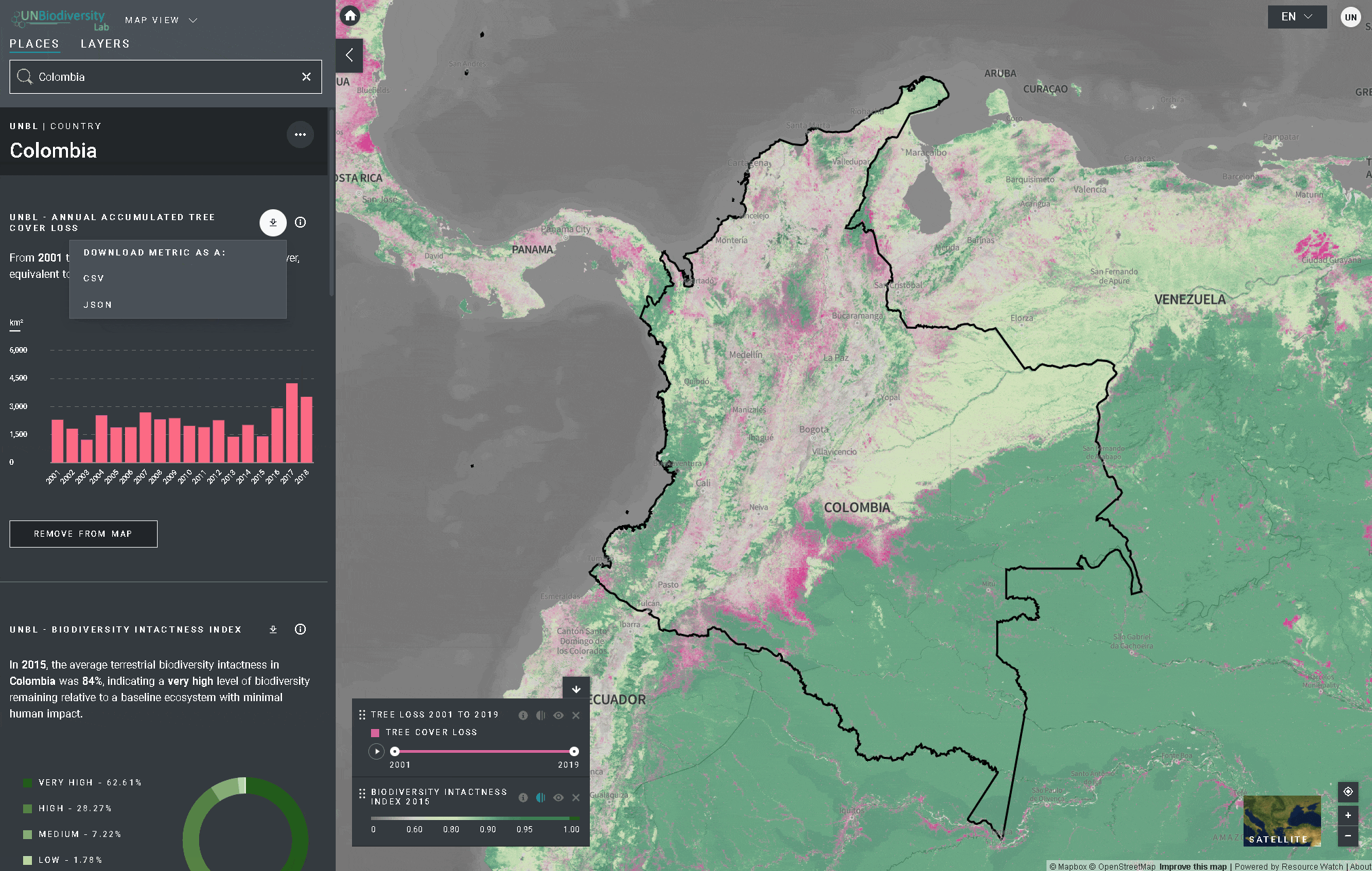
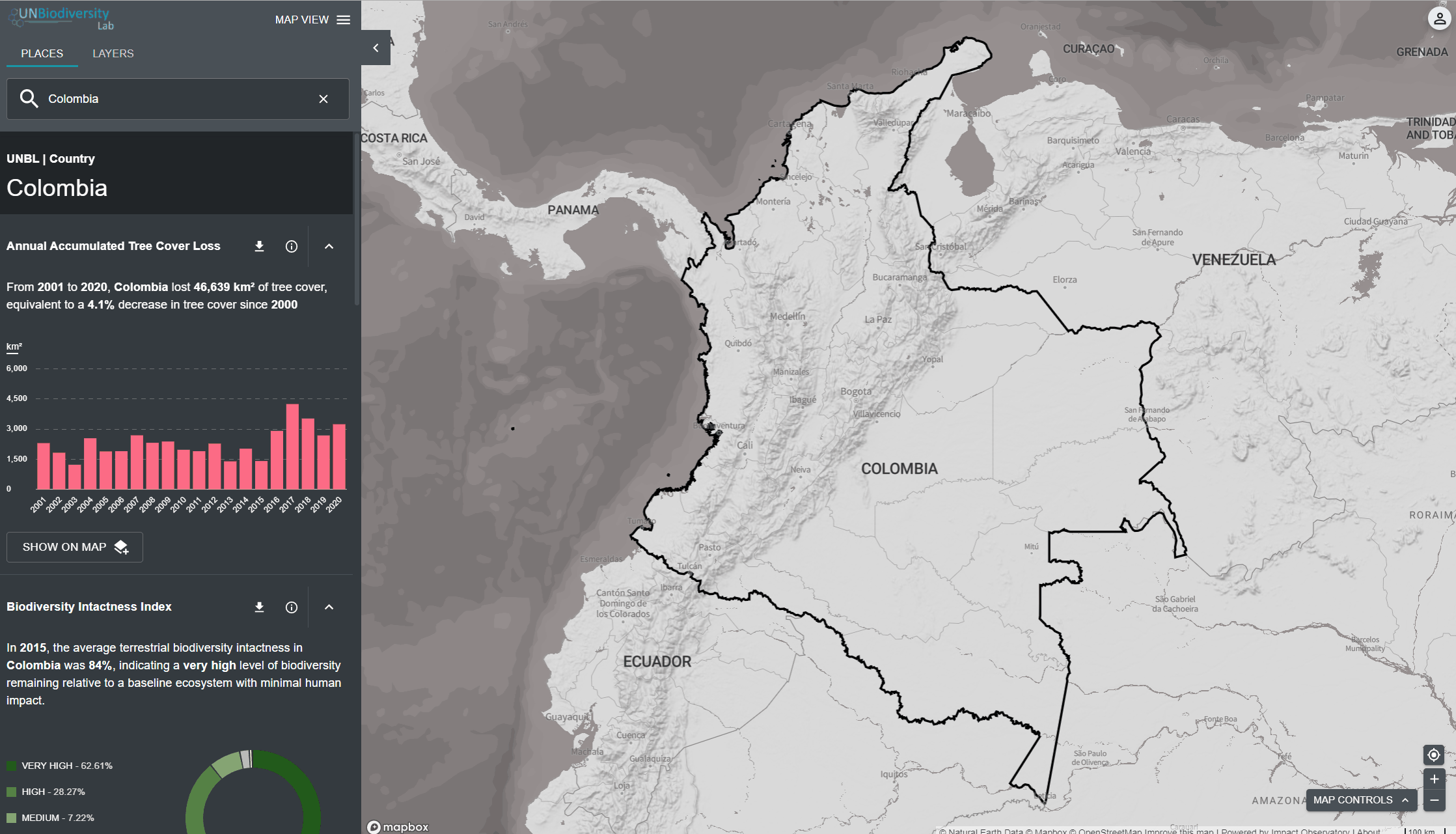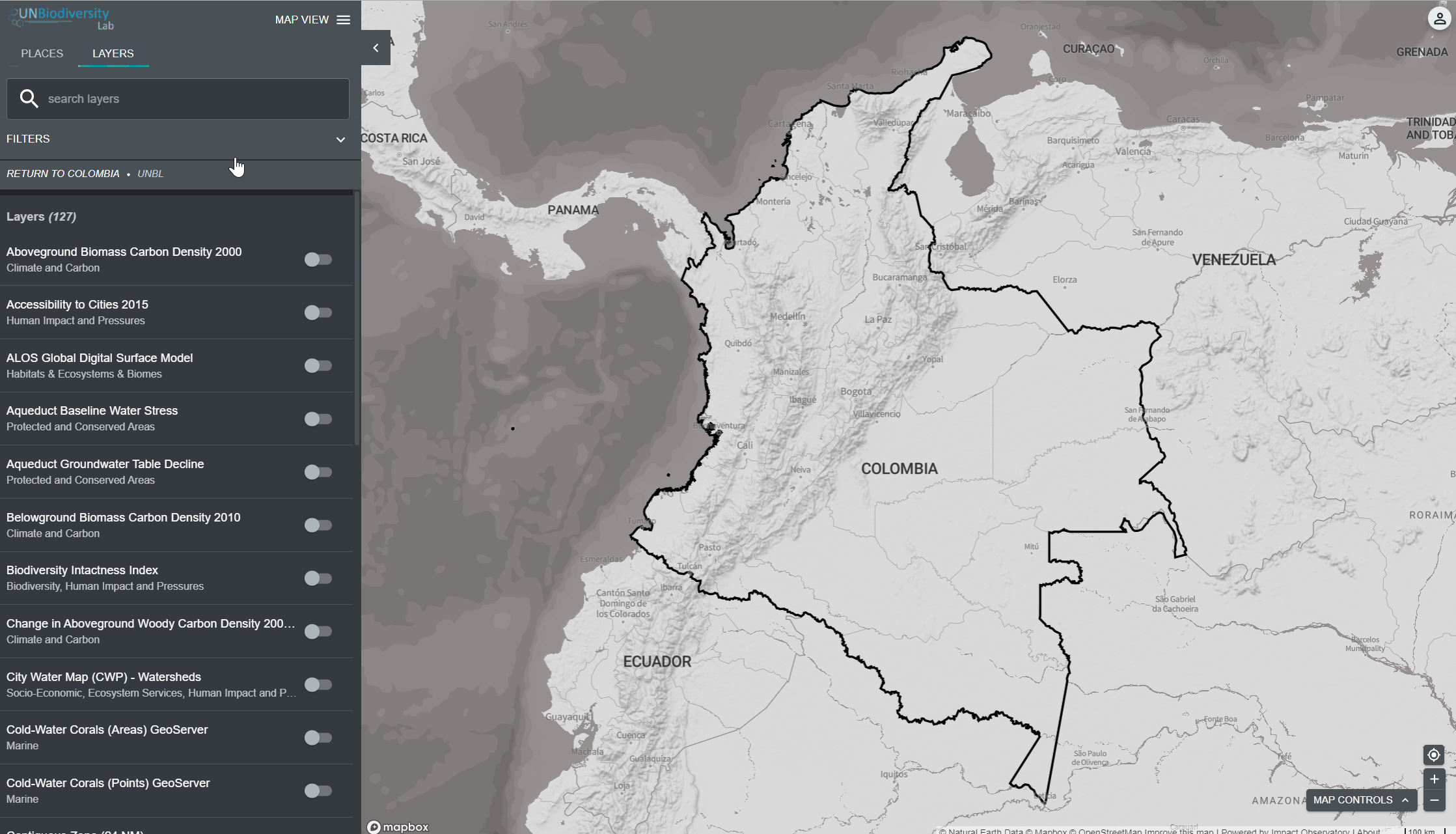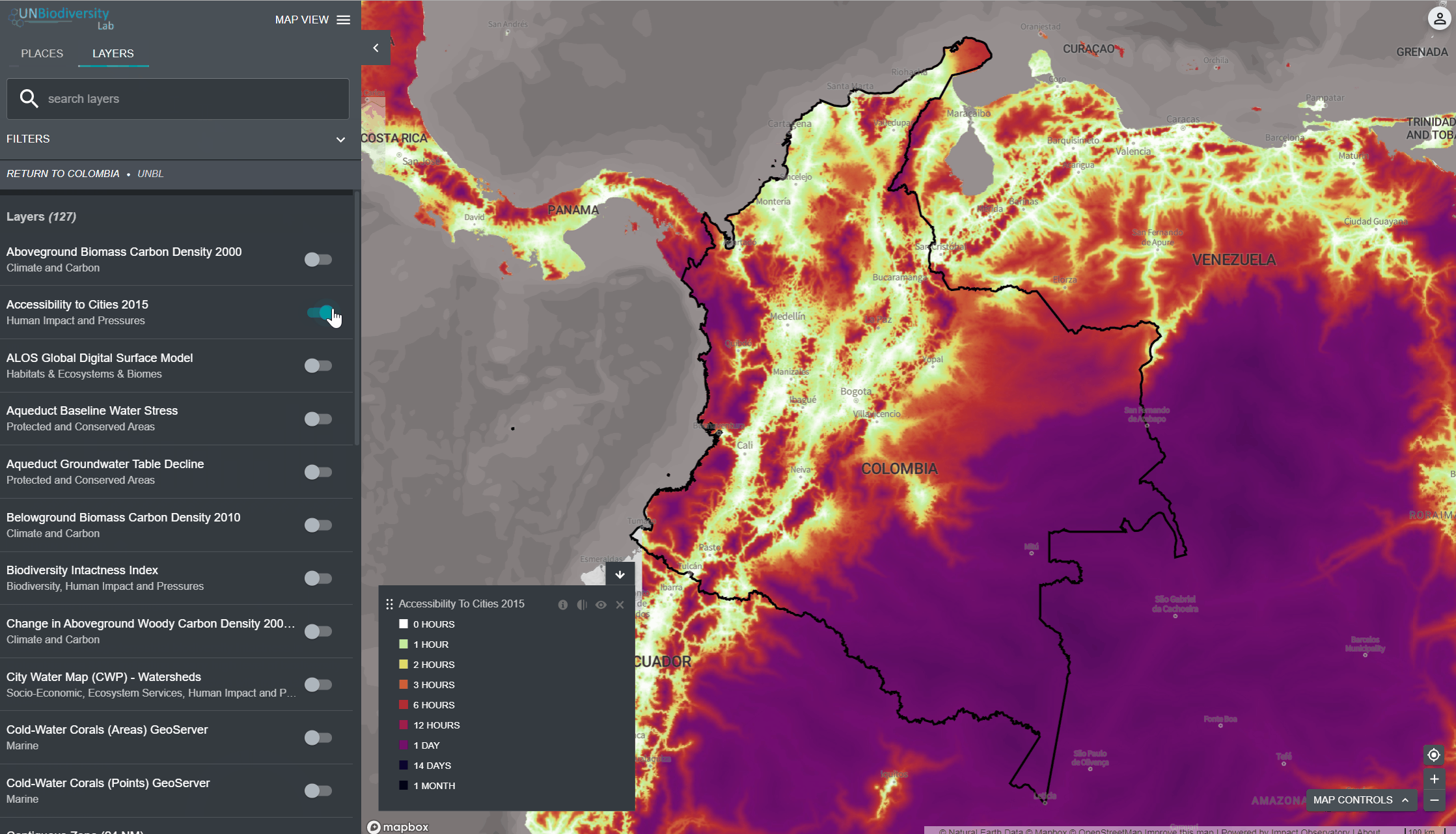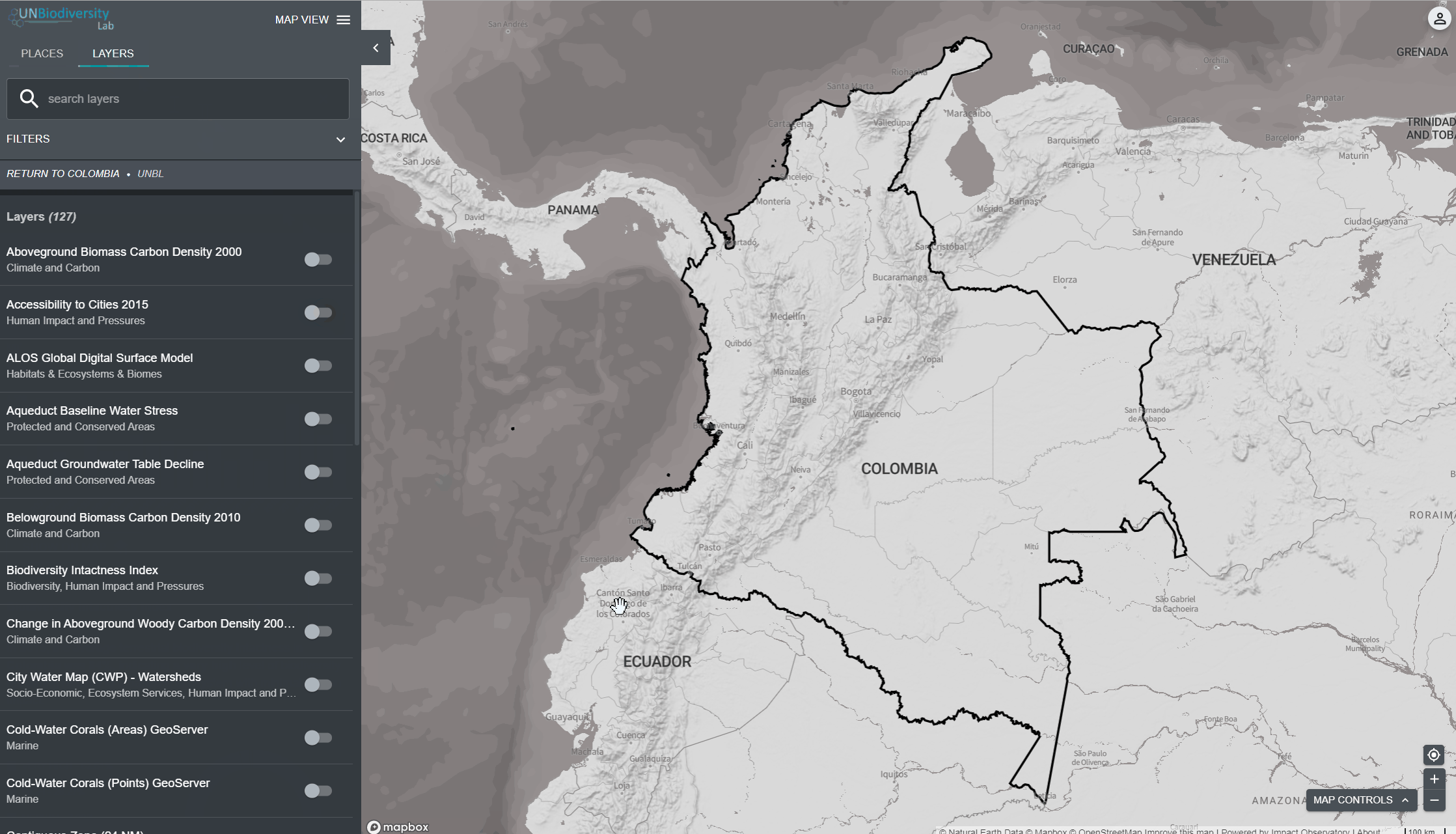
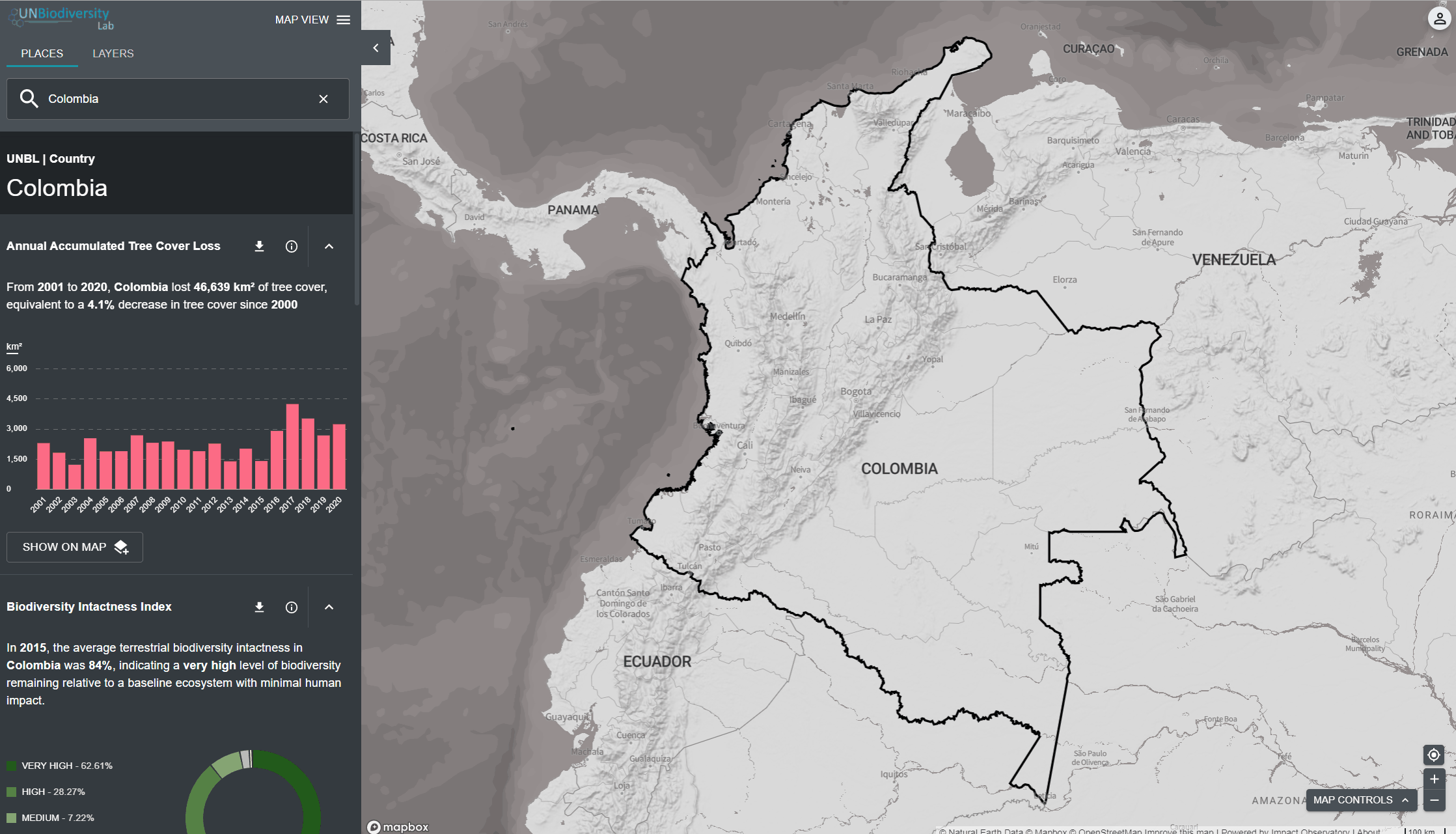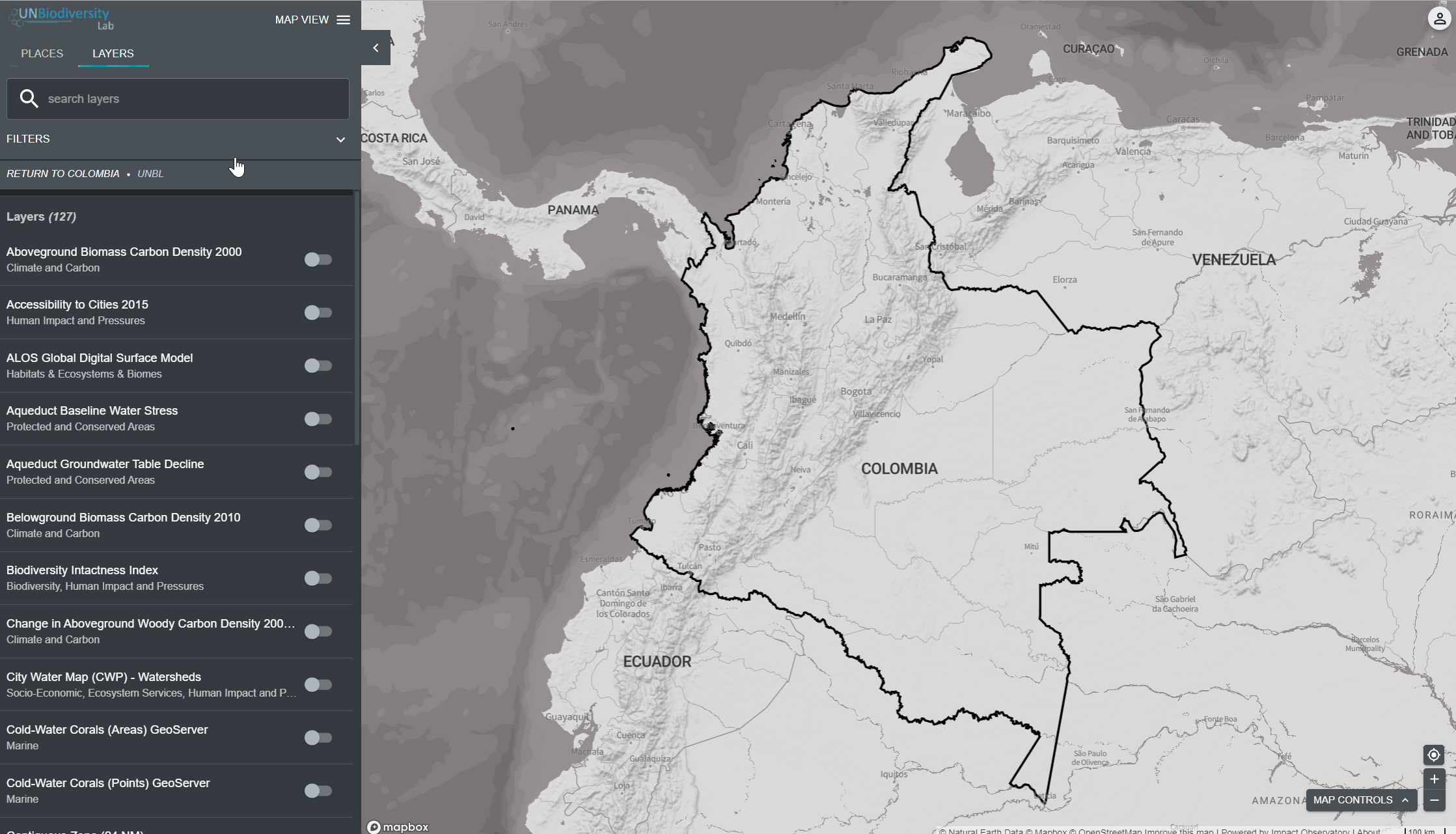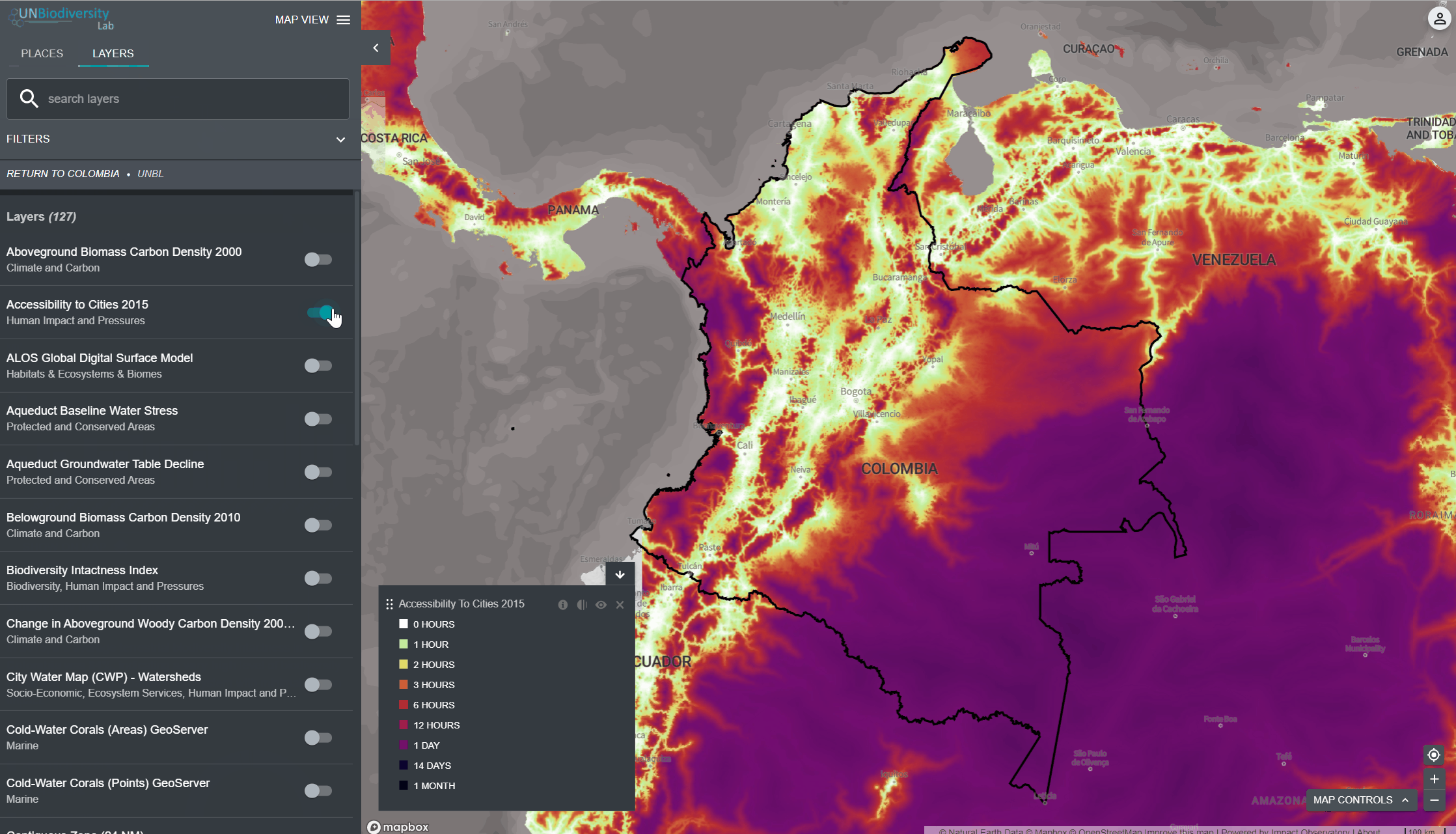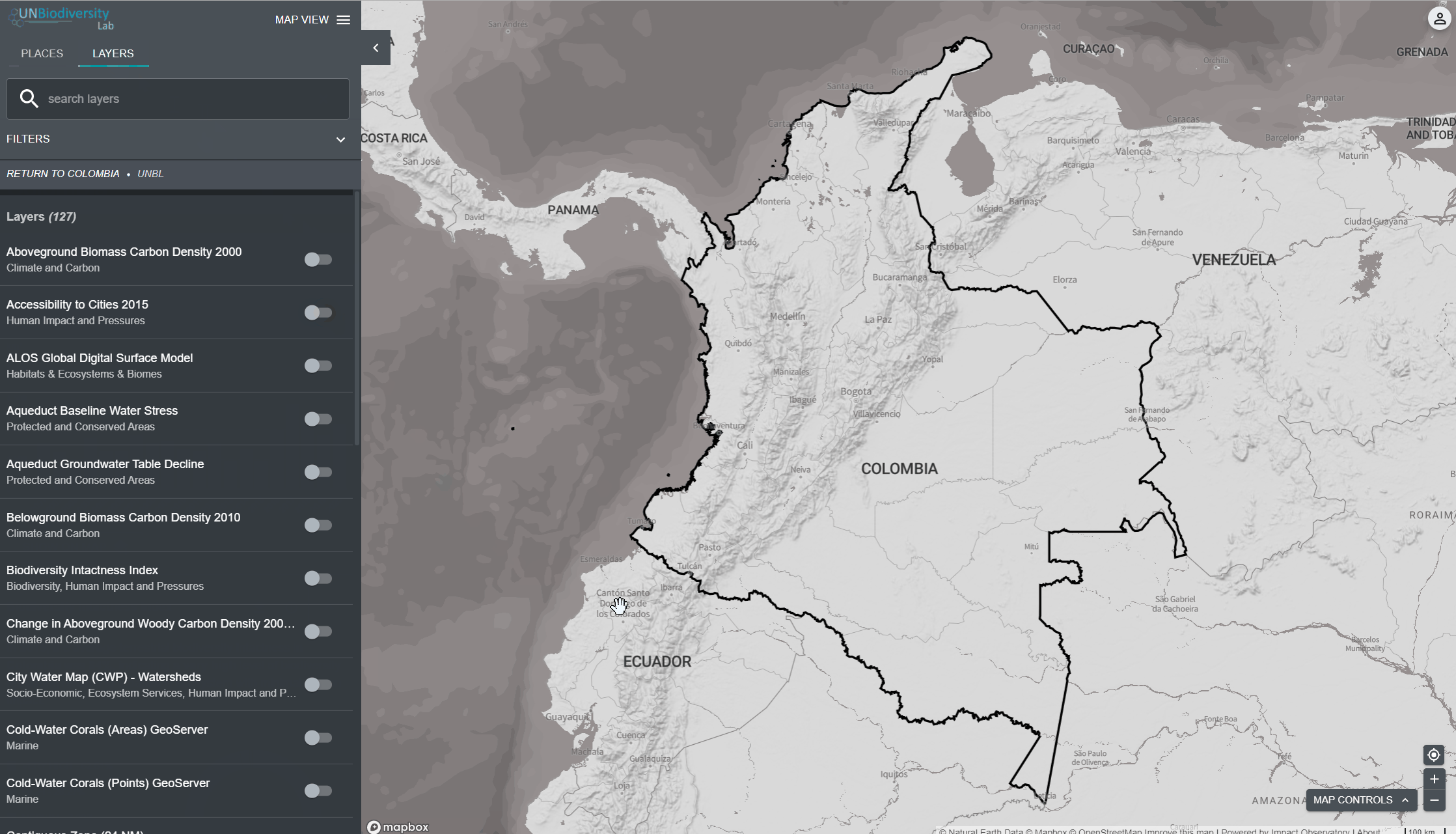
O UN Biodiversity Lab pode ajudá-lo a navegar para uma área específica de interesse e acessar conjuntos de dados e métricas dinâmicas para esta área. Em nossa plataforma pública, as áreas de interesse incluem países, jurisdições e áreas transfronteiriças selecionadas. Para pesquisar uma área de interesse, você pode:
- Clicar no ícone LOCAIS, digite o nome do país ou jurisdição que deseja visualizar na caixa de pesquisa e selecione o resultado desejado na lista de resultados da pesquisa.
OU
- Clique no ícone LOCAIS, clique para expandir a caixa de filtros e selecione o filtro de seu interesse.

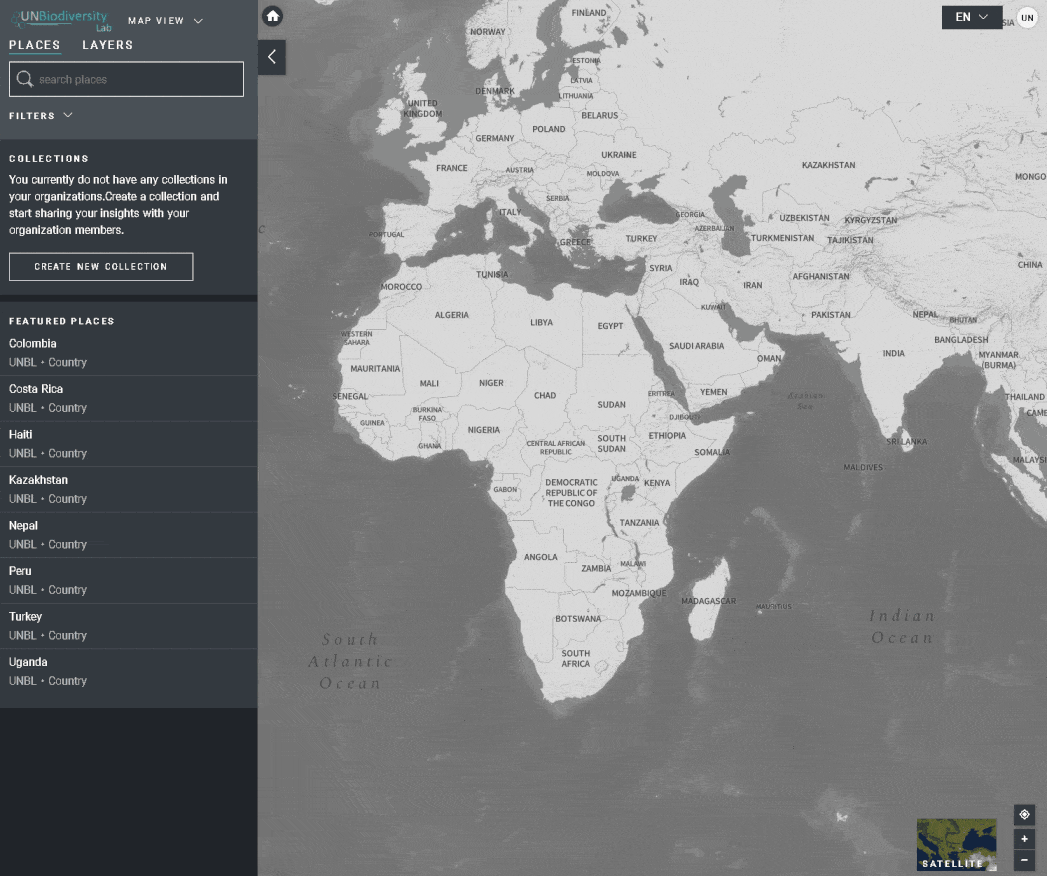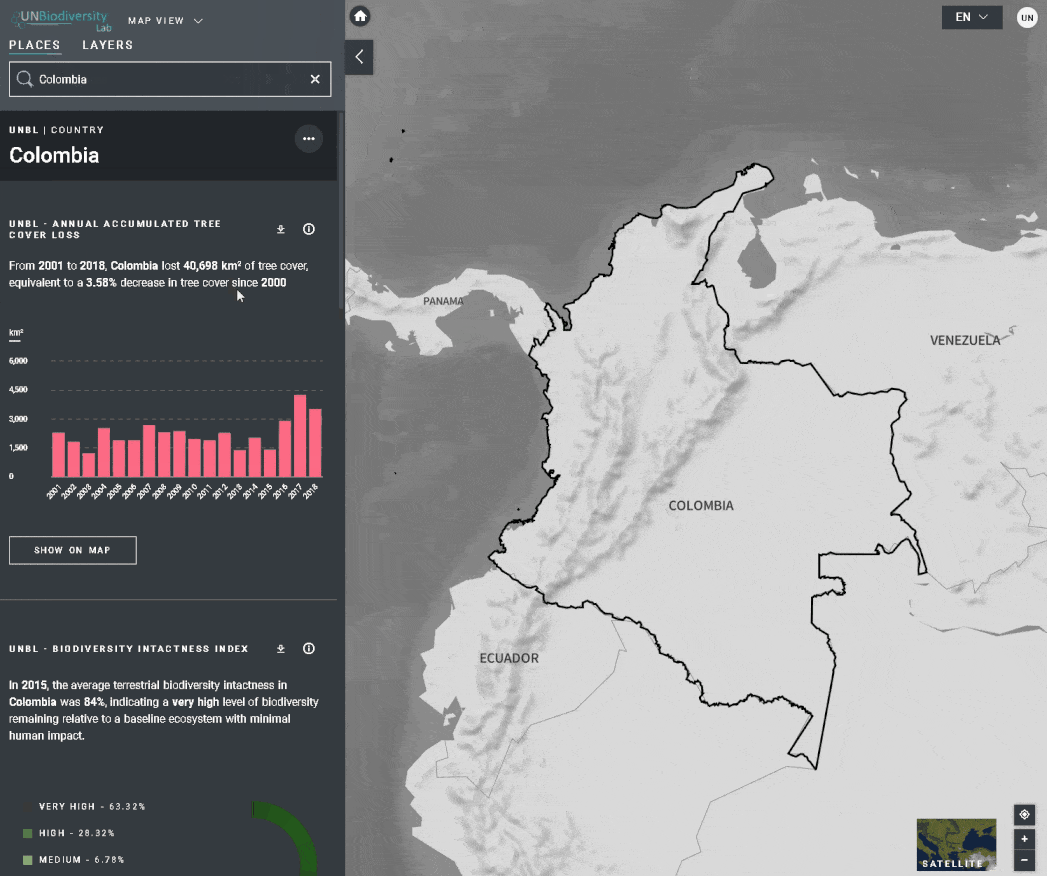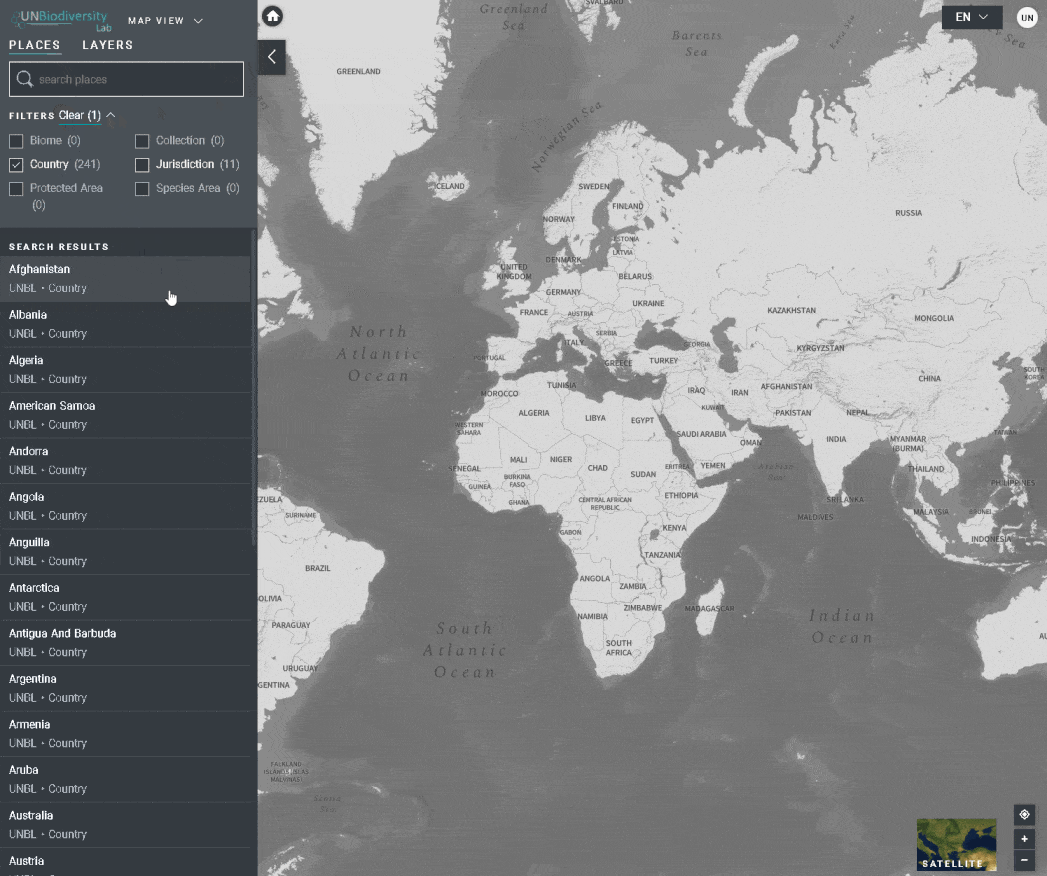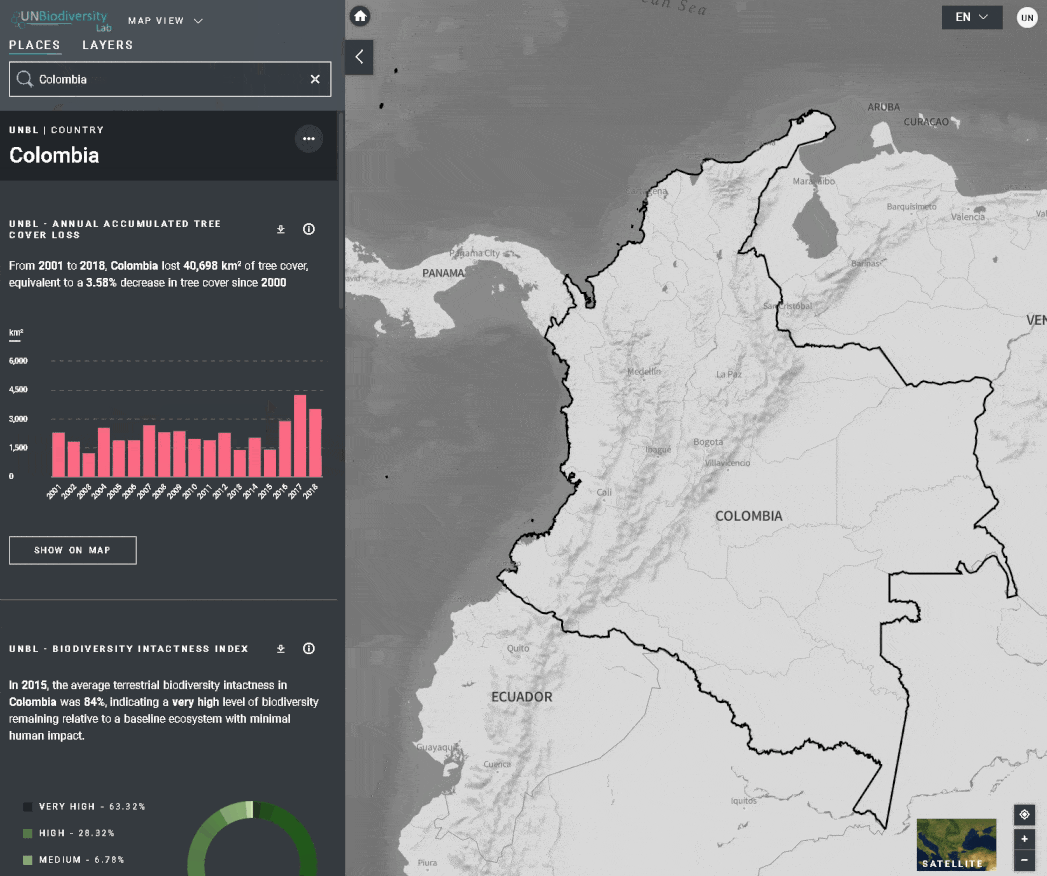
O UN Biodiversity Lab oferece métricas baseadas nos melhores conjuntos de dados espaciais globais disponíveis. Estas métricas podem ser usadas para reportar o estado da natureza e do desenvolvimento humano em seu país. As métricas disponíveis incluem:
- Perda de cobertura arbórea (2001-2018)
- Índice de Integridade da Biodiversidade (2015)
- Índice de vegetação melhorado (2000-2019)
- Cobertura Terra Global (2015)
- Atividade de fogo mensal (2018)
- Áreas Protegidas (2019)
- Densidade de carbono terrestre (2010)
- Pegada humana terrestre (1993 & 2009)
Para visualizar métricas dinâmicas no UN Biodiversity Lab:
- Selecione uma área de interesse.
- Revise as métricas no painel à esquerda.
- Clique no ícone MOSTRAR NO MAPA se você quiser ver esta camada no mapa. Clique no ícone REMOVER DO MAPA ou no ícone remover camada na legenda para limpar a tela.
- Clique no
 ícone para ver as informações da camada, as páginas de informação fornecem uma breve descrição dos dados, publicações relacionadas para leitura e links de origem.
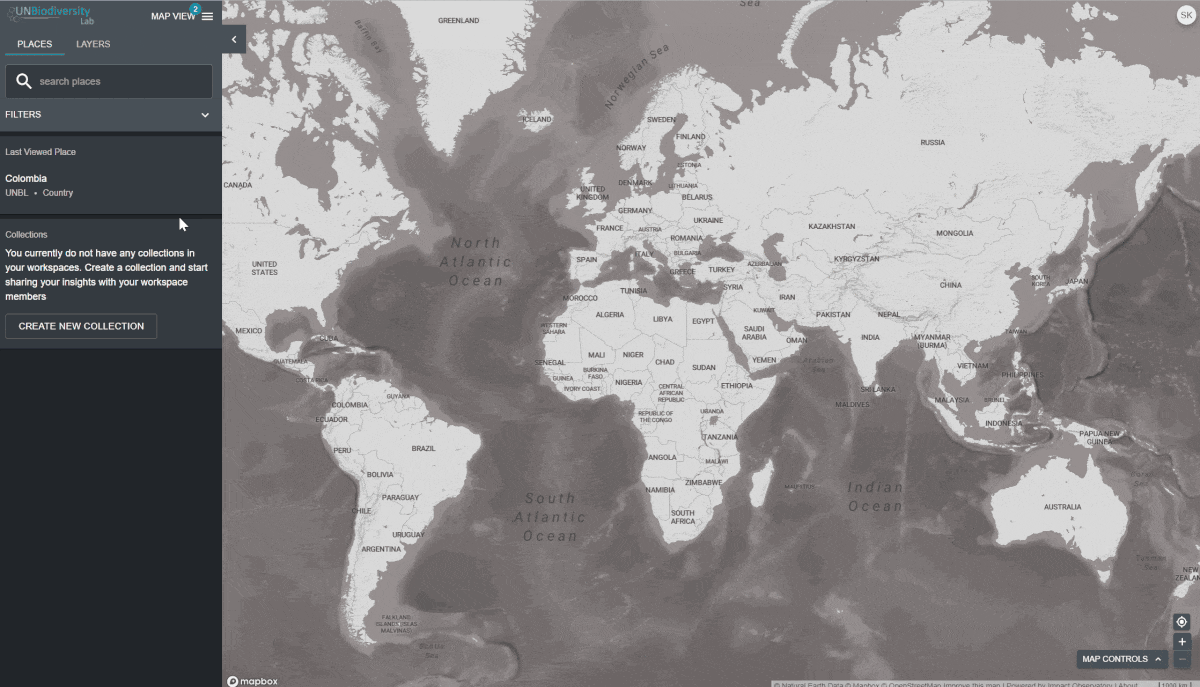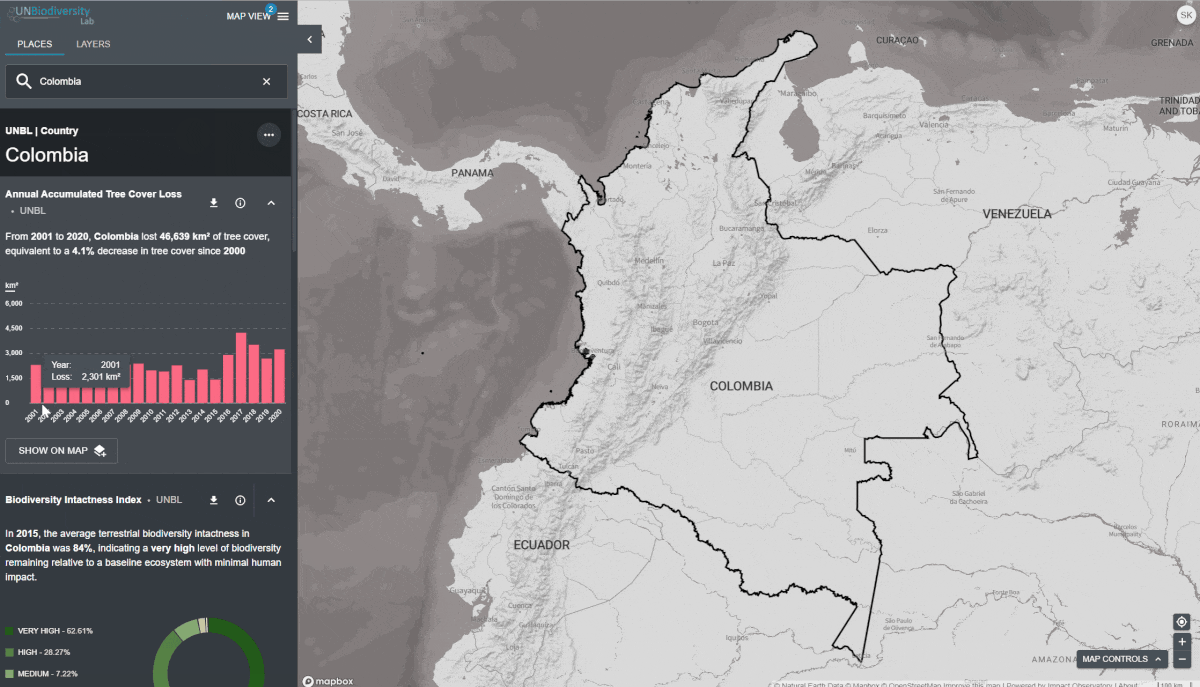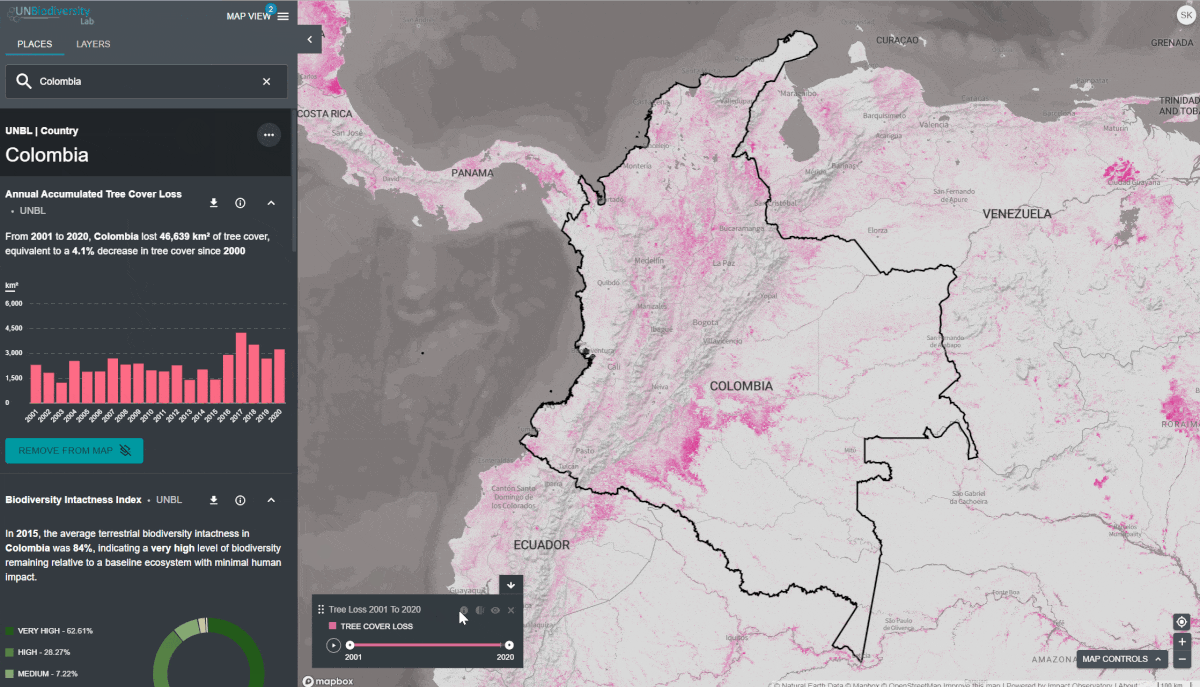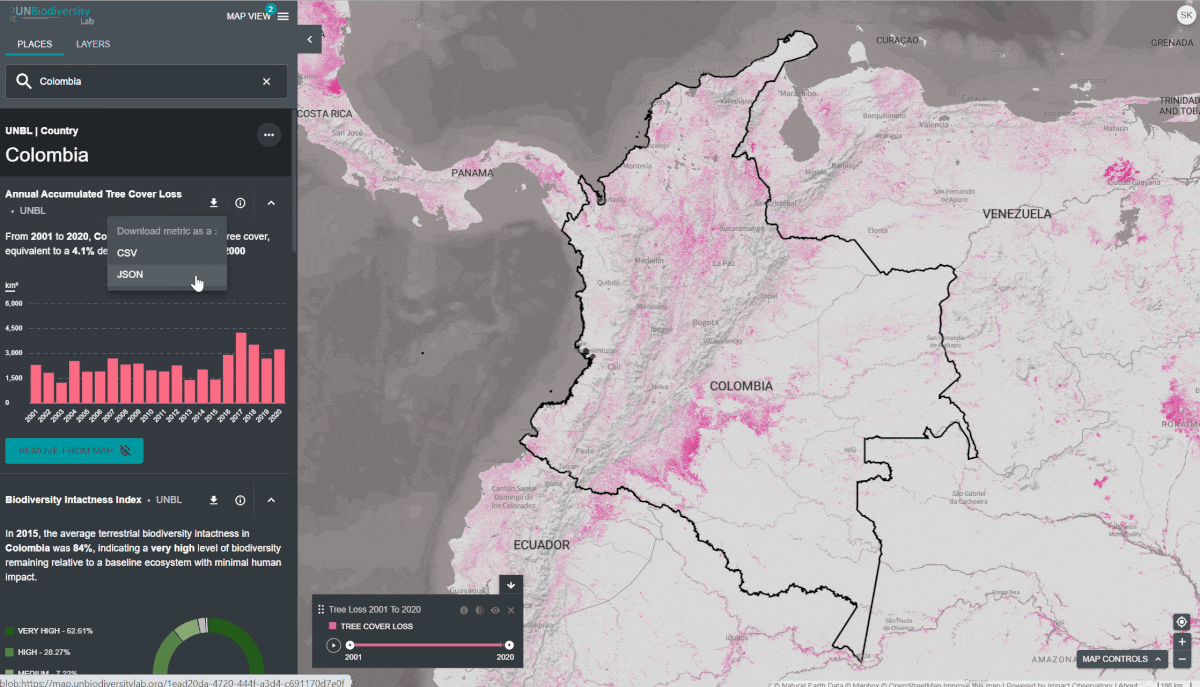
ícone para ver as informações da camada, as páginas de informação fornecem uma breve descrição dos dados, publicações relacionadas para leitura e links de origem. - Para baixar dados resumidos da métrica em formato .csv ou .json, clique no ícone da seta
 . Você também pode baixar os dados dos links de origem na página de informação da camada.
. Você também pode baixar os dados dos links de origem na página de informação da camada.
- Selecione a camada e carregue-a para o mapa.
- No canto esquerdo do mapa, haverá uma legenda mostrando o nome e a simbologia das camadas de informação no mapa.
- Clique no ícone i para ver as informações das camadas. As informações fornecem uma descrição da camada, organização de origem, citações e links para baixar os dados.

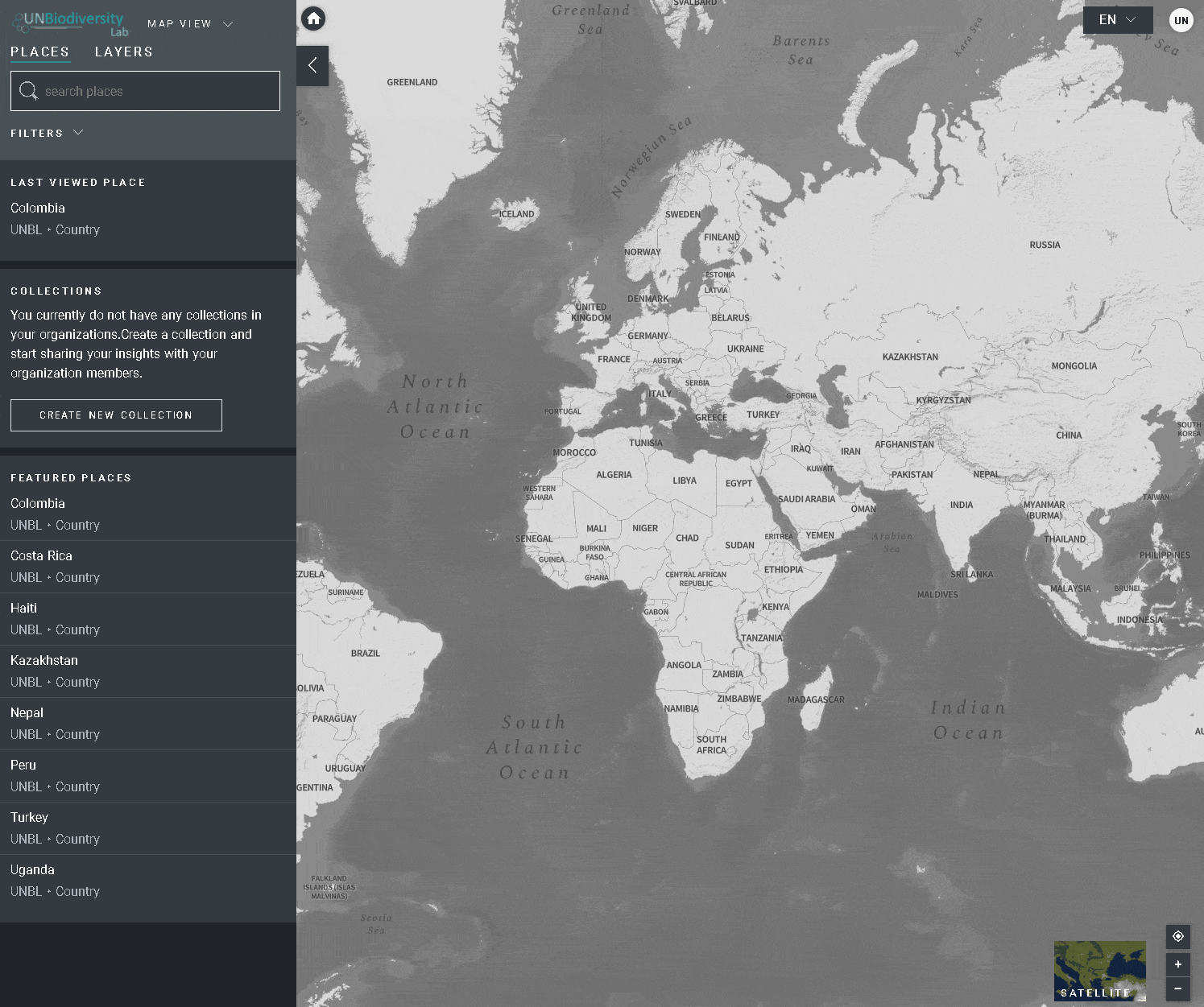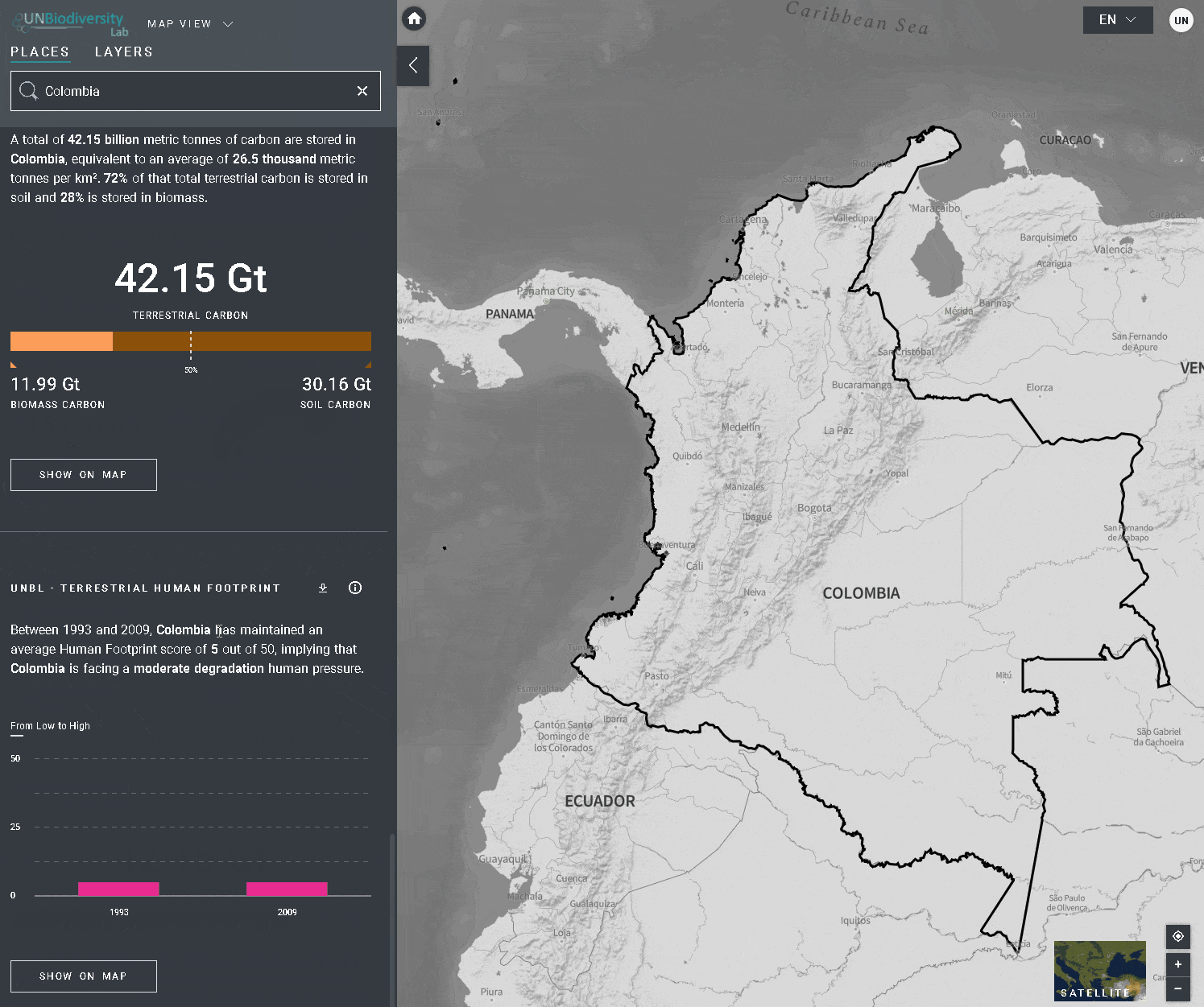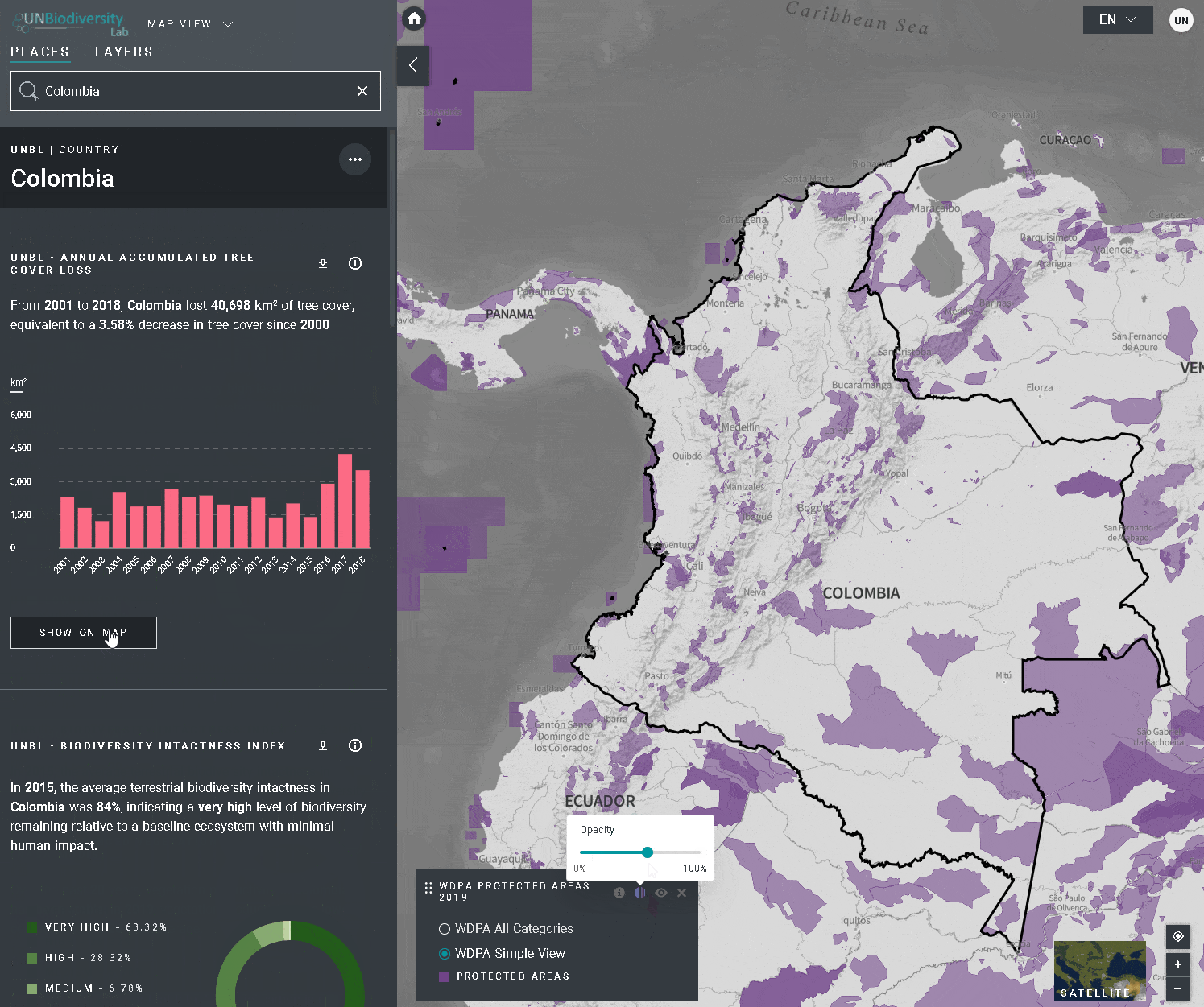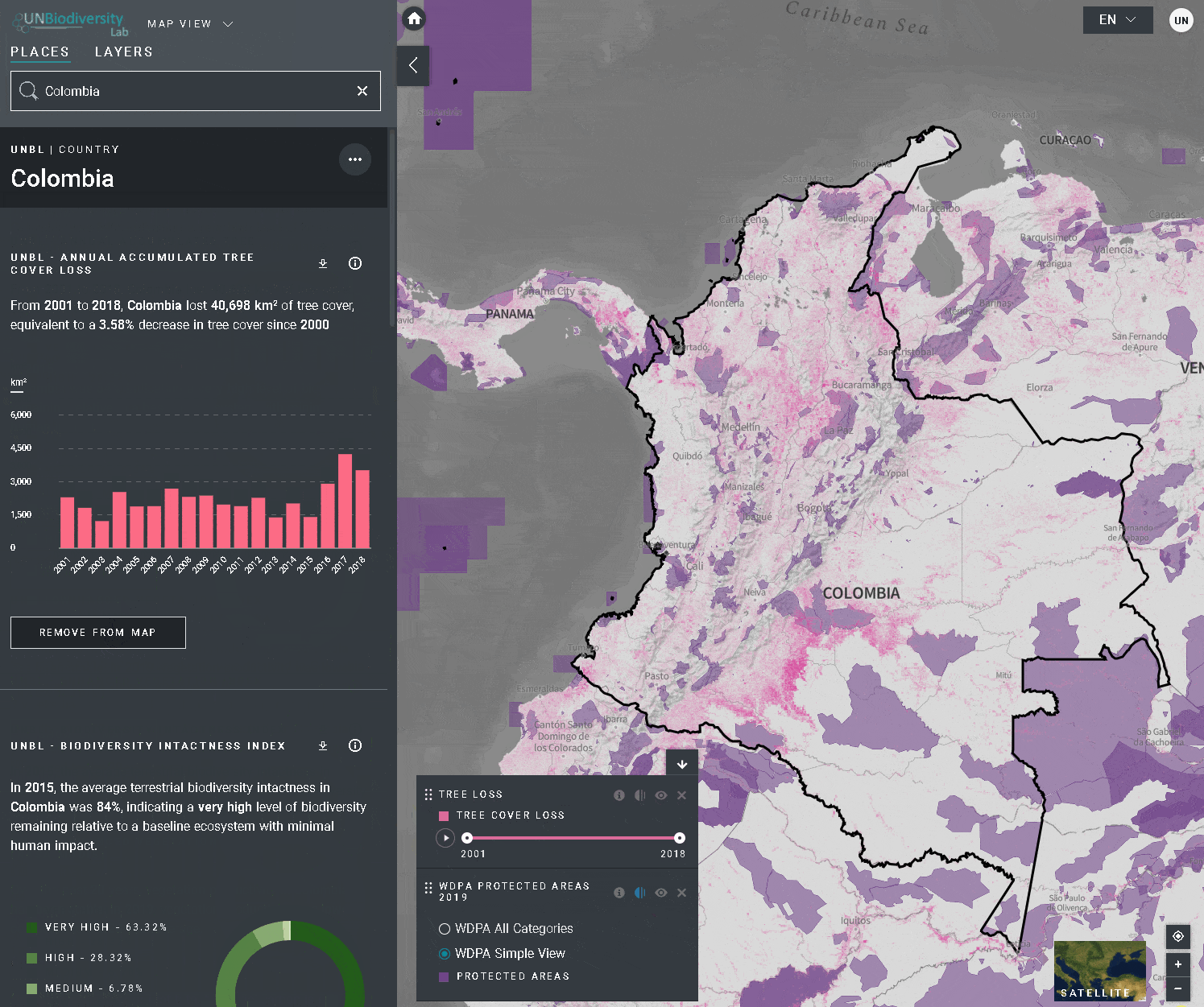
Ao selecionar várias camadas, você pode personalizar o mapa ajustando sua ordem de sobreposição e opacidade:
- Para alterar a ordem de sobreposição, clique no ícone
 à esquerda do nome da camada na legenda e mova o ícone para cima ou para baixo, como preferir. A camada superior na legenda será a camada superior no mapa.
à esquerda do nome da camada na legenda e mova o ícone para cima ou para baixo, como preferir. A camada superior na legenda será a camada superior no mapa. - Para alterar a opacidade, clique sobre ícone
 . A redução da opacidade aumenta a transparência da camada. Por exemplo, para visualizar tanto a perda de cobertura arbórea quanto as áreas protegidas, você pode ordenar a camada de perda de cobertura arbórea acima da camada de áreas protegidas e ajustar a opacidade das áreas protegidas para 60%. Isso cria um mapa que mostra a perda de cobertura arbórea dentro das áreas protegidas, bem como a perda geral em todo o país.
. A redução da opacidade aumenta a transparência da camada. Por exemplo, para visualizar tanto a perda de cobertura arbórea quanto as áreas protegidas, você pode ordenar a camada de perda de cobertura arbórea acima da camada de áreas protegidas e ajustar a opacidade das áreas protegidas para 60%. Isso cria um mapa que mostra a perda de cobertura arbórea dentro das áreas protegidas, bem como a perda geral em todo o país. - Para esconder temporariamente uma camada no mapa, clique no ícone
 . Para torná-la visível novamente, clique no ícone
. Para torná-la visível novamente, clique no ícone  .
.

Para visualizar as camadas das séries temporais:
- Reveja nossa lista de dados para confirmar quais camadas estão disponíveis como séries cronológicas.
- Selecione a camada de interesse.
- Personalizar com base nas opções disponíveis:
- Apenas Animação: Clique no ícone de reprodução à esquerda para ver a animação das mudanças ao longo deste período de tempo.
- Apenas um ano específico: Selecione a hora (ano, mês ou data) que pretende mostrar no mapa clicando na barra da linha do tempo.
- Animação personalizada: Selecione o intervalo de tempo (ano, mês ou data) que pretende mostrar no mapa, clicando na barra da linha do tempo. Clique no ícone de reprodução à esquerda para ver a animação das alterações ao longo deste período de tempo.

- Navegue até à sua área de interesse, se preferir. Você também pode ficar na visão global.
- Clique no ícone das CAMADAS.
- Para procurar por uma camada, você pode:
a. Digitar na caixa de pesquisa o nome da camada que você deseja visualizar e selecionar a opção desejada na lista de camadas.
OU
b. Clicar para expandir as opções de filtro e selecionar o filtro de seu interesse. Você pode então selecionar a camada desejada na lista de resultados da pesquisa
4. Clique na chave à esquerda do nome da camada para carregar esta camada no mapa.
5. Clique na chave novamente ou clique no ícone X na informação da camada para remover esta camada.
Compartilhar camadas de informações é fácil. Para fazer isso:
- Ative a(s) camada(s) de interesse no seu visualizador de mapa.
- Copie o URL exibido no seu navegador.
- Compartilhe! Quaisquer camadas de dados em nossa plataforma pública serão acessíveis por qualquer pessoa, independentemente de ser um usuário registrado.

- Clique no ícone LOCAIS e selecione os seus locais de interesse.
- Clique no ícone … à direita do nome do país, e clique em Recortar e Exportar Camadas.
- Digite o nome ou selecione os dados que você deseja baixar. Se os dados contiverem camadas de vários anos, selecione o ano que você deseja baixar.
- Clique em Baixar.
- A camada de informações selecionada será recortada na caixa de delimitação ao redor do país.
- Há um pequeno buffer adicionado à caixa de delimitação, que irá aumentar ligeiramente a área do raster recortado. Isto ajuda a garantir que quaisquer incongruências entre a fronteira nacional usada na UNBL e o arquivo nacional oficial que você possa querer usar não resultem em perda de dados. Isto assume que as diferenças são potencialmente pequenas. Se este não for o caso, por favor contate-nos em support@unbiodiversitylab.org para obter assistência. Nota: estes são os dados bruto e não incluirão informações de estilo.
- Acesse o arquivo comprimido .zip baixado em sua pasta de downloads assim que o download estiver concluído.
- Os dados baixados podem ser abertos em qualquer software de GIS para análise posterior.

- Selecione a camada de interesse.
- Clique no ícone de informação da camada.
- Clique no link em APRENDA MAIS para baixar os dados de sua fonte original.
- Se encontrar algum problema no acesso aos dados, por favor contate em: support@unbiodiversitylab.org para mais apoio.

- Personalize a visualização das camadas que selecionou, como desejar.
- Use a função de captura de tela no seu computador para capturar o mapa.
- Para inclusão em relatórios formais ou publicações, por favor, certifique-se de que você atende aos padrões de mapeamento:
-
- Os mapas devem ser claros e concisos.
- O texto importante nos mapas deve ser claro e legível (por exemplo, cidades, nomes de lugares, itens de lendas, etc.).
- O mapa deve incluir elementos básicos de mapeamento, incluindo: uma legenda das camadas de dados relevantes e barra de escala.
- O mapa deve fornecer atribuição(ões) e citação(ões) correta(s) da(s) fonte(s) de dados utilizada(s) na sua criação, seja no próprio mapa ou em uma legenda descrevendo o mapa, por exemplo:
Exemplo (se no próprio mapa):
Fontes: Sanderman, et al., 2018; UNEP-WCMC e UICN, 2021.
Exemplo (se em uma legenda):
A Figura 2 mostra a estimativa de carbono orgânico do solo presente nos manguezais (de Sanderman, et al., 2018) dentro de áreas protegidas no Vietnã (UNEP-WCMC e IUCN, 2021).
Certifique-se também de incluir citações completas para os conjuntos de dados utilizados na secção de referências do documento, por exemplo:
Sanderman, J. et al. (2018) ‘A global map of mangrove forest soil carbon at 30 m spatial resolution’, Environmental Research Letters, 13(5), p. 055002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aabe1c.
UNEP-WCMC and IUCN (2021), Protected Planet: The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) [On-line], 02/2021, Cambridge, UK: UNEP-WCMC and IUCN Available at: www.protectedplanet.net.
Incluir informações no mapa (ou na citação descrevendo o mapa) sobre: quem criou o mapa; a data em que o mapa foi produzido no UN Biodiversity Lab; e uma nota indicando que o mapa foi criado usando o UN Biodiversity Lab.
Exemplo:
Criado por James Bond usando o UN Biodiversity Lab (www.unbiodiversitylab.org) em 14 de Fevereiro de 2021.
Finalmente, certifique-se de que inclui também uma citação para o mapa na seção de referências do documento. Recomendamos este formato:
Autor. “Título do mapa” [formato]. Escala. (Data de produção). Mapa gerado no UN Biodiversity Lab [web]. Versão 2. PNUD e PNUMA, 2021.
Exemplo:
Bond, James. “Carbono Orgânico de Solo de Manguezal nas Áreas Protegidas do Vietnam” [mapa]. Escala não dada. (14 Fev 2021). Mapa gerado no UN Biodiversity Lab (www.unbiodiversitylab.org) [web]. Versão 2. PNUD e PNUMA, 2021.
Agradecemos sugestões sobre dados que possam enriquecer o UN Biodiversity Lab! Se os seus dados tratam da biodiversidade, conservação ou desenvolvimento sustentável a nível local, nacional ou internacional, por favor preencha este formulário.
A nossa equipa receberá sugestões à medida que forem recebidas. UNDP, UN Environment e UN Environment-WCMC formalizaram critérios para os dados publicados na plataforma pública para ajudar a identificar e manter as melhores camadas de dados disponíveis sobre estes temas, a fim de permitir análises e relatórios mais racionalizados e padronizados. Os critérios estão disponíveis aqui.
Para carregar dados para uso por sua instituição em uma área de trabalho privada, veja a próxima pergunta sobre como solicitar área de trabalho privada.
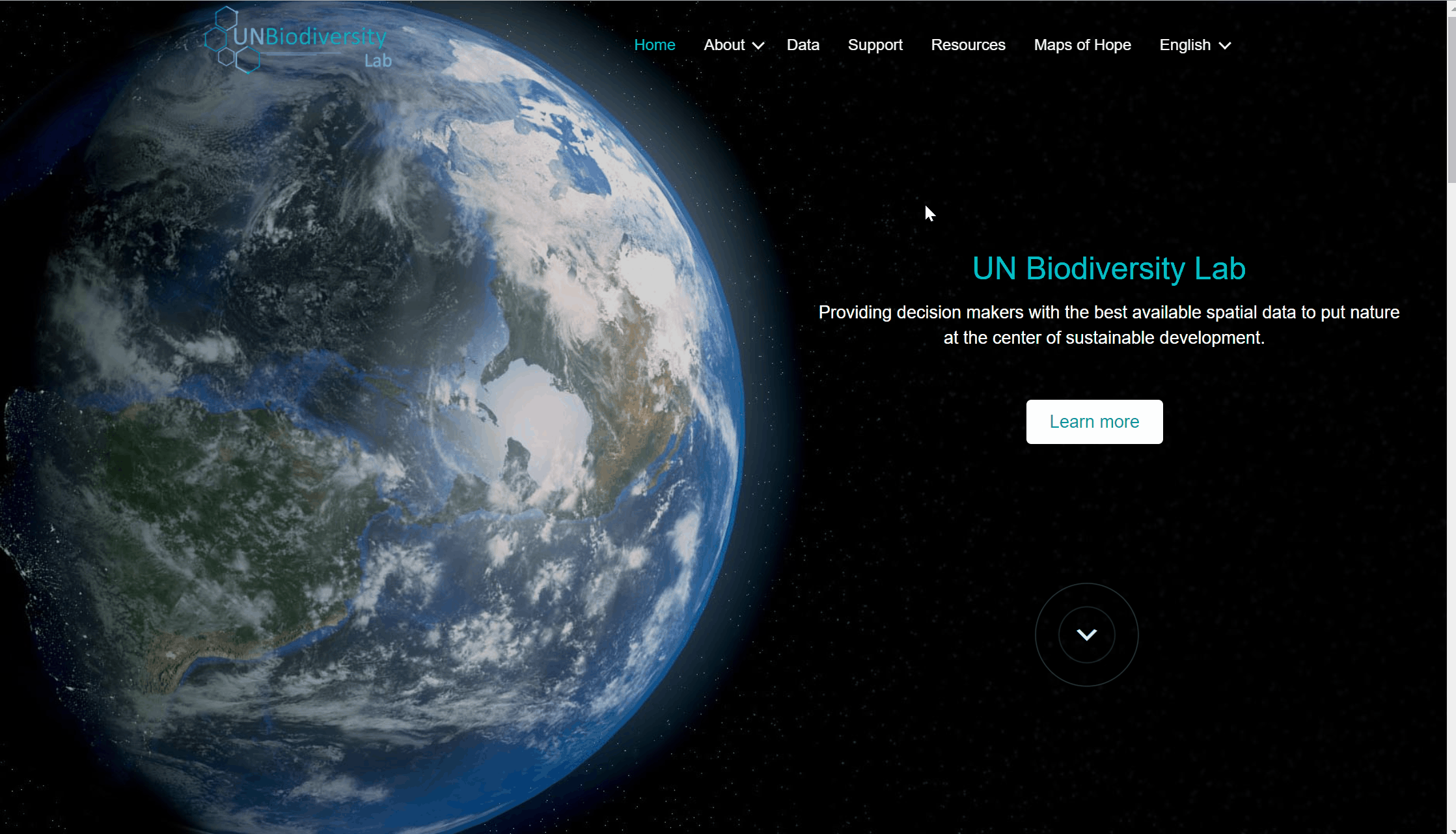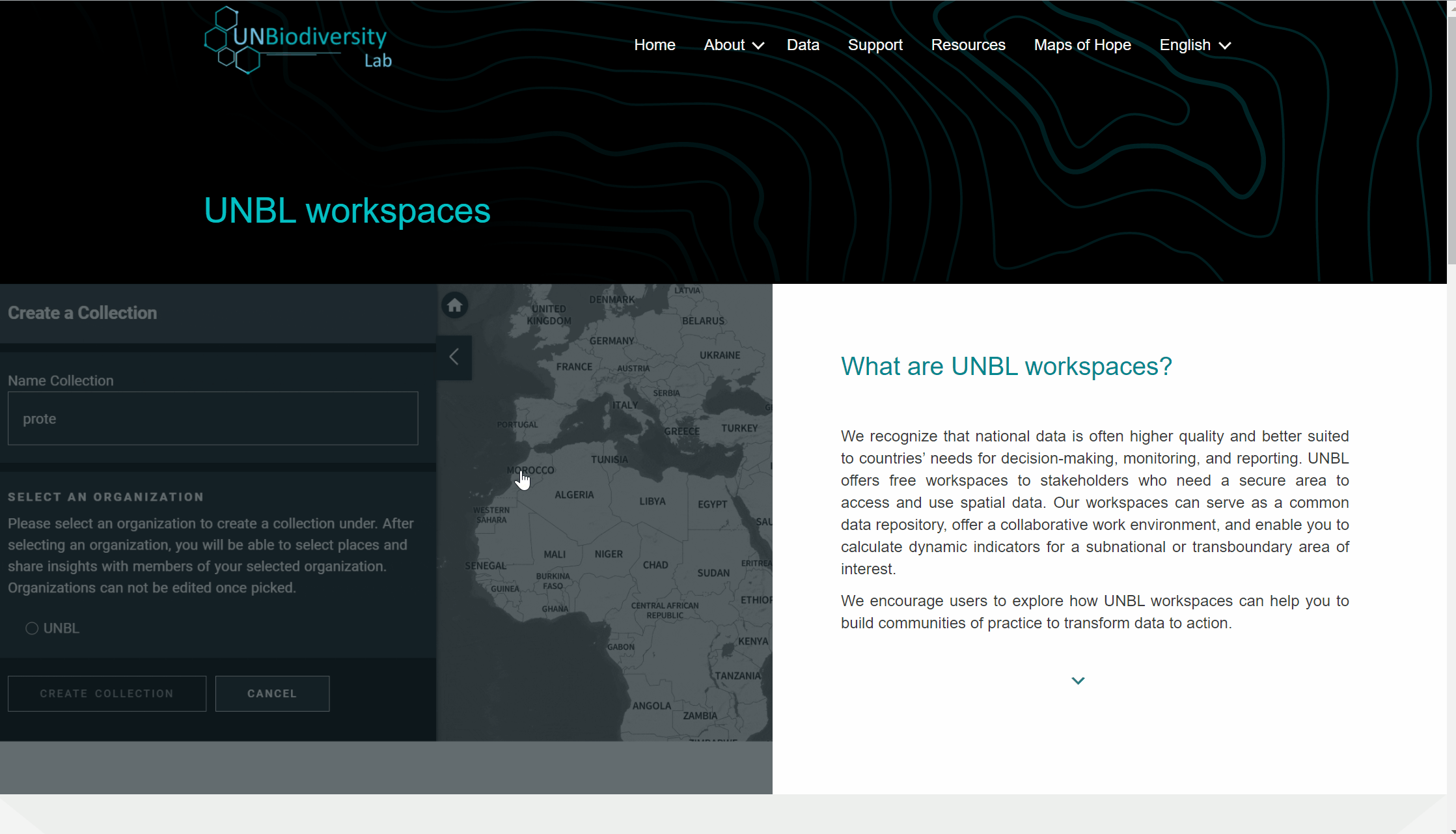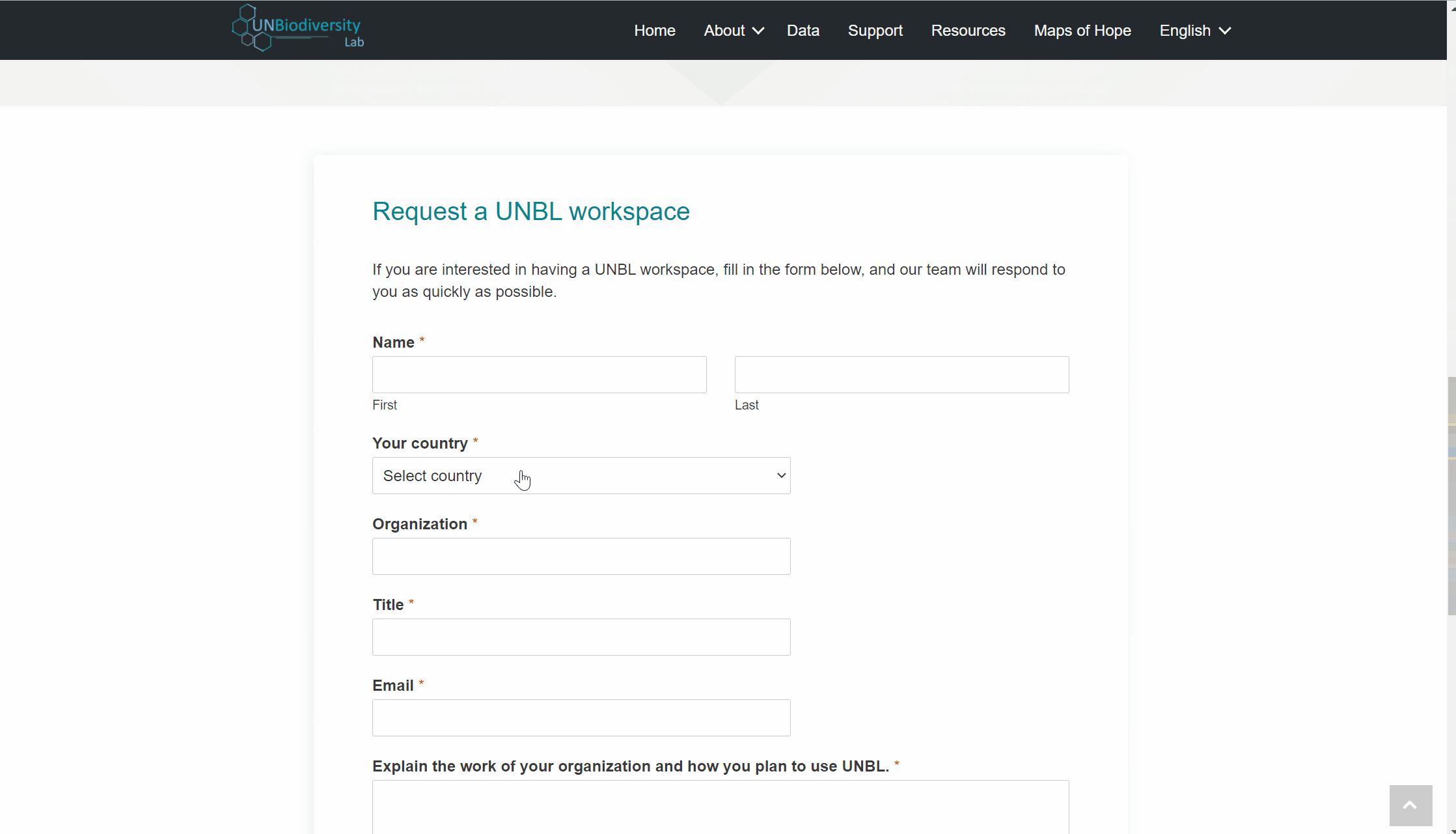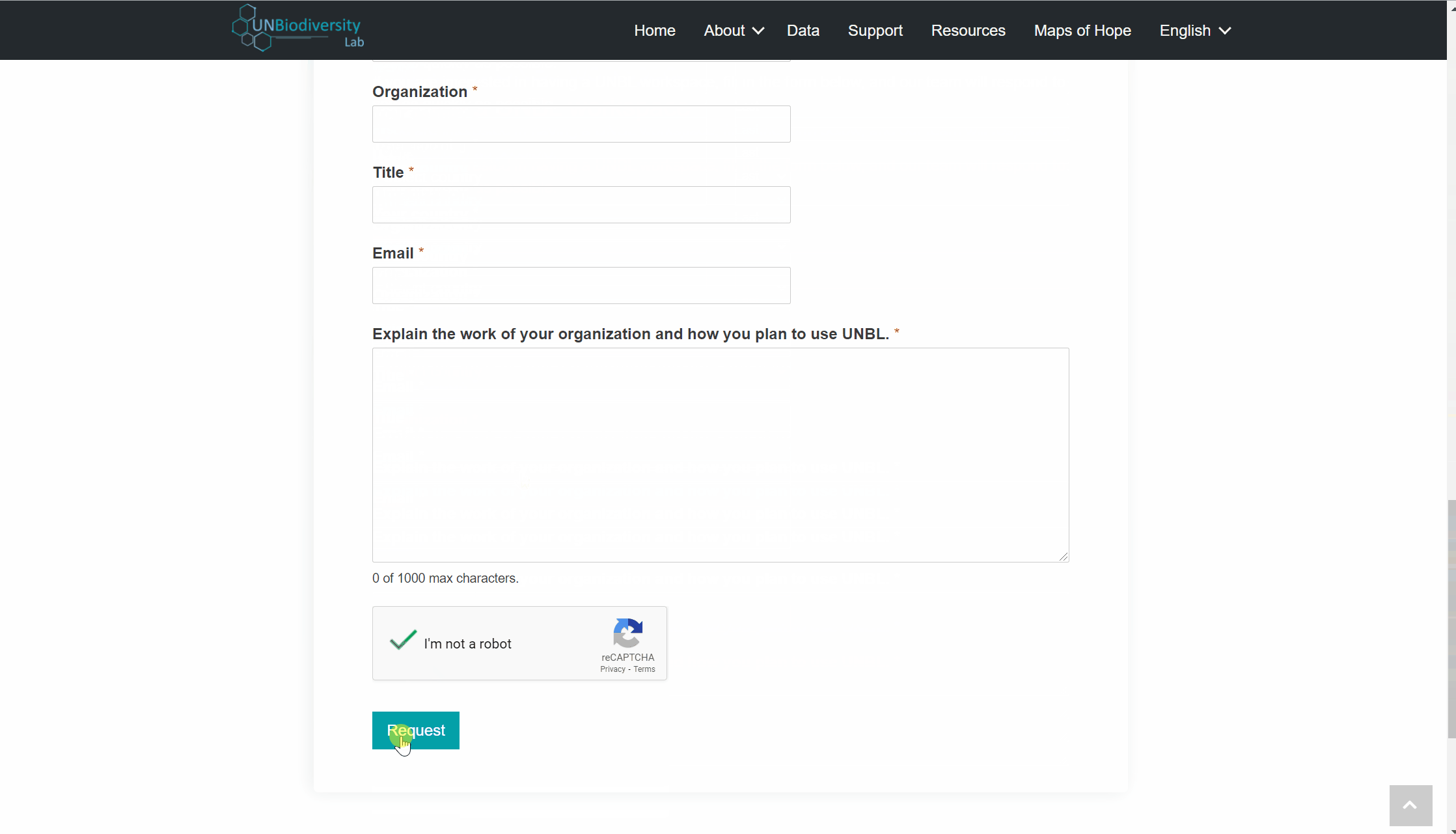
As áreas de trabalho privadas proporcionam uma área de trabalho segura onde dados nacionais ou subnacionais podem ser adicionados e compartilhados com um conjunto de usuários especificados. Eles oferecem uma área segura para colaborar em seus projetos, independentemente da experiência em SIG.
As áreas de trabalho privadas são concedidas a critério dos parceiros do UN Biodiversity Lab. Para solicitar uma área de trabalho privada, por favor clique no aba áreas de trabalho privadas na nossa página de apoio e preencha o formulário.
Baixar o guia do usuário da plataforma pública : Inglês | Francês | Espanhol | Português | Russo
- Faça o login na sua conta.
- Clique no botão VISÃO DO MAPA. Isto irá exibir as áreas de trabalho às quais você pertence.
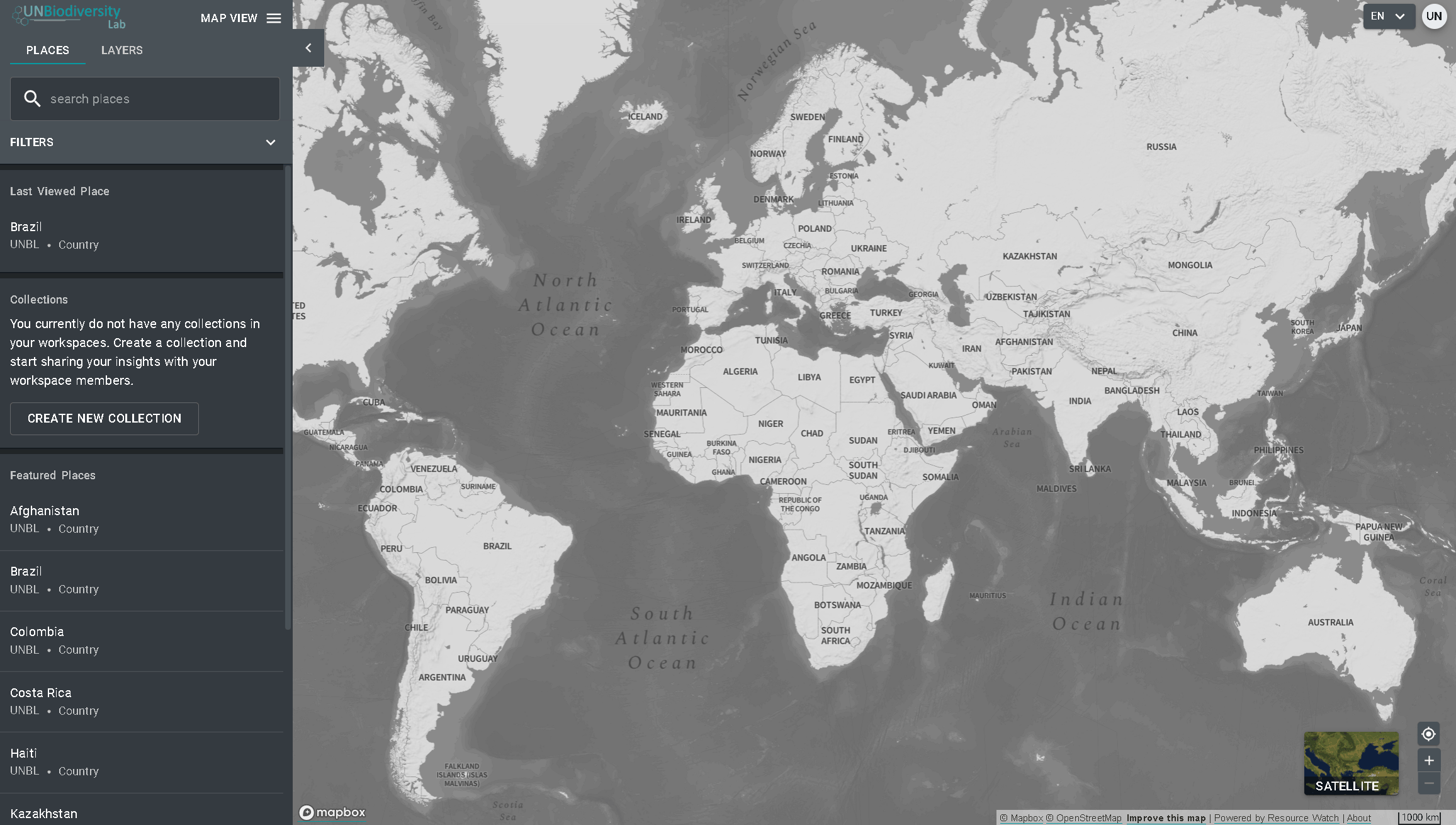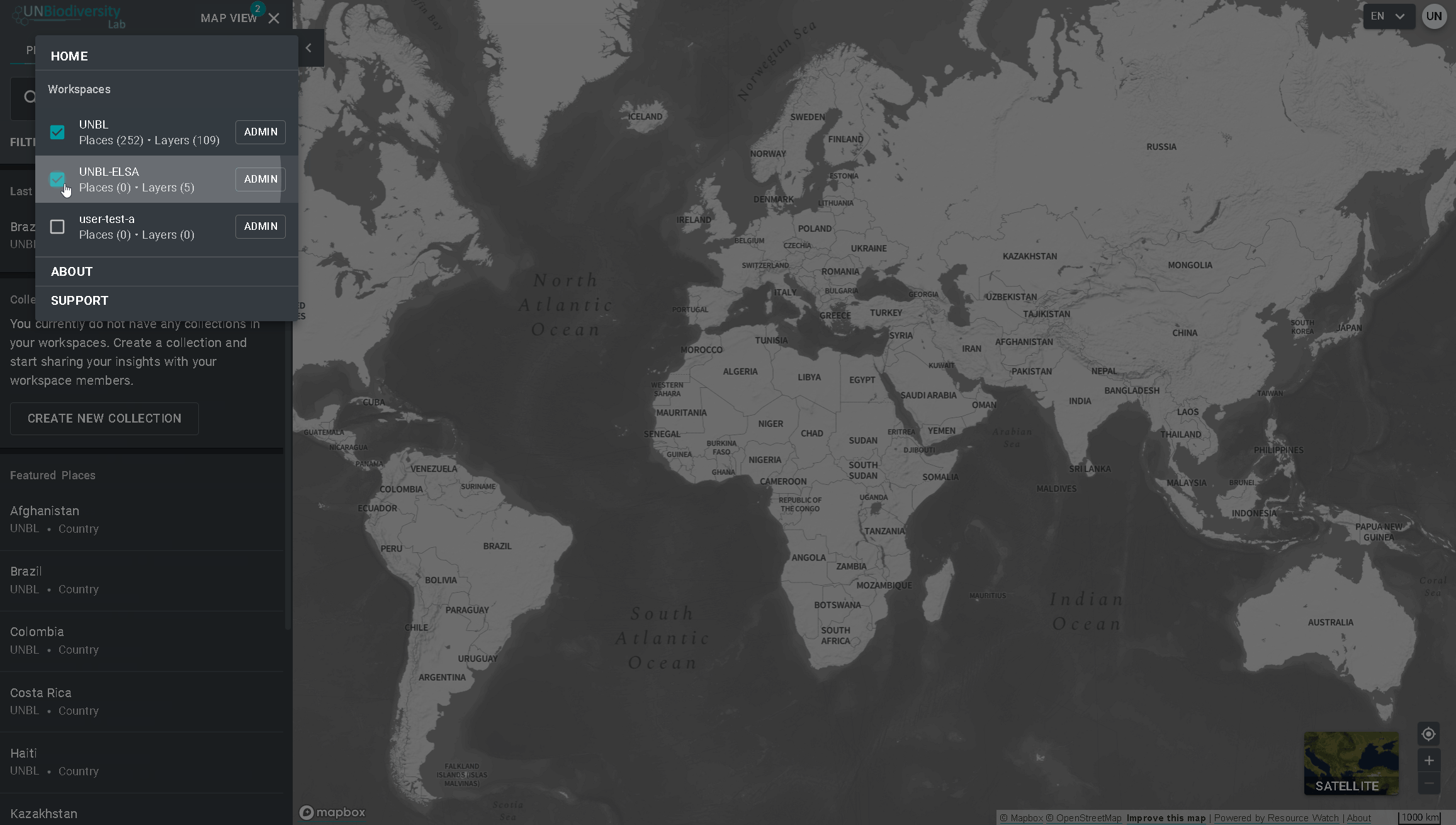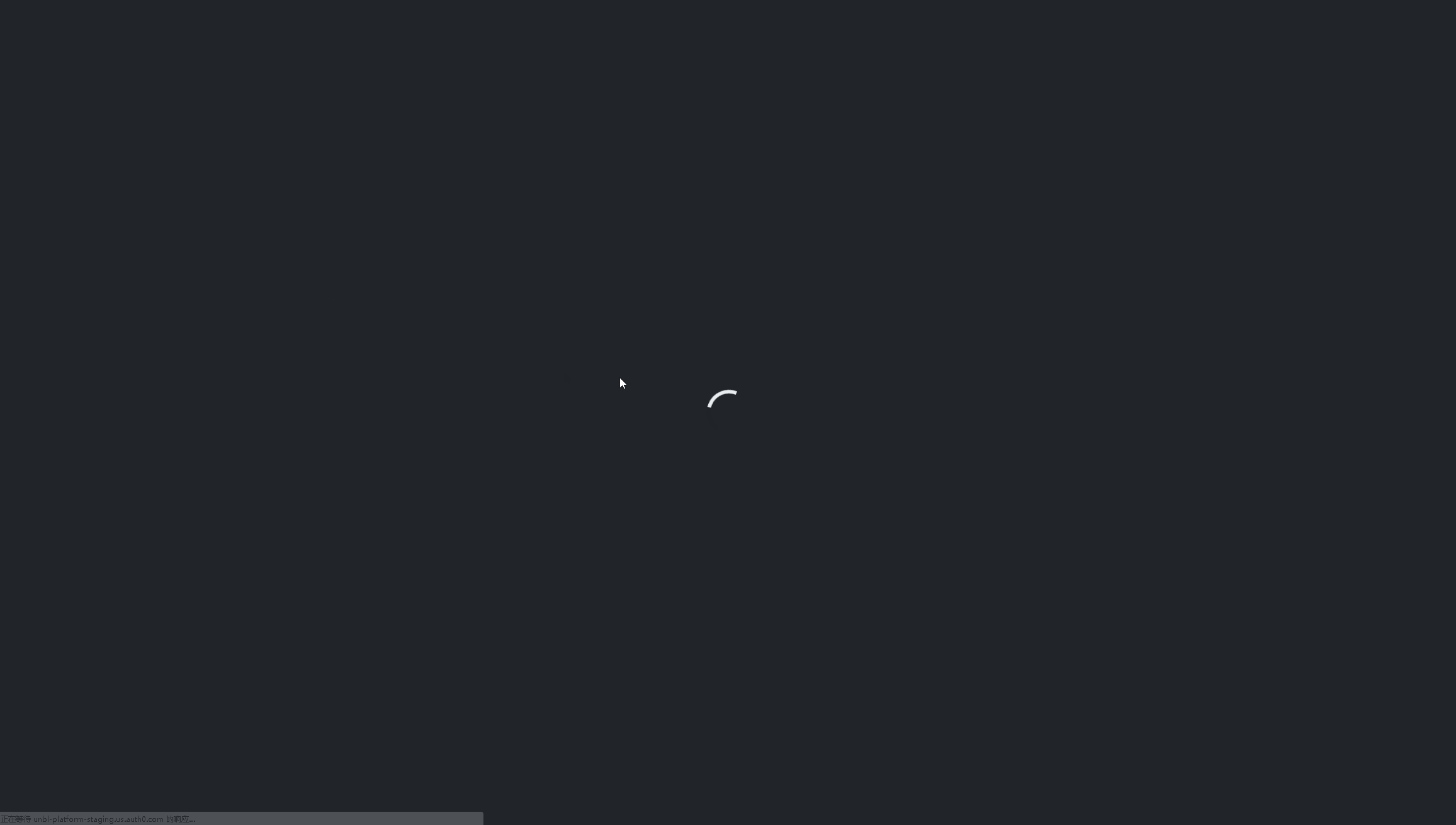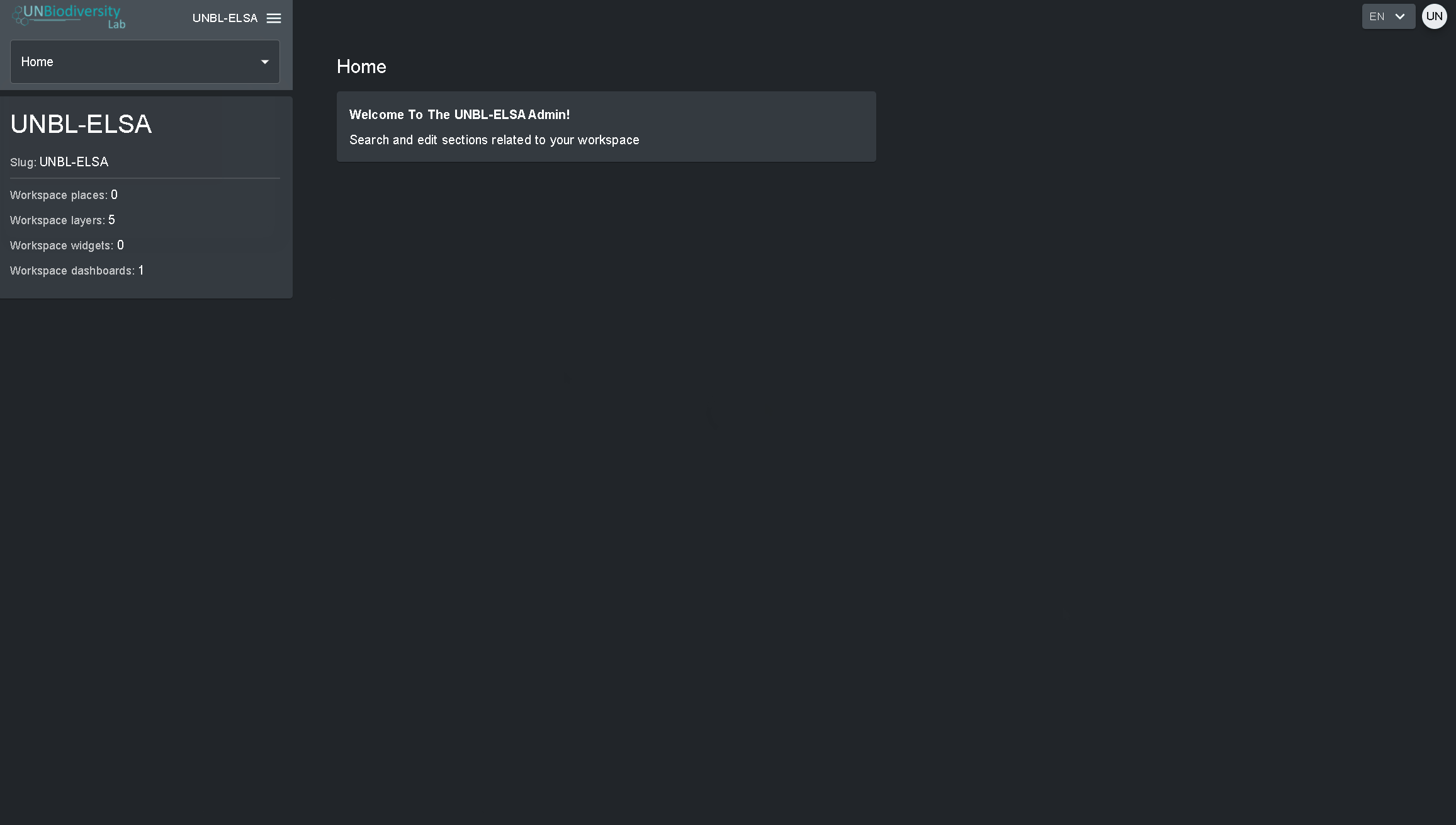
- É possível visualizar os ativos (locais e camadas de informação) para cada área de trabalho independentemente, ou para todas ao mesmo tempo. Marque as opções das áreas de trabalho que pretende incluir na visualização. Nota: se nenhuma área de trabalho for selecionada, é como se todas as áreas de trabalho fossem selecionadas.
- Desmarque as áreas de trabalho que você não quer visualizar. Isso permite que você só veja os locais carregados na sua área de trabalho privada e não filtre os ativos não desejados. Nota: não recomendamos que você desmarque a plataforma pública UNBL pois isso removerá o acesso às camadas públicas globais e o painel de métricas para todas as áreas.
Para procurar por uma área de interesse, você pode:
- Clique no ícone LOCAIS, digite na caixa de pesquisa o nome do país ou jurisdição que deseja visualizar e selecione o resultado desejado na lista de resultados da pesquisa.
OU
- Clique no ícone LOCAIS, então clique para expandir as opções de filtro e selecione o filtro de seu interesse. Você pode então selecionar o local desejado na lista de resultados da pesquisa.
Para visualizar métricas dinâmicas para locais da sua área de trabalho UNBL:
- Selecione uma área de interesse.
- Revise as métricas no painel à esquerda.
- Clique no ícone MOSTRAR NO MAPA se você quiser ver esta camada no mapa. Clique no ícone REMOVER DO MAPA ou no ícone remover camada na legenda para limpar a tela.
- Clique no ícone (i) para ver as informações da camada; a páginas de informações fornece uma breve descrição dos dados, publicação relacionada para leitura e link para a origem dos dados.
- Para baixar dados resumidos da métrica em formato .csv ou .json, clique no ícone com a seta. Você também pode baixar os dados dos links de origem na página de informação da camada.
- Clique no ícone das CAMADAS. As camadas de informação dos áreas de trabalho que selecionou irão preencher esta aba automaticamente.
- Para procurar por uma camada, você pode:
- Digitar na caixa de pesquisa o nome da camada que você deseja visualizar e selecionar a opção desejada na lista de camadas. OU
- Clicar para expandir as opções de filtro e selecionar o filtro de seu interesse. Você pode então selecionar a camada desejada na lista de resultados da pesquisa.
- Clique na chave à esquerda do nome da camada para carregar esta camada no mapa.
- Clique na chave novamente ou clique no ícone X na informação da camada para remover esta camada.
- Clique no menu VISÃO DO MAPA.
- Selecione o botão ADMIN associado ao área de trabalho de sua escolha.
- A página de administração do seu área de trabalho também pode ser acessada na seguinte URL: https://map.unbiodiversitylab.org/admin//YOURWORKSPACESLUGNAME
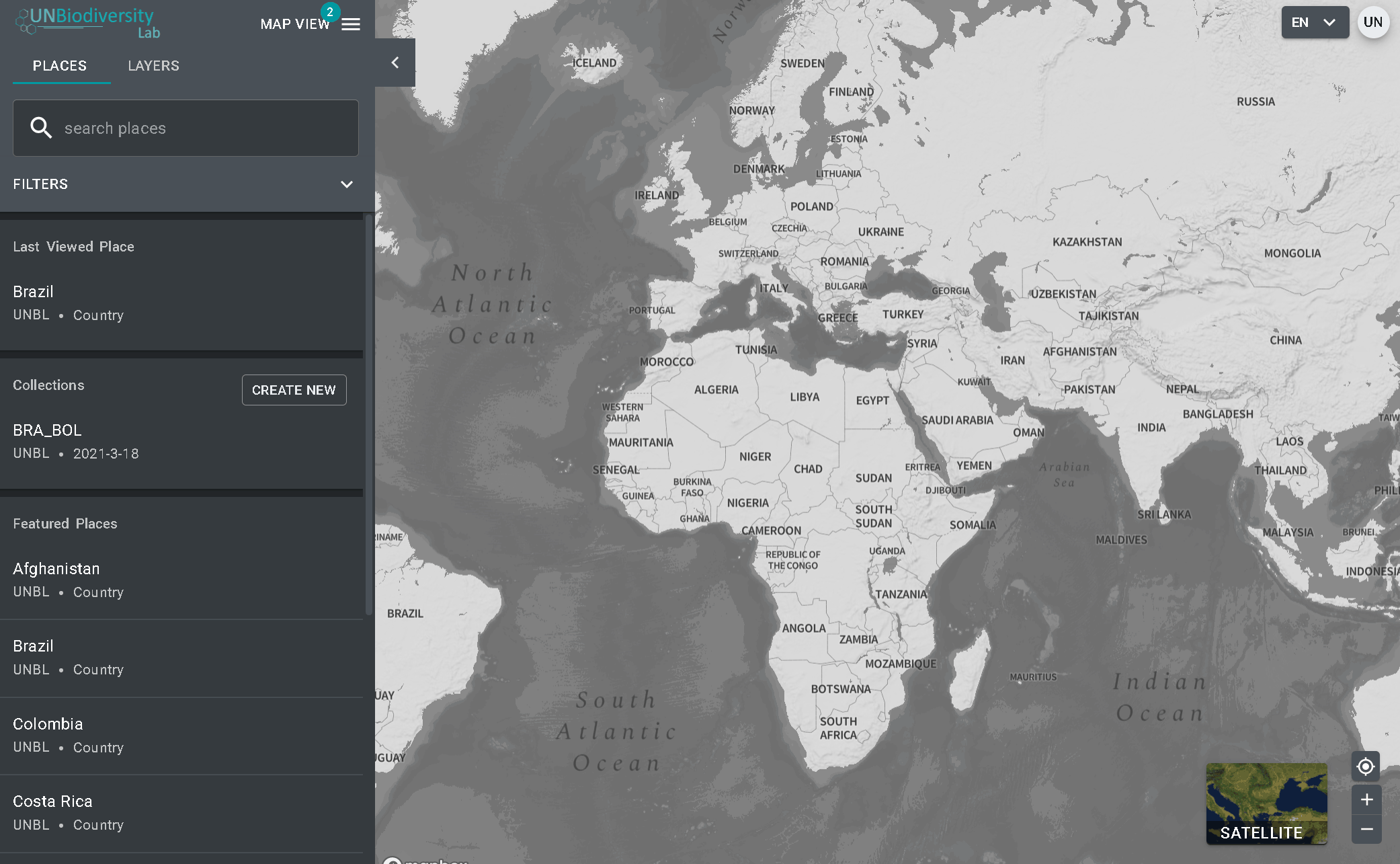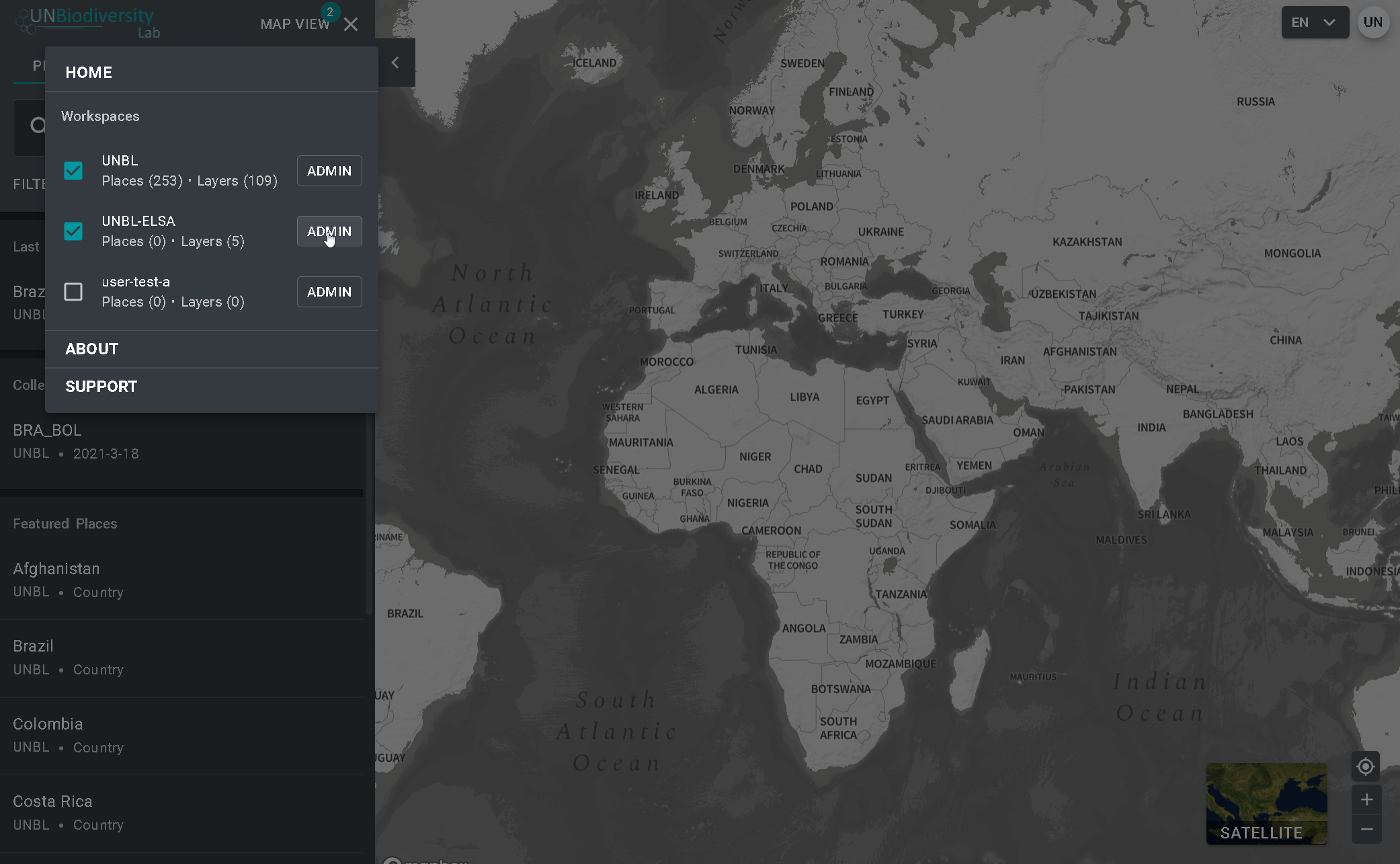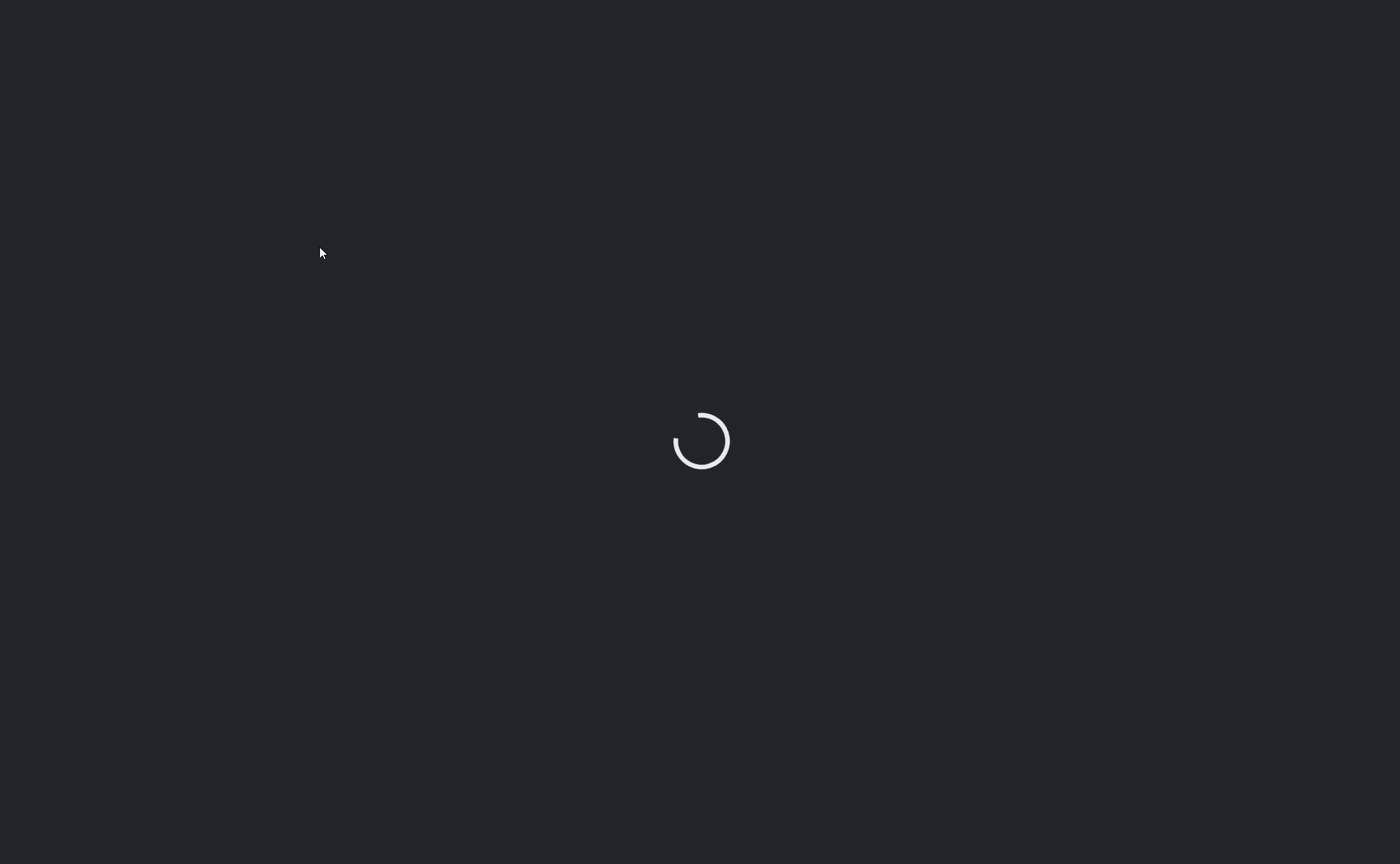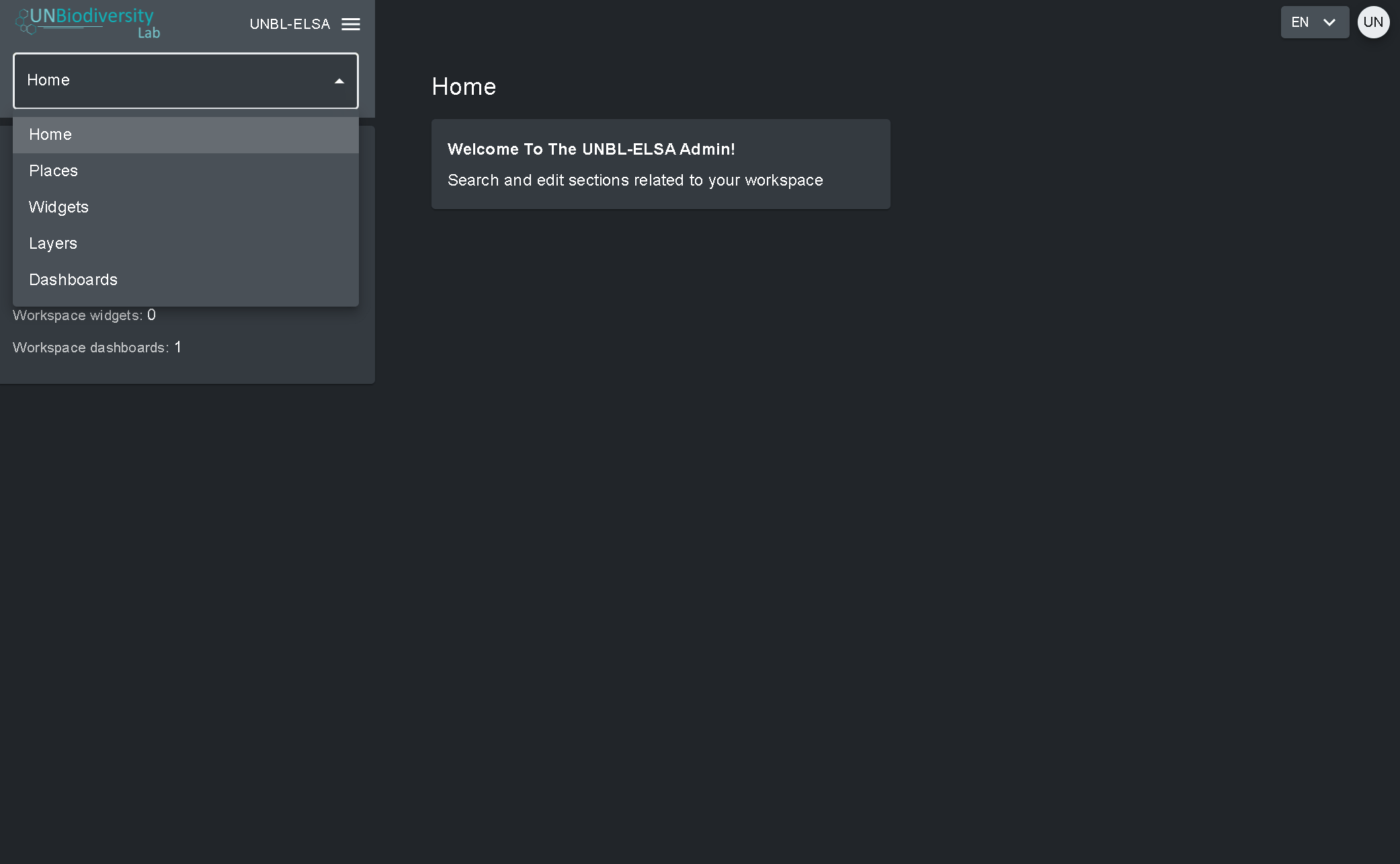
Para acessar os vários componentes:
- Clique na aba à direita do botão de início para expandir o menu suspenso.
- Selecione o componente que você gostaria de visualizar. Mais informações sobre cada componente são fornecidas no restante deste guia do usuário.
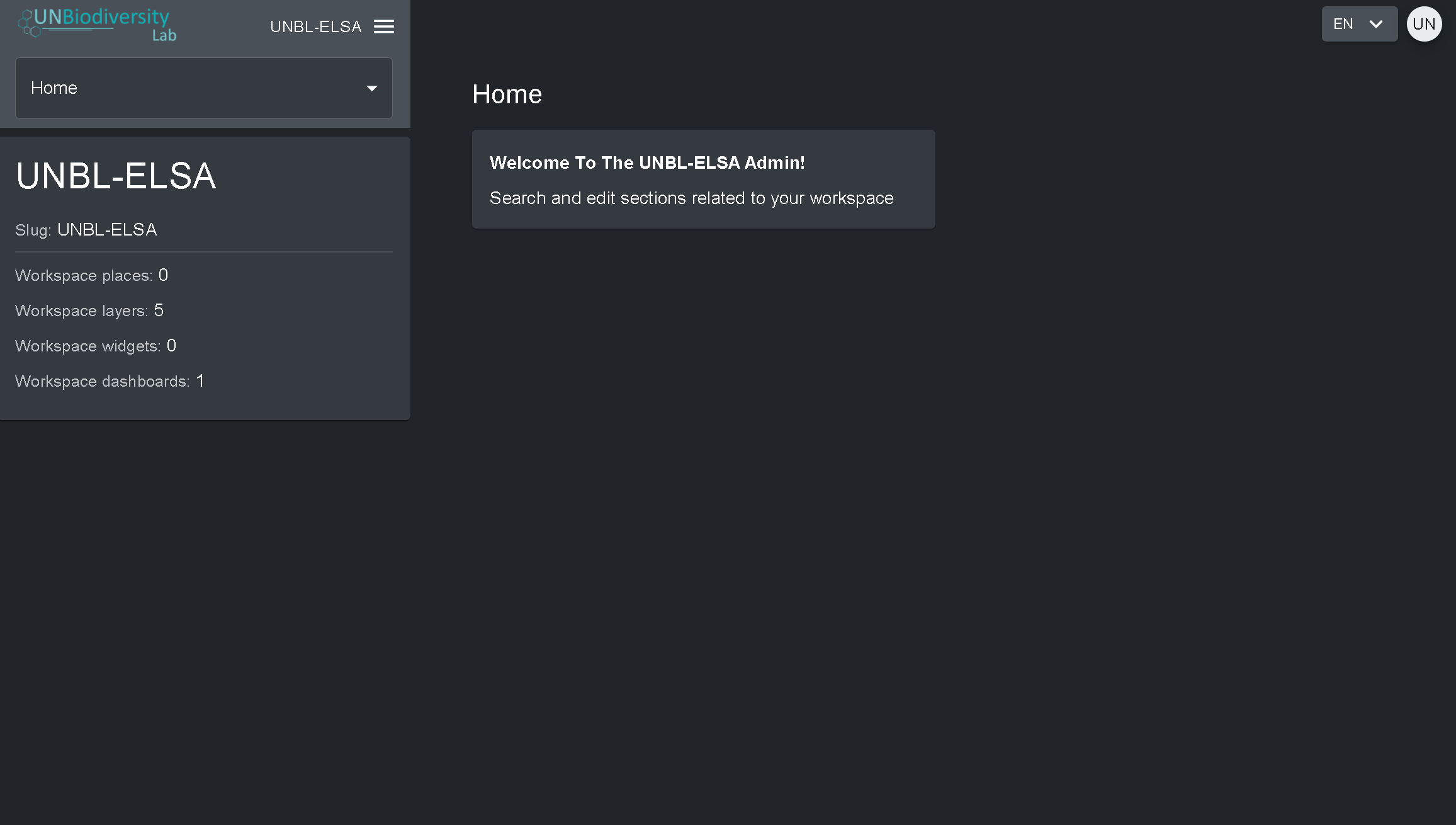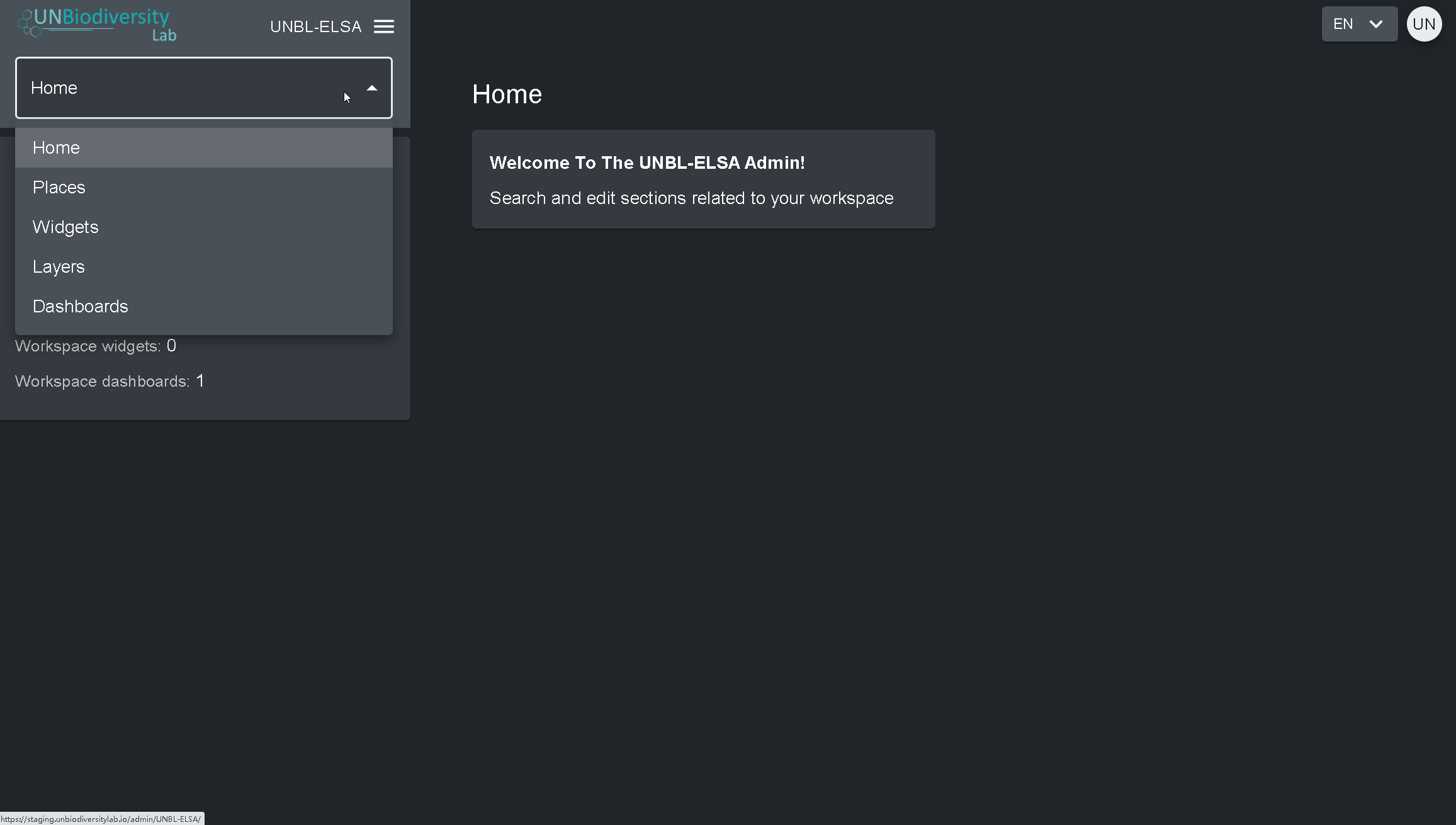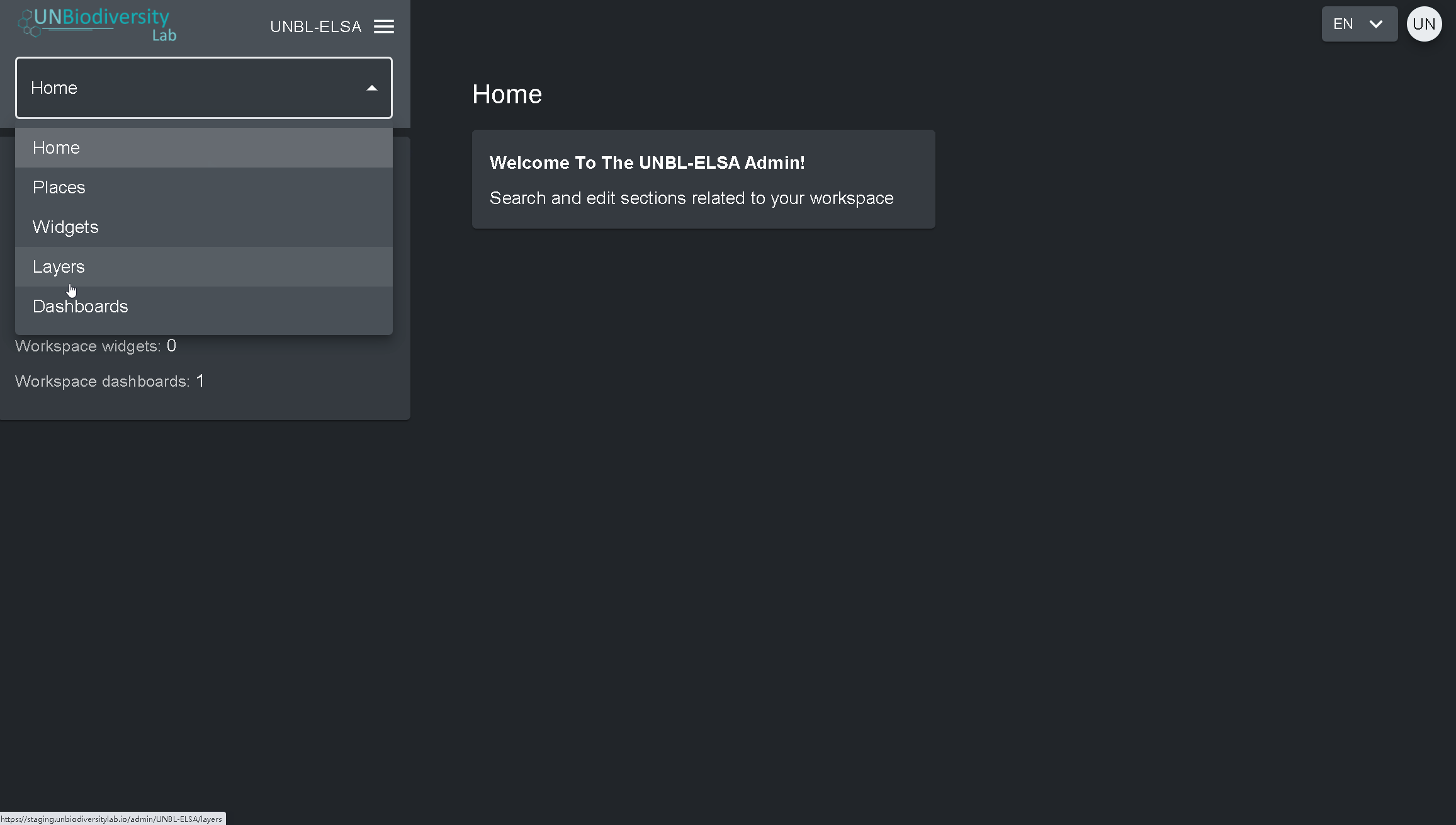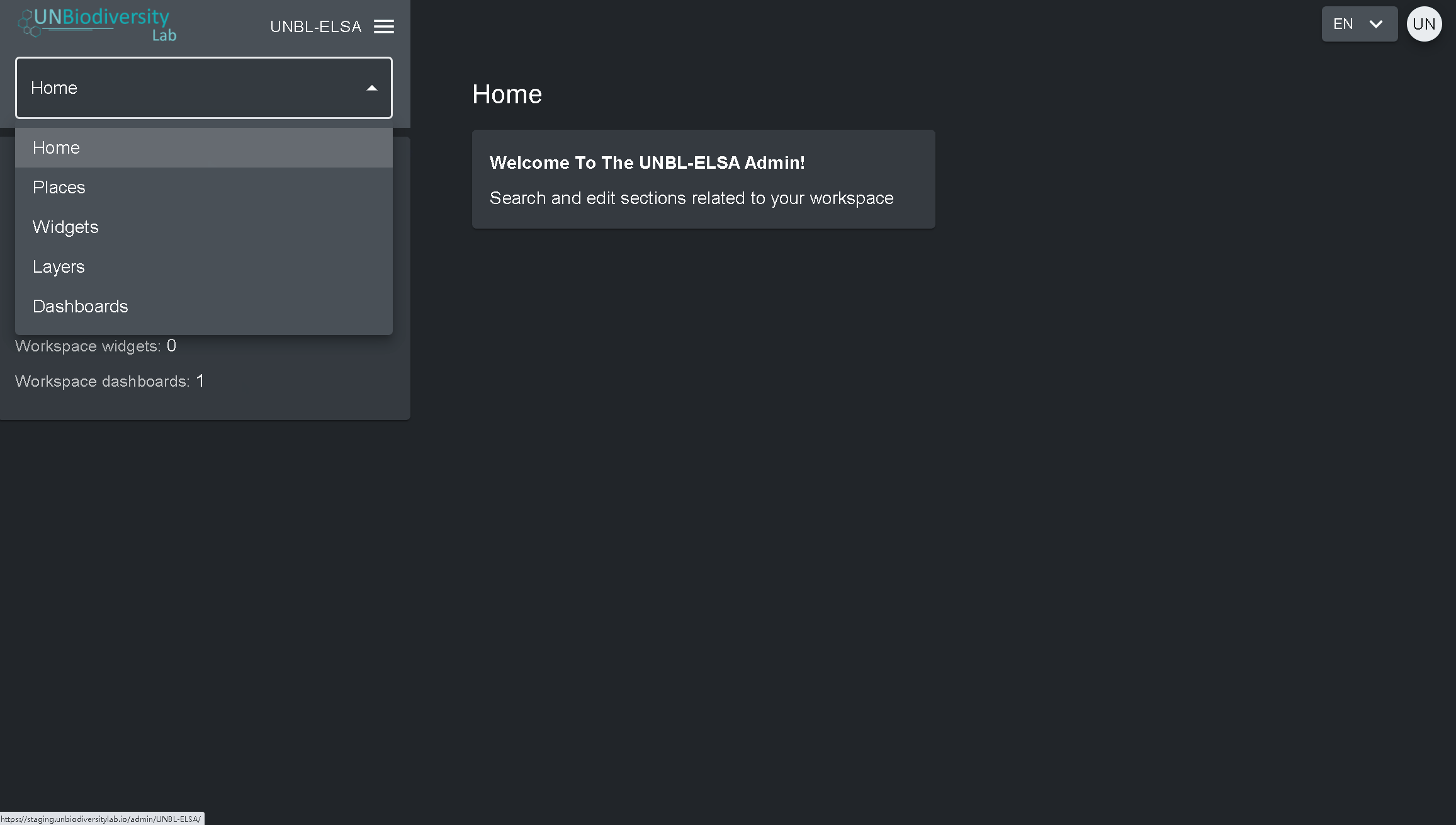
Proprietários – o criador do área de trabalho. Atualmente só os administradores da plataforma UNBL podem criar áreas de trabalho UNBL e lhes atribuir um Proprietário. Os Proprietários têm a capacidade de adicionar todos os tipos de usuários, gerenciar os ativos da área de trabalho (locais e camadas) através da ferramenta de administração e visualizar todos os ativos do área de trabalho na visualização do mapa.
Administradores – pode adicionar e gerenciar usuários, atribuir perfis aos usuários como editores e visualizadores, gerenciar ativos da área de trabalho através da página de administração e visualizar todos os ativos do área de trabalho na visualização do mapa.
Editores – pode gerir os ativos da área de trabalho através da página de administração, e visualizar todos os ativos da área de trabalho na visualização do mapa. Os editores devem ter experiência em trabalhar com software GIS para que possam carregar e editar camadas de informação.
Visualizadores – podem visualizar todos os ativos da área de trabalho na visualização do mapa. Os visualizadores não têm acesso à página de administração.
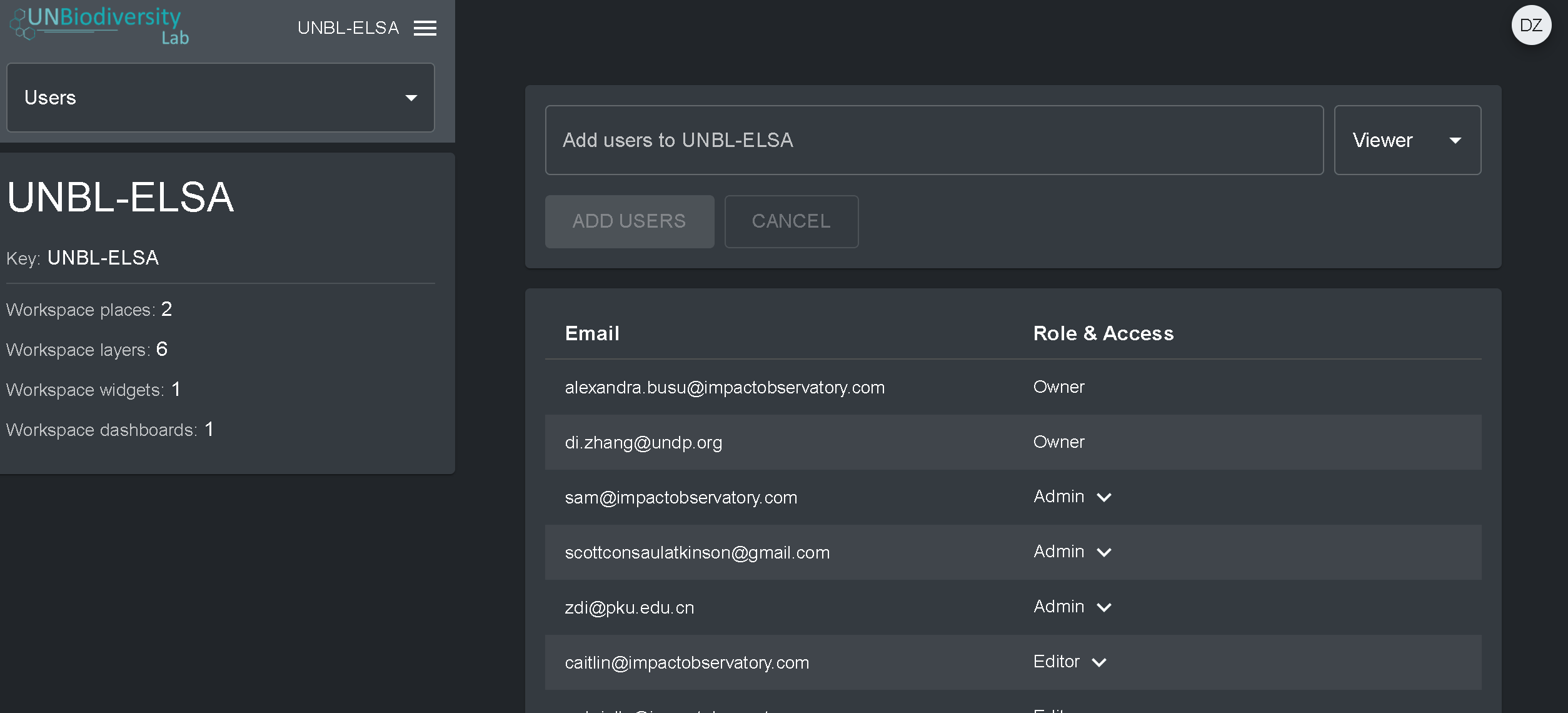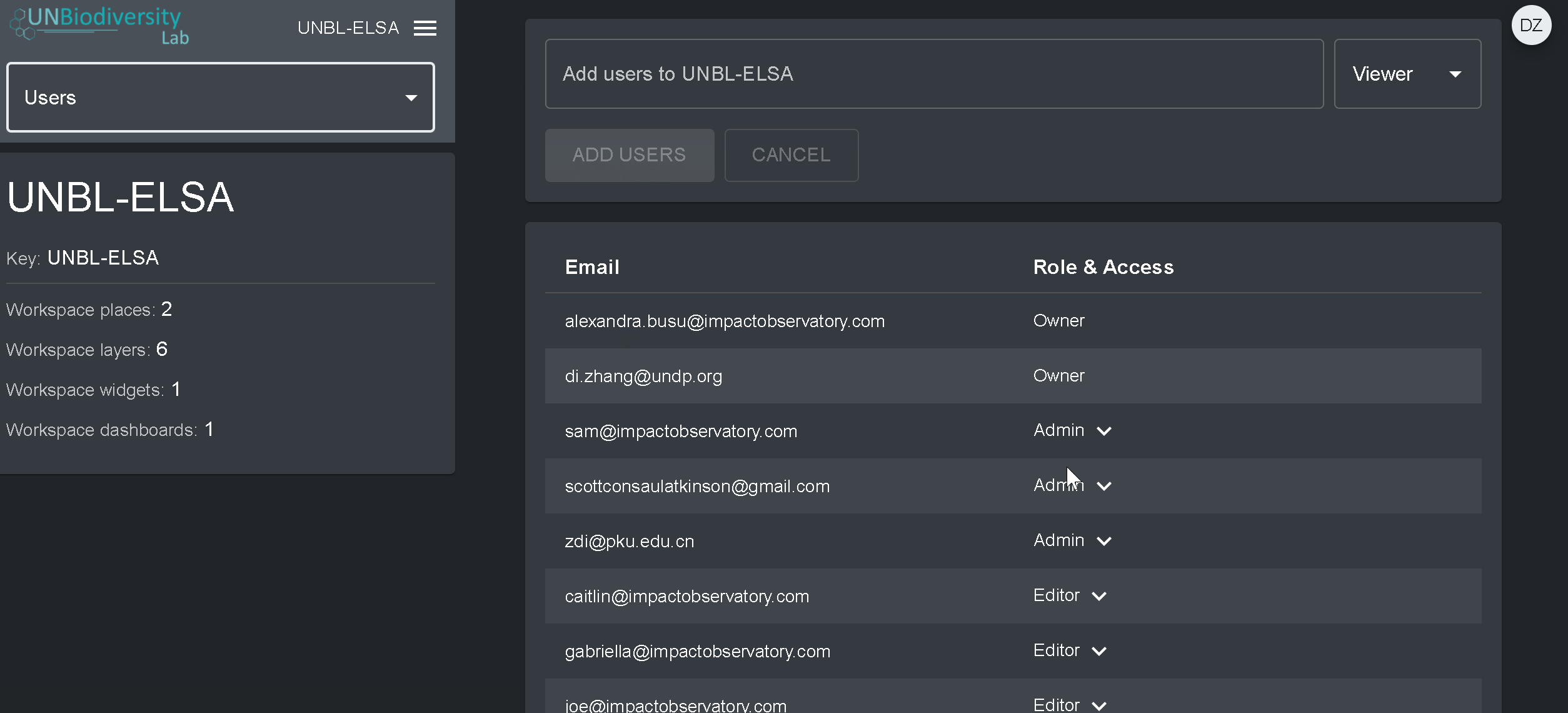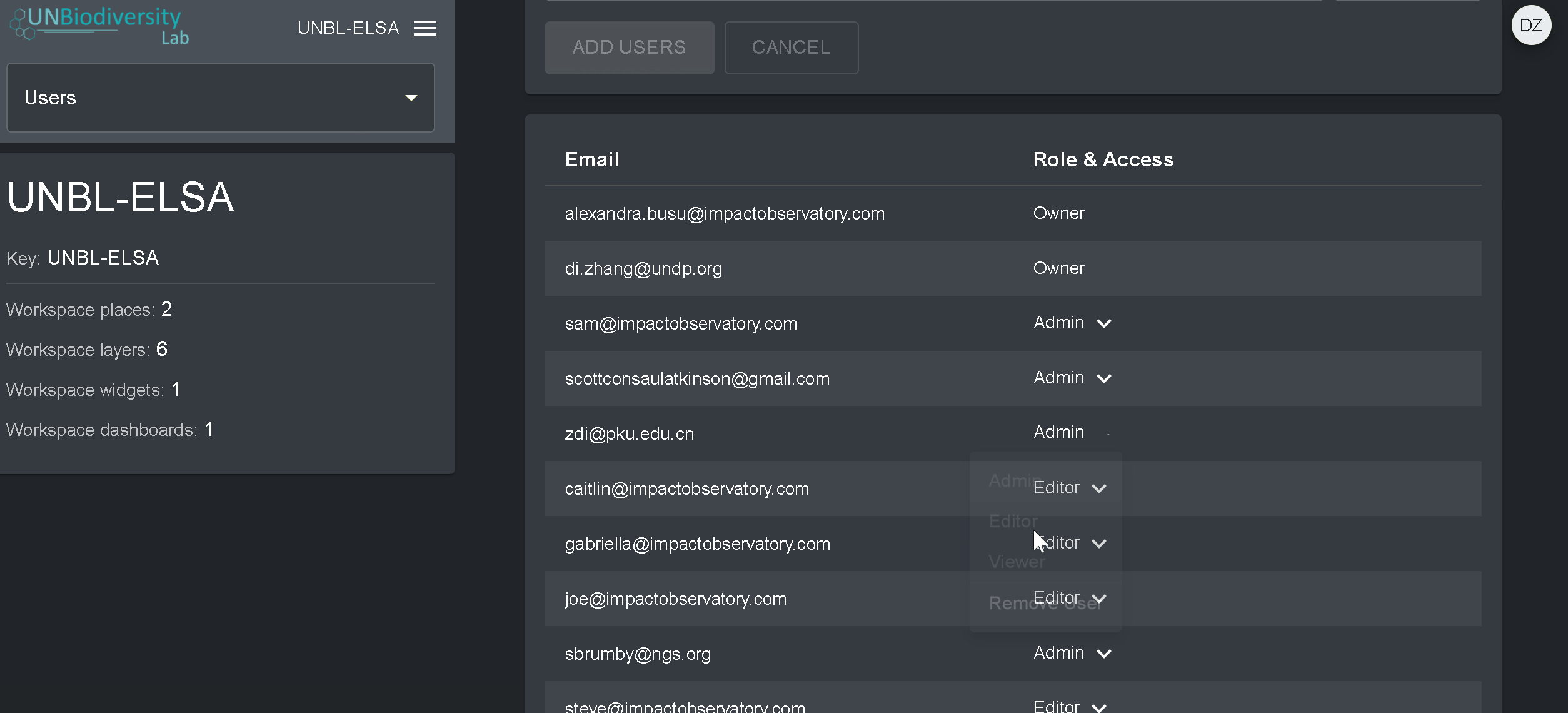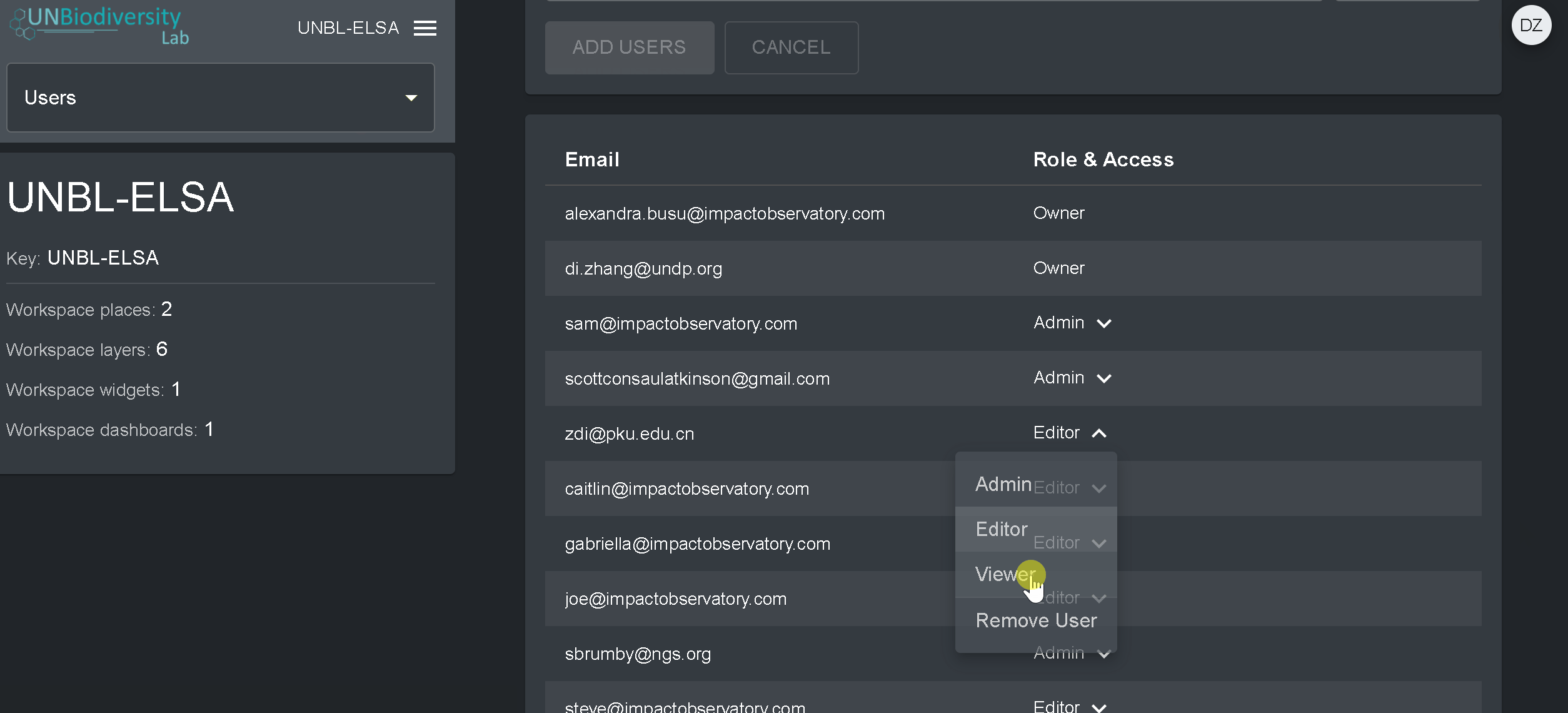
Para adicionar usuários à sua área de trabalho:
- Solicite que o usuário se inscreva em uma conta na UNBL (consulte nosso Guia do Usuário da Plataforma Pública da UNBL para obter detalhes).
- Navegue até a opção Usuários a partir do menu suspenso no lado esquerdo da tela da página de administração.
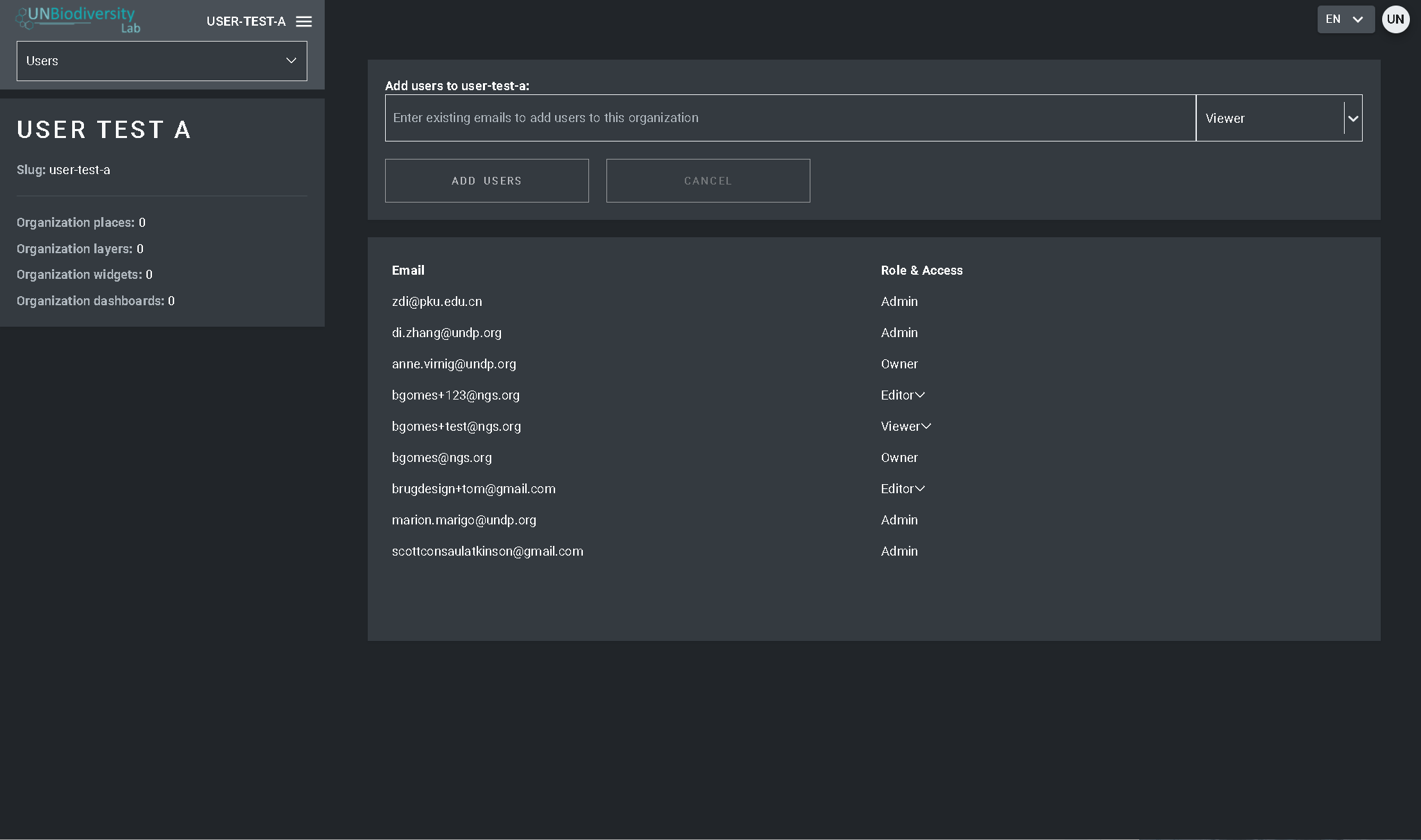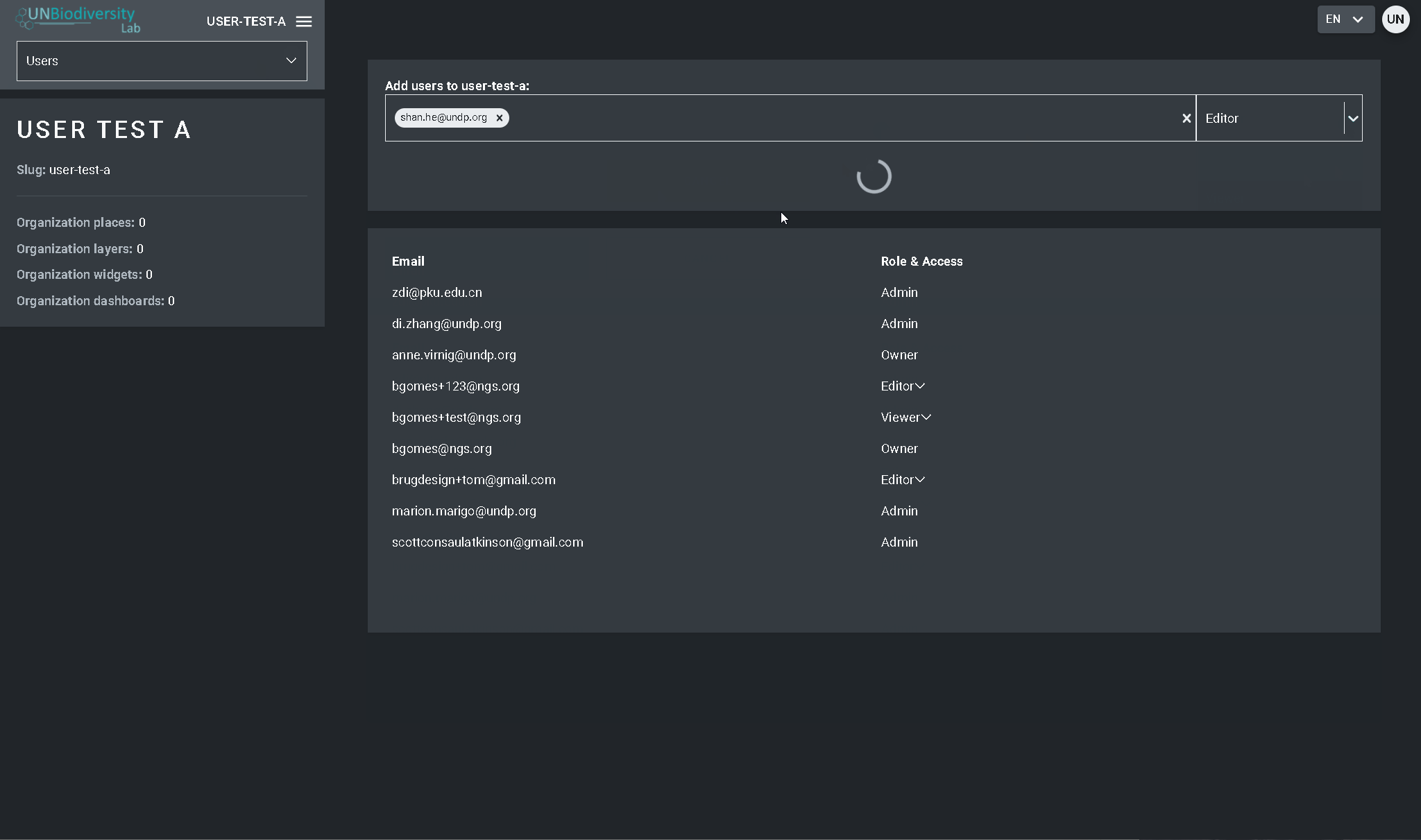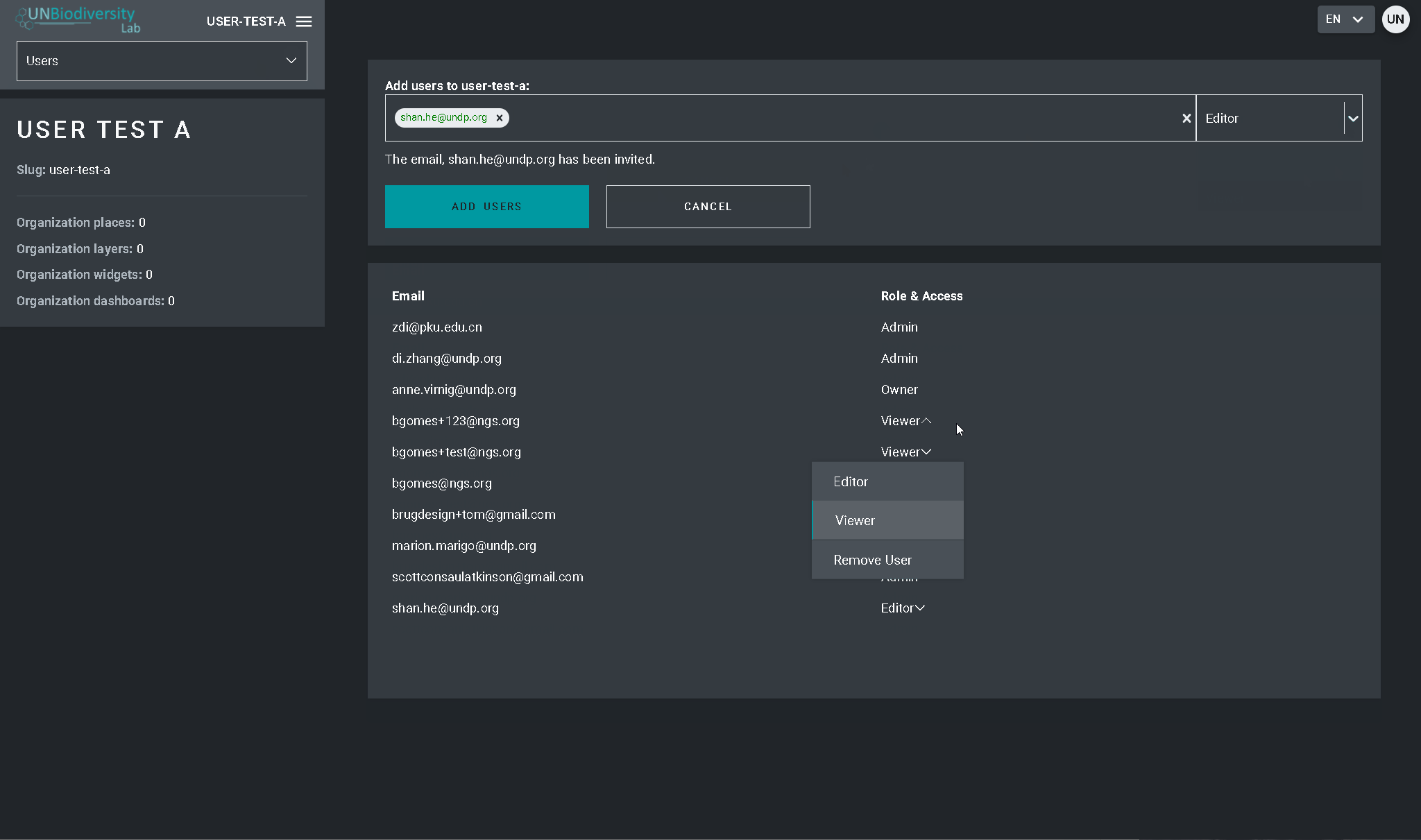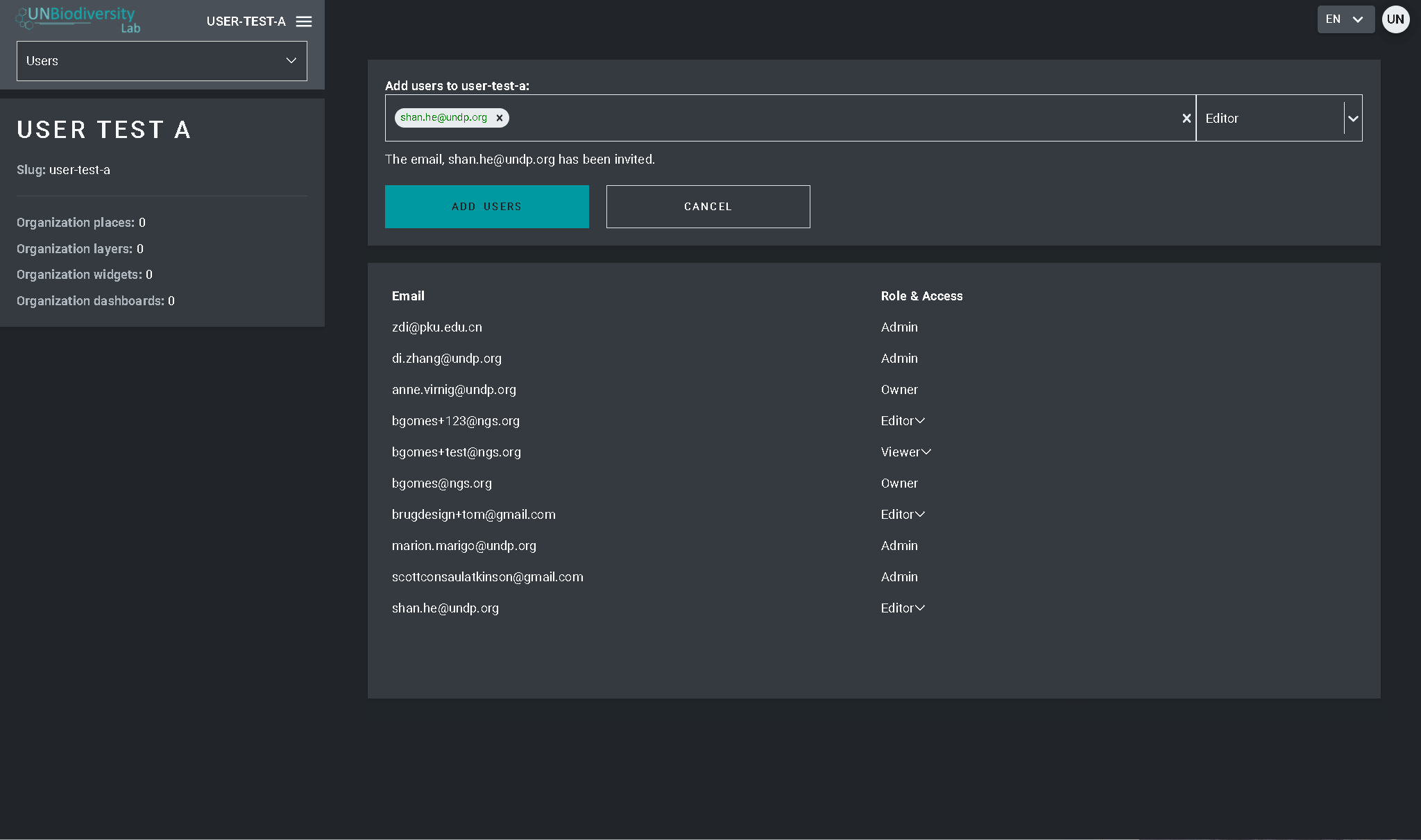
- Selecione o botão “ADICIONAR USUÁRIOS PARA…”. Digite os endereços de e-mail dos usuário na barra “E-mail do usuário” e associe-os a um ou mais grupos de usuários na barra “Grupos de usuários”. Os nomes são gerados automaticamente a partir do endereço de e-mail do usuário.
- Nota: o usuário já deve ser um usuário registrado na plataforma UNBL para que possa ser adicionado à sua área de trabalho. Se ainda não forem usuários registrados na plataforma, você receberá uma mensagem de erro.
Para excluir ou editar usuários existentes:
- Navegue para a página Usuários a partir do menu suspenso no lado esquerdo da página de administração. Quando você entrar na opção Usuários, todos os usuários dentro do seu área de trabalho serão listados no painel do lado esquerdo.
- Selecione um nome de usuário no painel.
- Para alterar a perfil e as permissões do usuário da sua área de trabalho, selecione EDITAR USUÁRIO e atribua o perfil desejado a partir da barra de pesquisa Perfil do usuário. Certifique-se de remover quaisquer permissões desnecessárias clicando no [x].
- Para apagar o usuário, clique na caixa APAGAR USUÁRIO.
- ver métricas dinâmicas automaticamente calculadas para este local; e
- recortar qualquer camada raster (disponível publicamente) para este local e fazer o download para usar em um software GIS para desktop.
- Navegue para a página Locais a partir do menu suspenso no lado esquerdo da página de administração.
- Clique no botão CRIAR NOVO LOCAL.
- Na página Novo Local, preencha as seguintes informações:
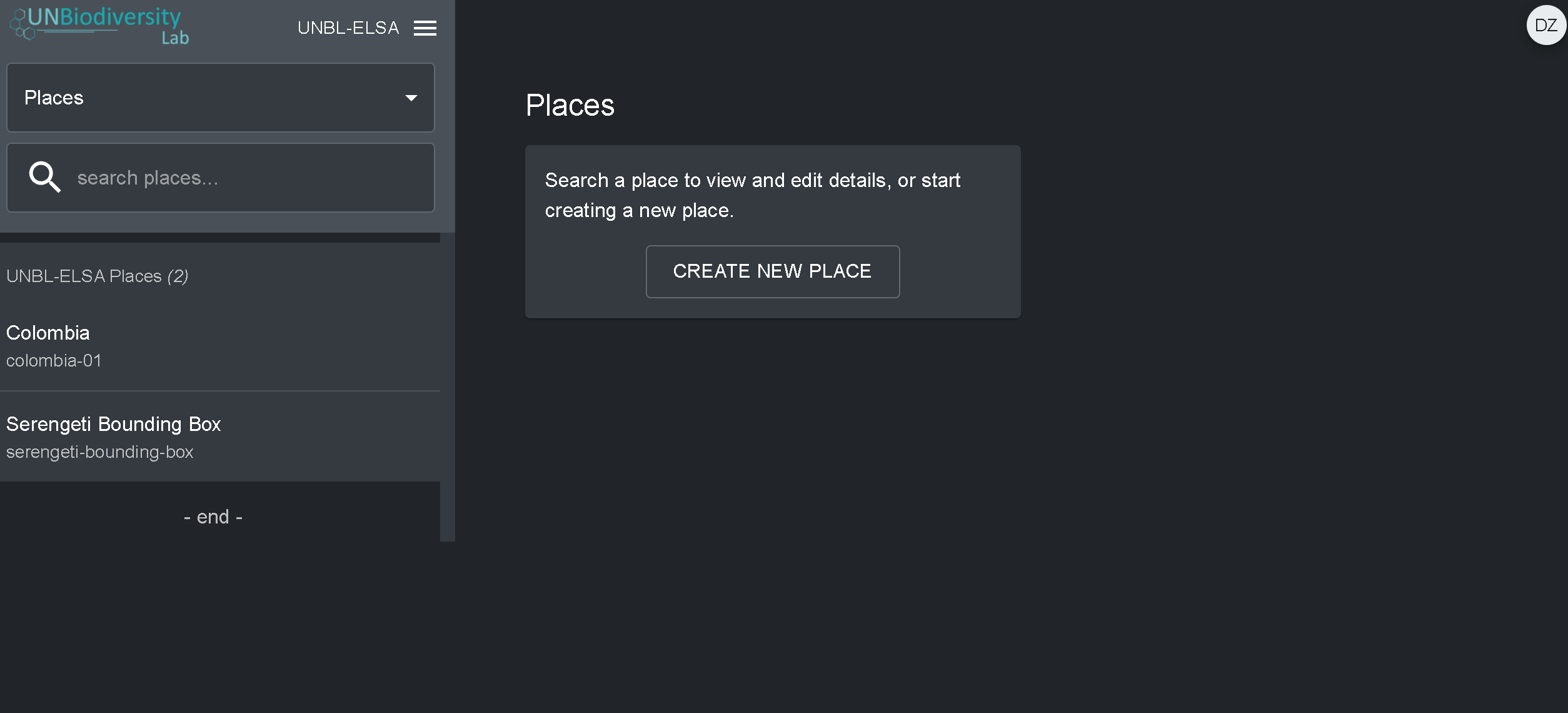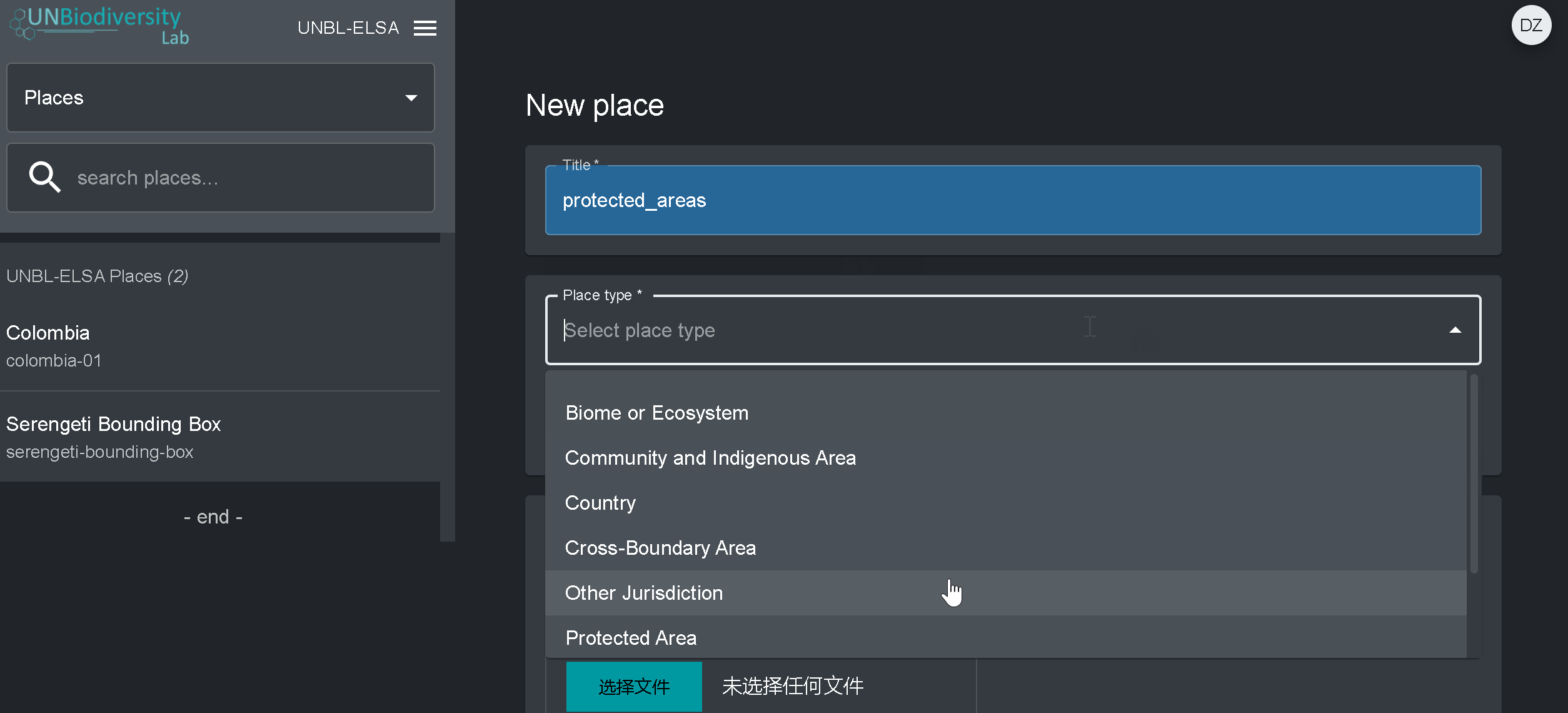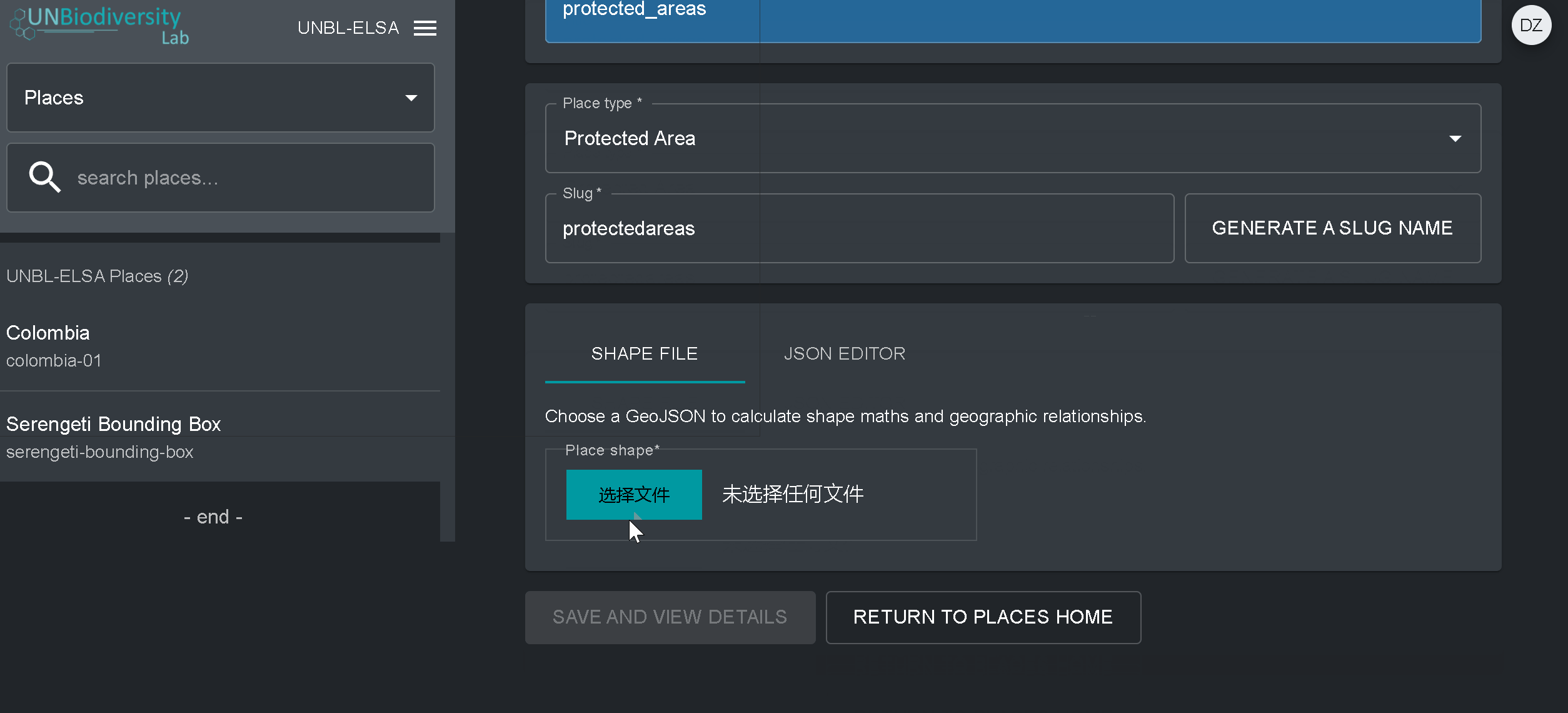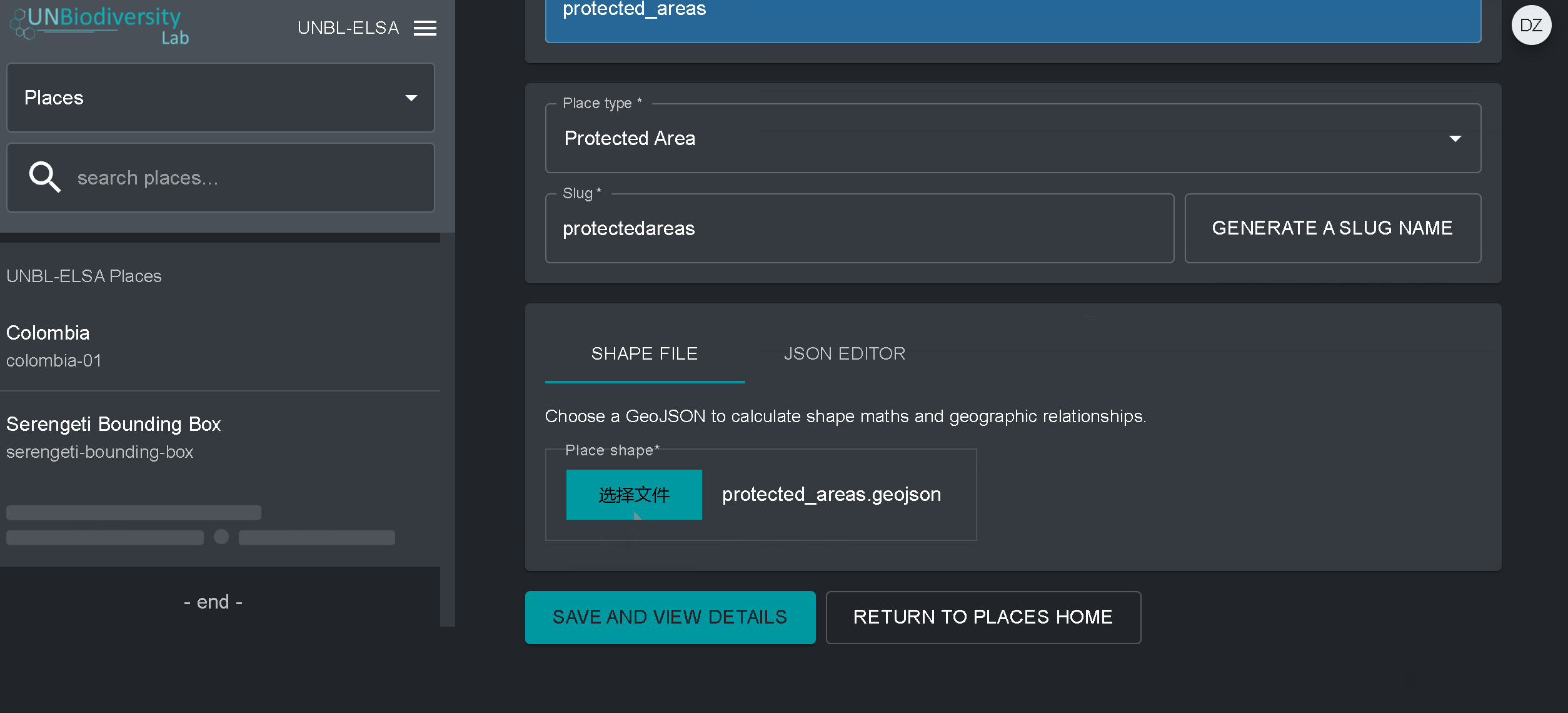
- Título: Insira o nome do local. Recomendamos manter estes curtos e claros. Atualmente, não são permitidos caracteres especiais.
- Tipo do local: Selecione a classe apropriada no menu suspenso. Isto será útil para filtrar as suas pesquisas mais tarde. Você pode escolher entre País, Jurisdição, Bioma, Área Protegida ou Área de Distribuição de Espécie.
- Slug: Insira um identificador único para o local que contenha apenas letras minúsculas, números e hifens. Nenhum espaço pode ser usado. Recomendamos o uso do botão GERAR NOME DO SLUG para ajudá-lo a gerar um slug apropriado.
- Forma do local: Carregue o arquivo .GeoJSON representando o local usando o botão Choose file. O arquivo deve ser um .GeoJSON com menos de 6MB de tamanho e com não mais de 1 milhão de vértices. Embora o sistema permita carregamentos até 6MB, recomendamos fortemente a utilização de ficheiros não superiores a 2MB para optimizar a renderização e cálculos de métricas. Pode ser um único ou multipolígono, mas o nosso sistema não irá ler as sub-feições de um polígono. Aqui uma orientação mais completa sobre os requisitos de formato.
4. Assim que salvar o seu novo local, você será direcionado para a tela inicial do local. Para que seu local esteja acessível na visualização do mapa, você deve publicar o local clicando na chave Publicados. Os lugares não publicados permanecem na página de administração até que você esteja pronto para publicá-los na visualização do mapa da área de trabalho.
5. Para fazer deste um lugar de destaque para o seu área de trabalho, ative a chave Em destaque. Isto funcionará como um marcador de página para que o local apareça no topo da lista na guia Locais sempre que um local não for selecionado.
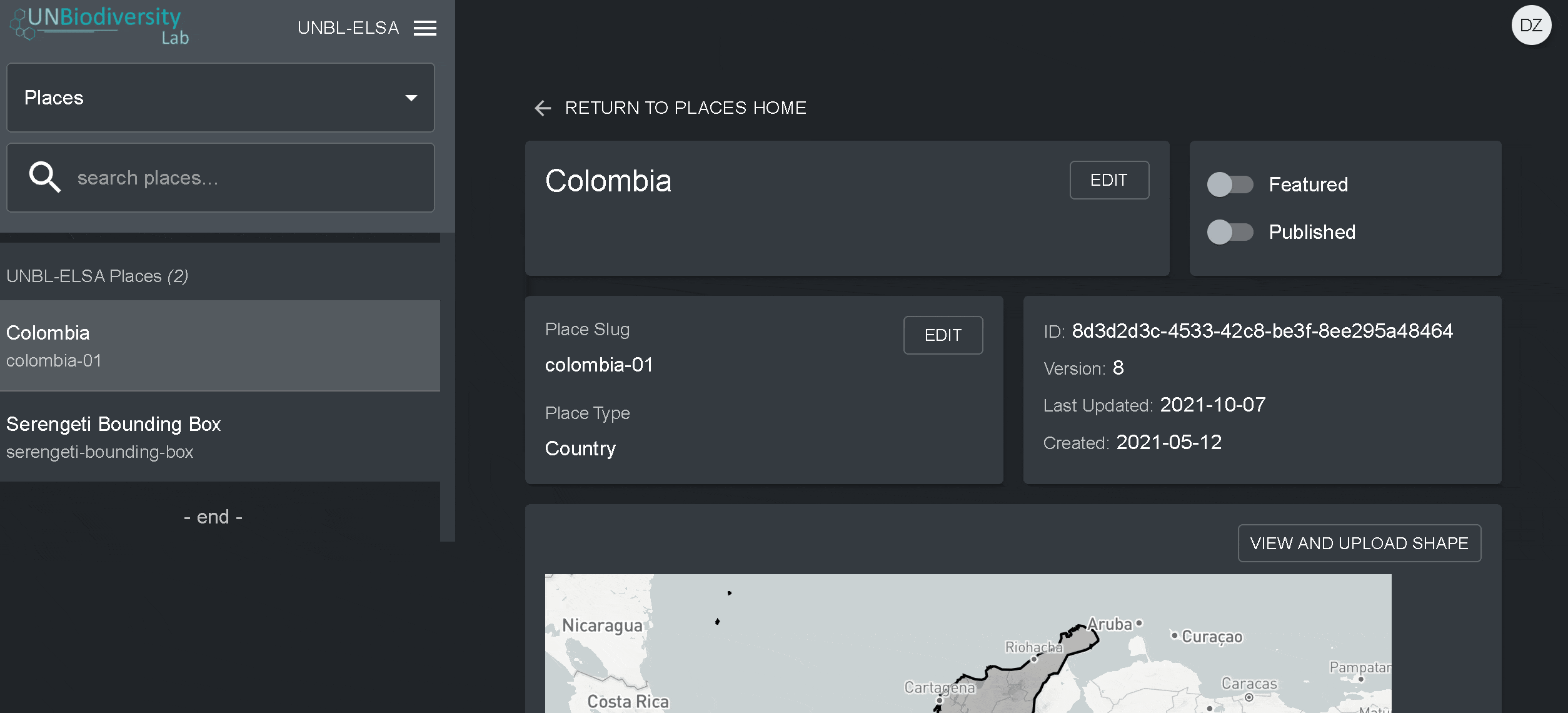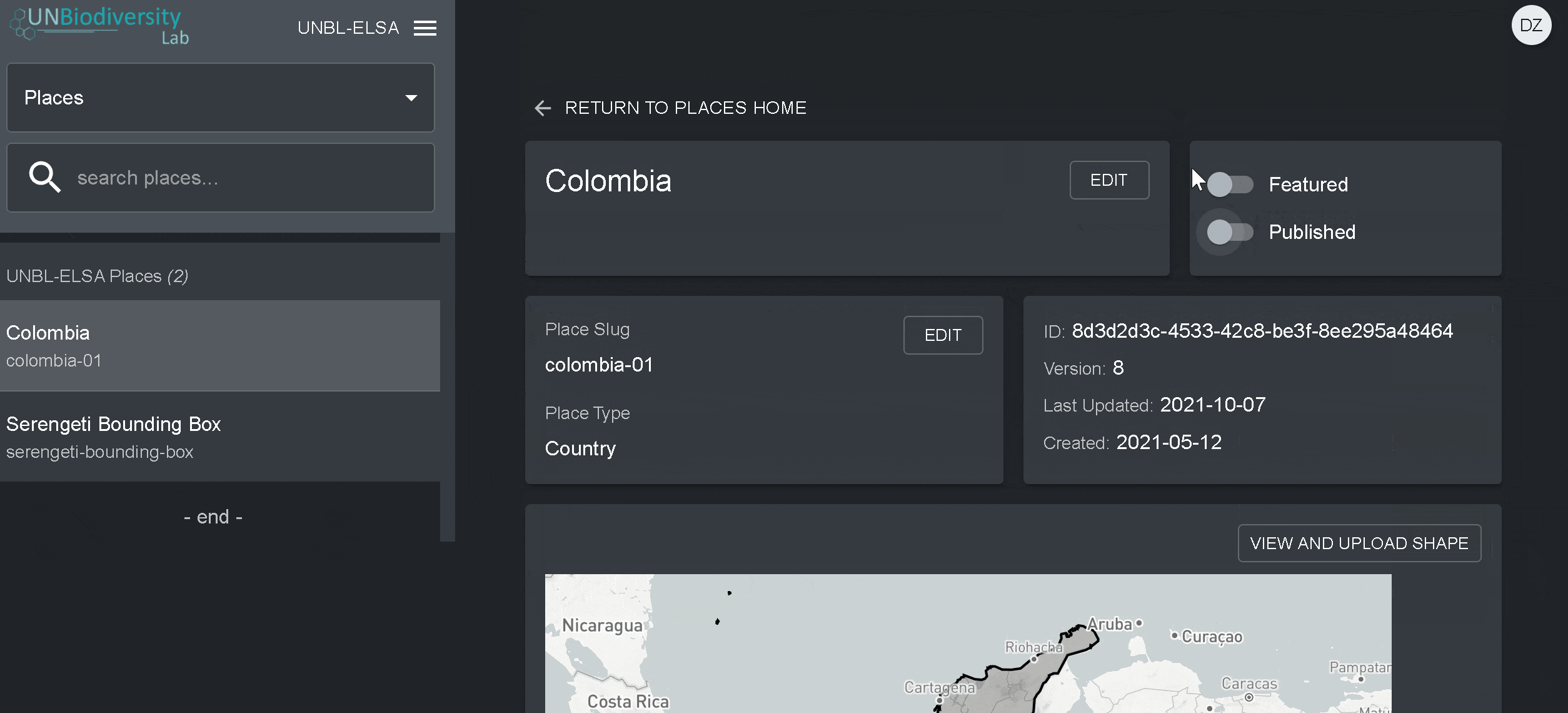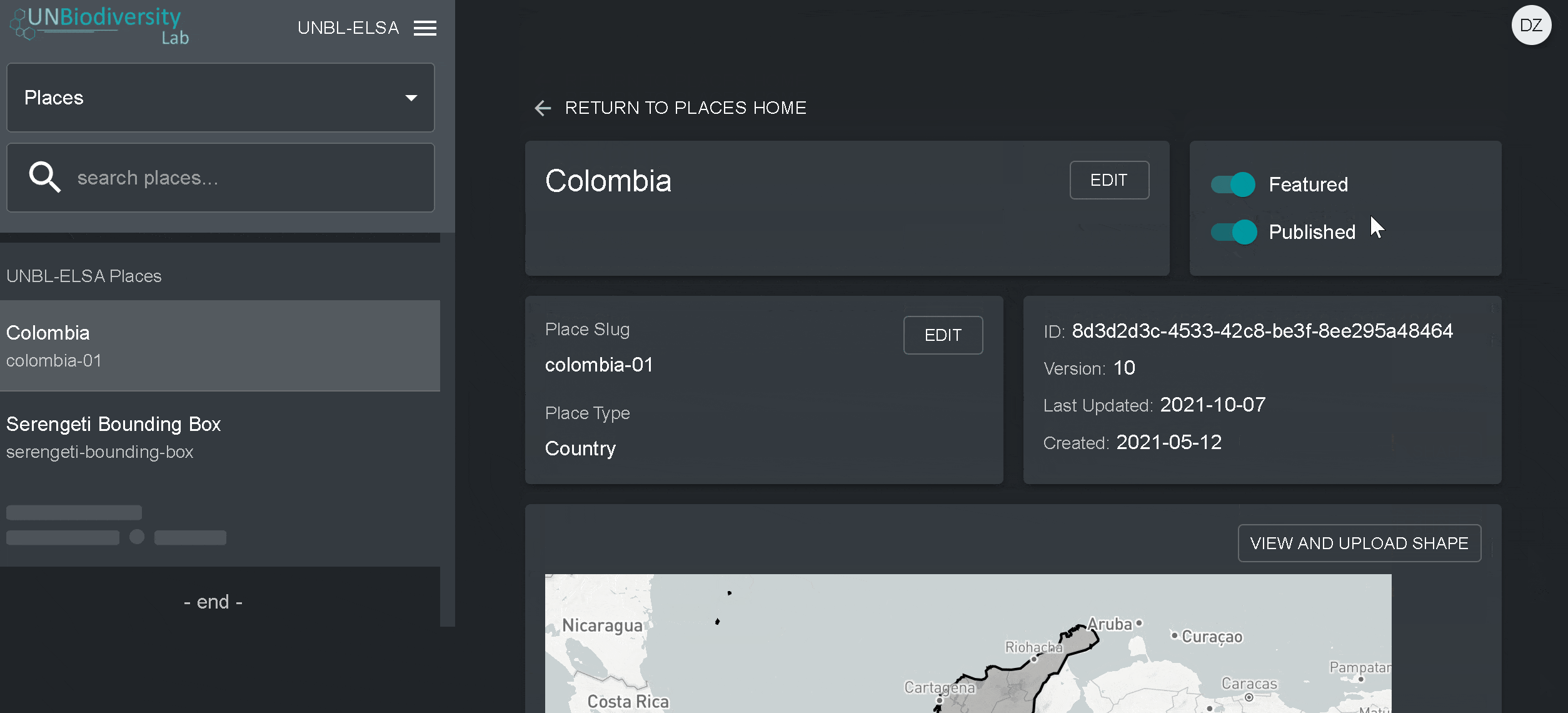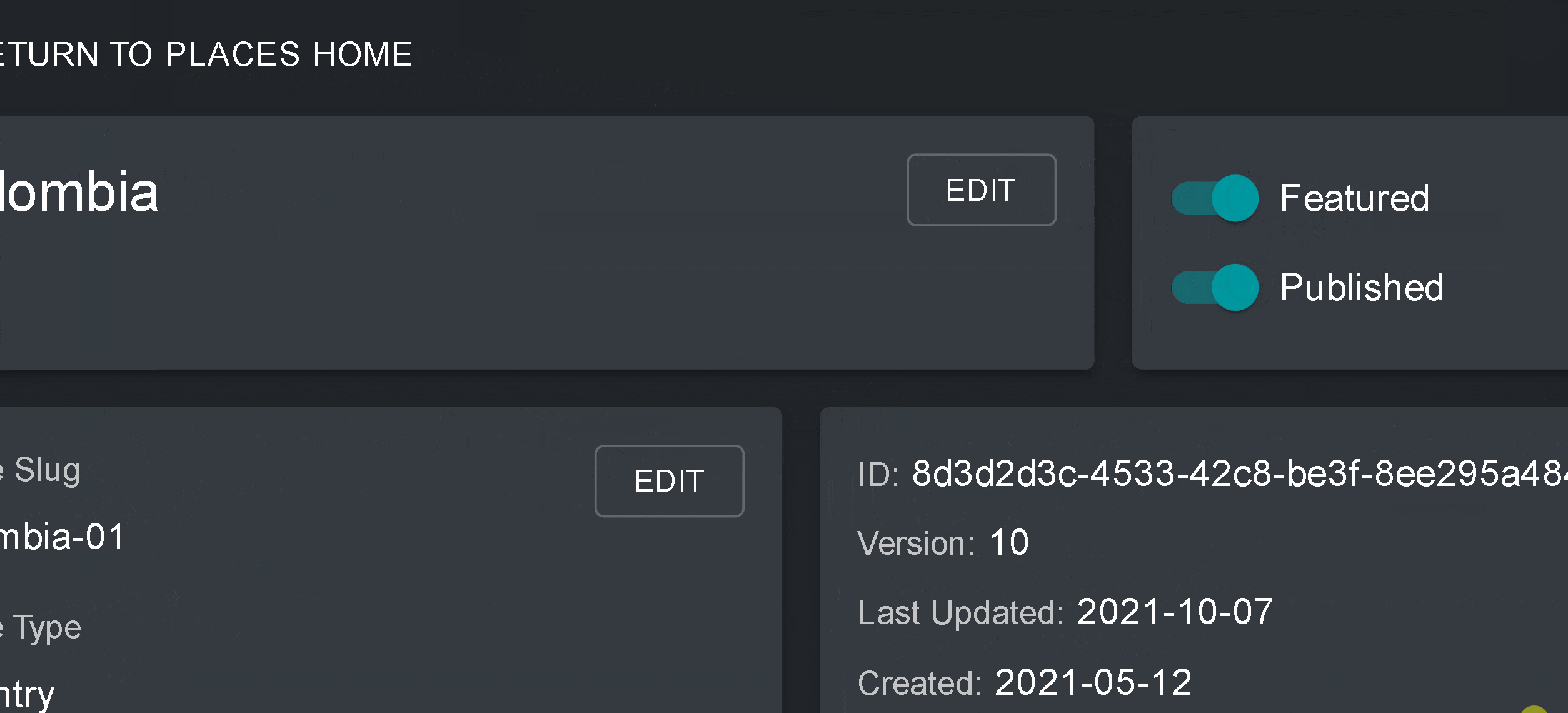
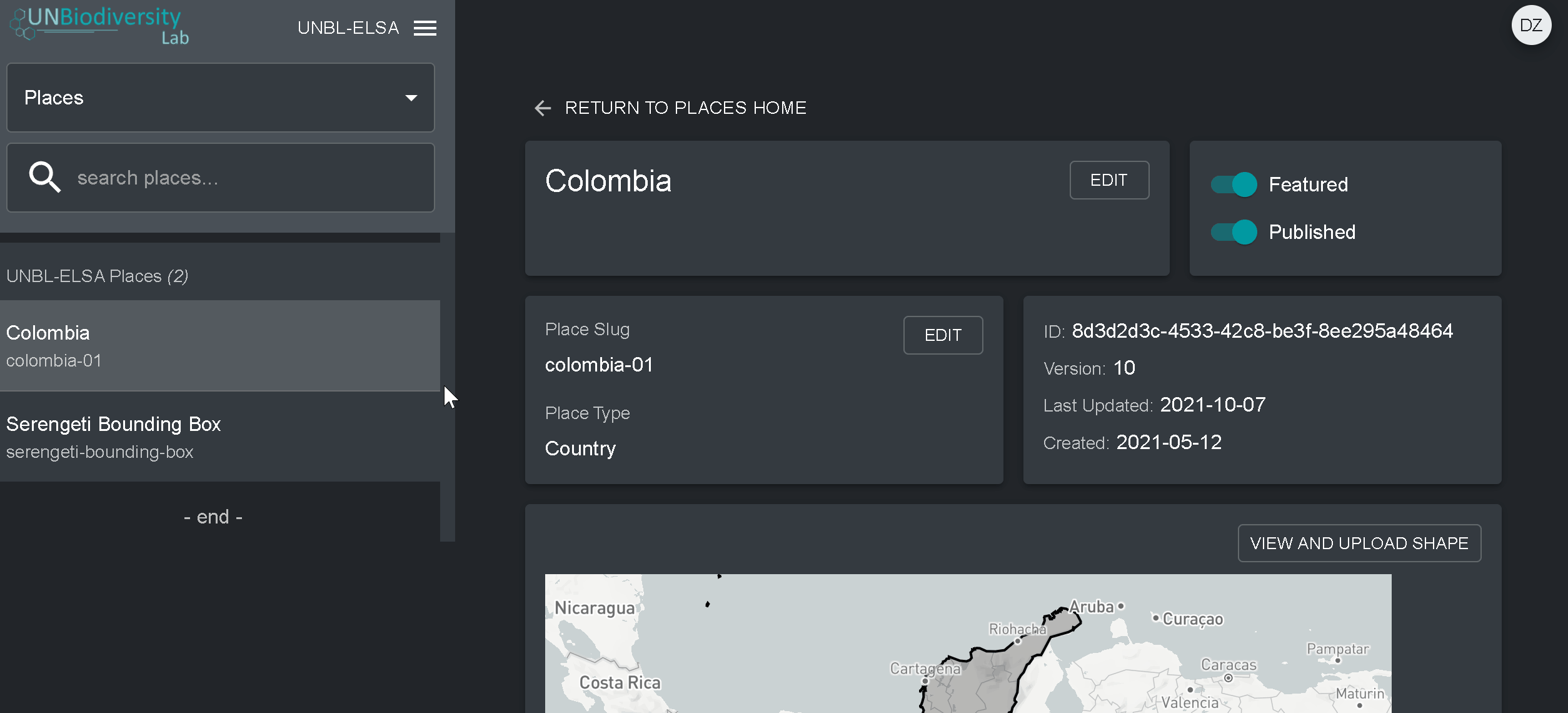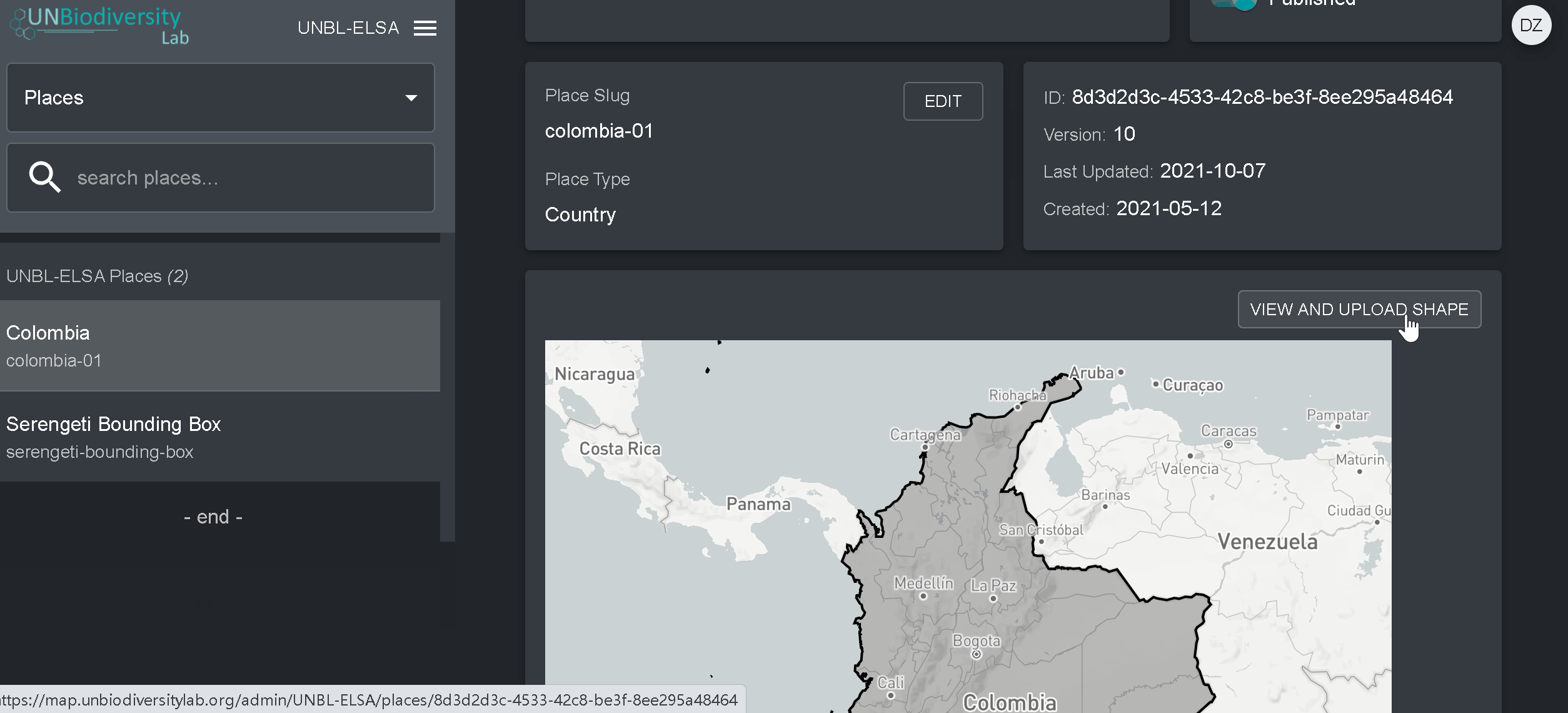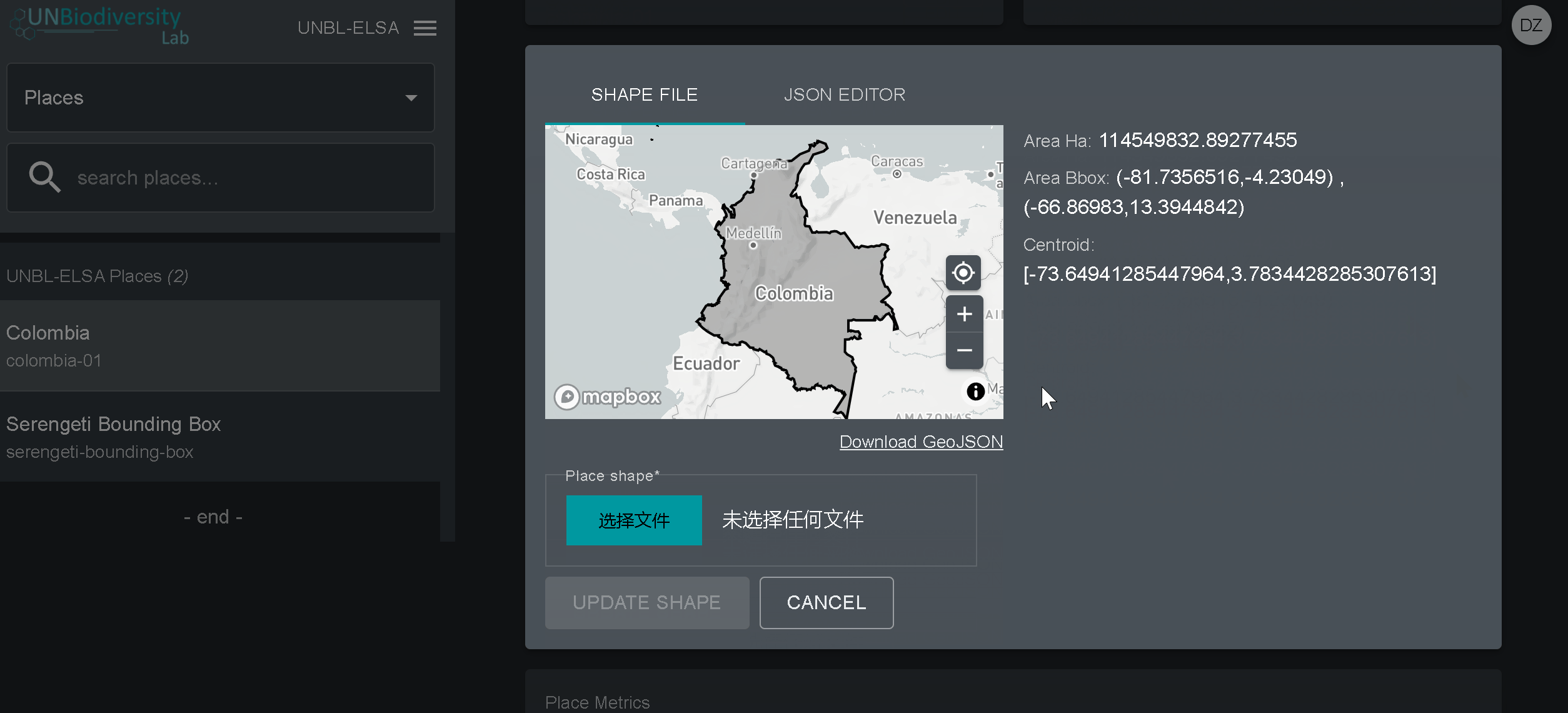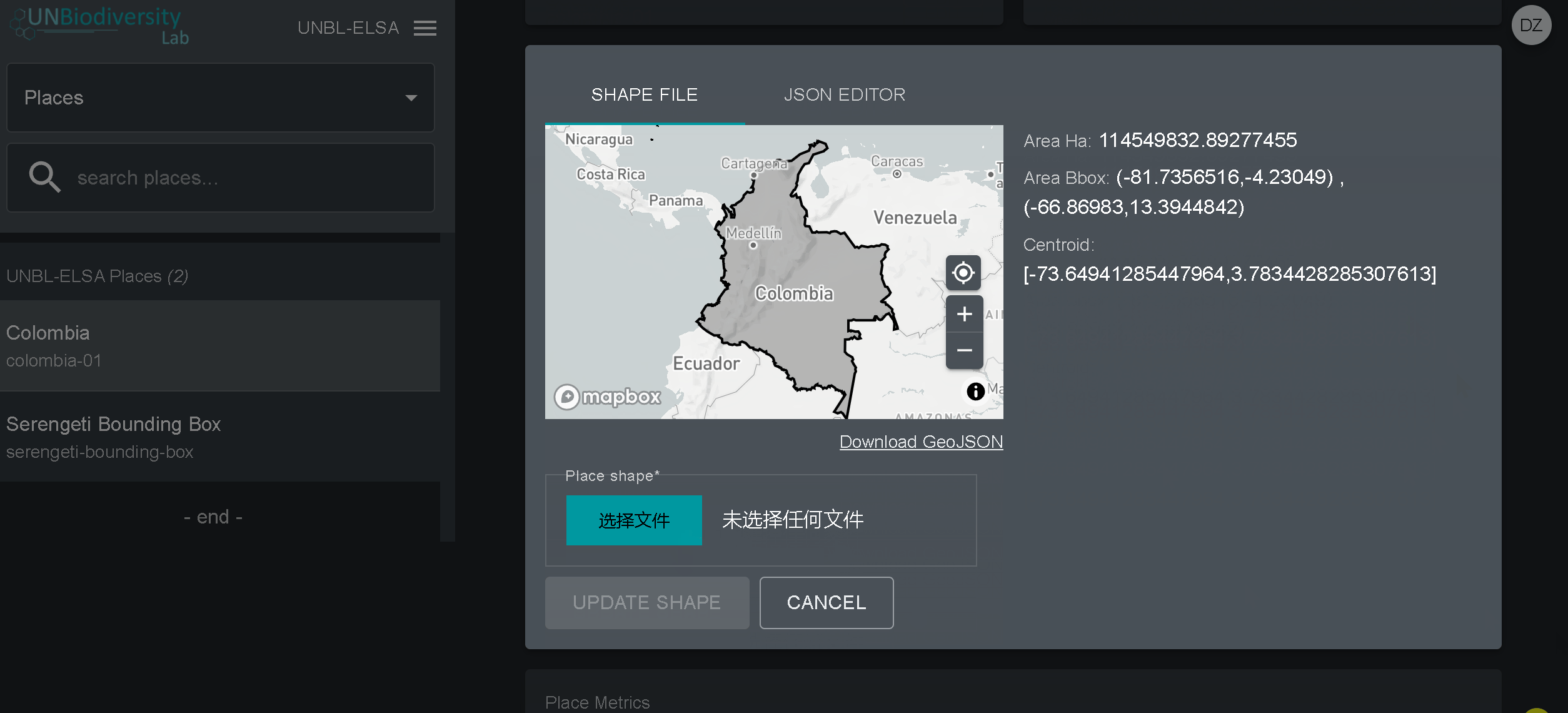
- Navegue para a página Locais a partir do menu suspenso no lado esquerdo da ferramenta de administração.
- Seleccione o lugar que lhe interessa na lista de lugares na barra do menu à esquerda. Depois de clicar no local, os seus detalhes aparecerão no painel direito.
- Clique no botão Visualizar e Fazer Upload de Forma acima da janela do mapa base para ver algumas informações geoespaciais básicas sobre a sua forma e carregar qualquer nova versão da forma que você possa ter no futuro.
- Navegue para a página Camadas a partir do menu suspenso no lado esquerdo da página de administração.
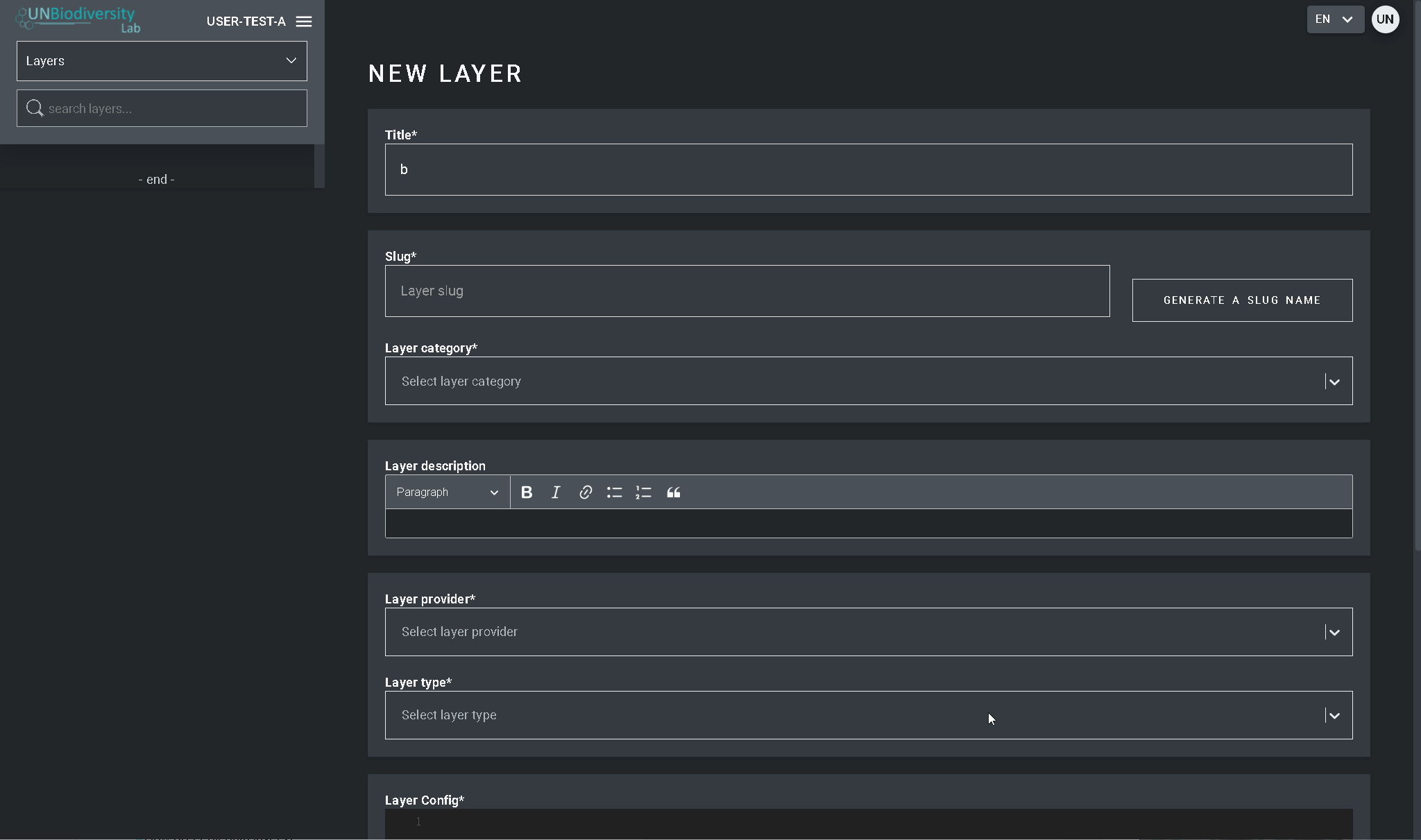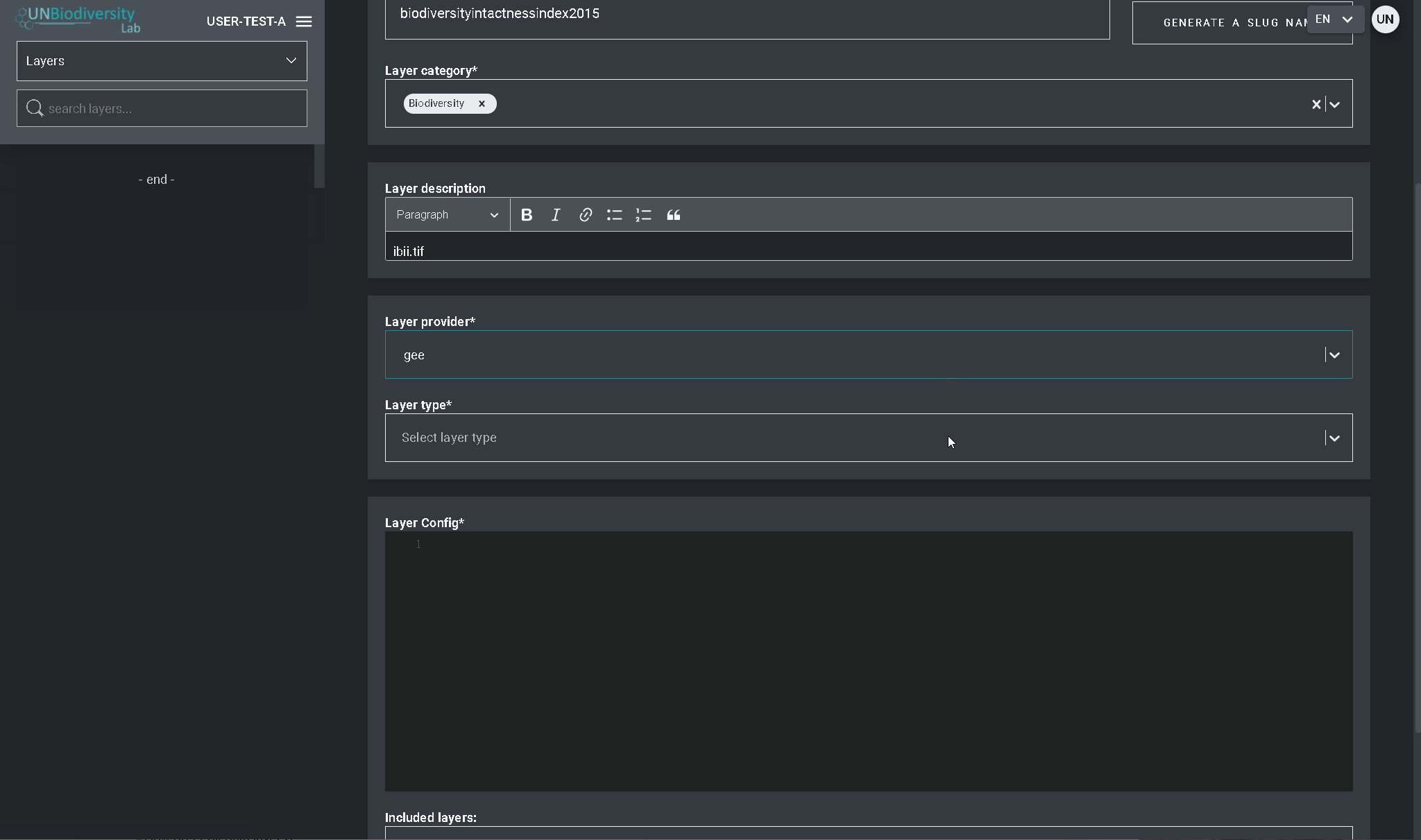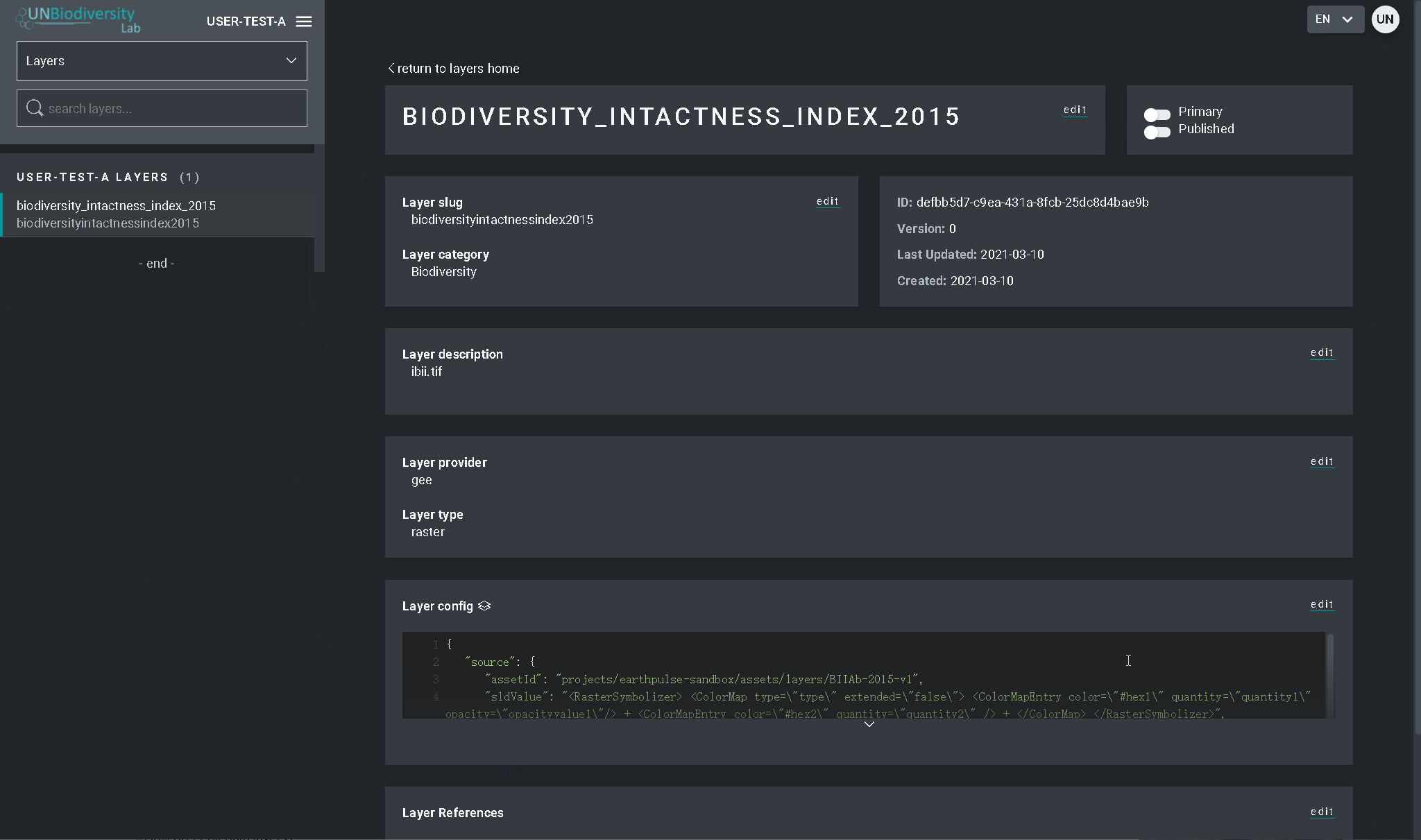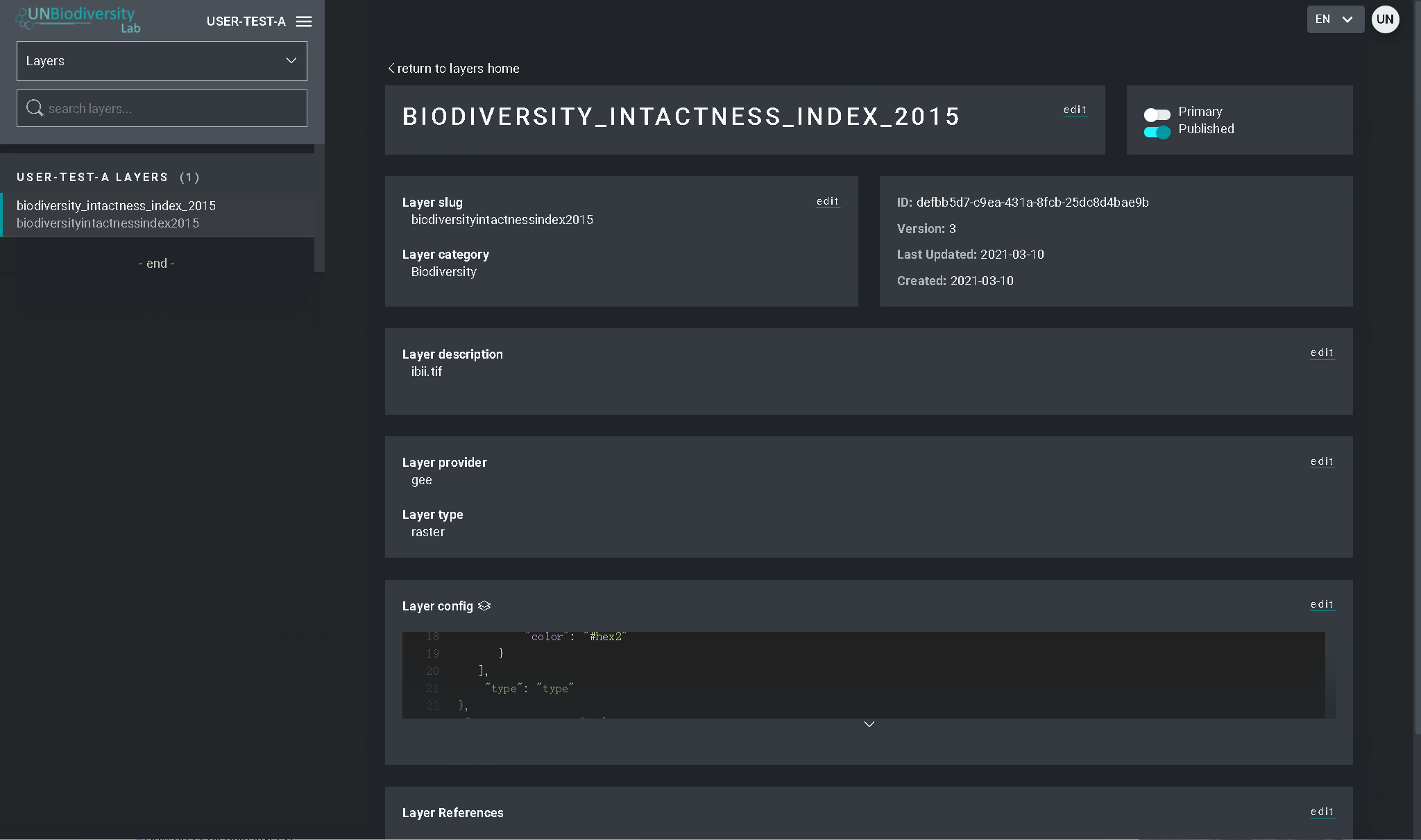
- Selecione o botão CRIAR NOVA CAMADA.
- Na página Nova Camada, preencha as seguintes informações:
- Nome da camada: Recomendamos manter estes curtos e claros. Atualmente, não são permitidos caracteres especiais.
- Slug: Insira um identificador único para a camada que contenha apenas letras minúsculas, números e hifens. Nenhum espaço pode ser usado. Recomendamos o uso do botão GERAR NOME DO SLUG para ajudá-lo a gerar um slug apropriado.
- Categoria da camada: Selecione a classe temática apropriada no menu suspenso. Isto será útil para filtrar as suas pesquisas mais tarde. Você pode escolher entre áreas administrativas; biodiversidade; clima e carbono; serviços dos ecossistemas; habitats, ecossistemas e biomas; impacto humano e pressões; cobertura terrestre; riscos marinhos; riscos naturais; áreas protegidas e conservadas; restauração; socioeconômico; e desenvolvimento sustentável.
- Provedor de camadas: Escolha a fonte de onde você está derivando a camada.
- Tipo de camada: Atribuir um tipo de camada; atualmente os áreas de trabalho privadas só podem suportar camadas rasterizadas.
- Navegue para a página Camadas a partir do menu suspenso no lado esquerdo da ferramenta de administração (poderá ter de actualizar a página para que esta nova camada seja mostrada na lista).
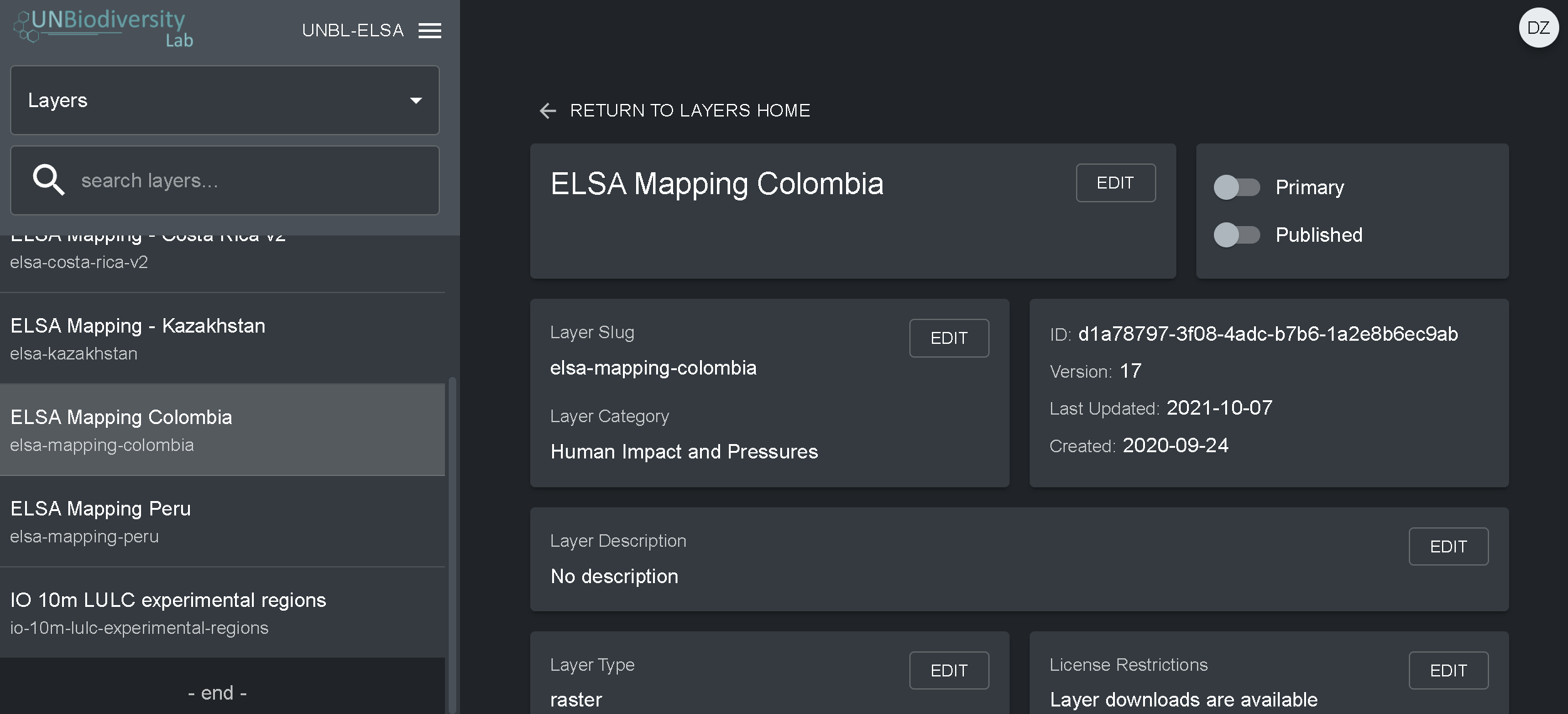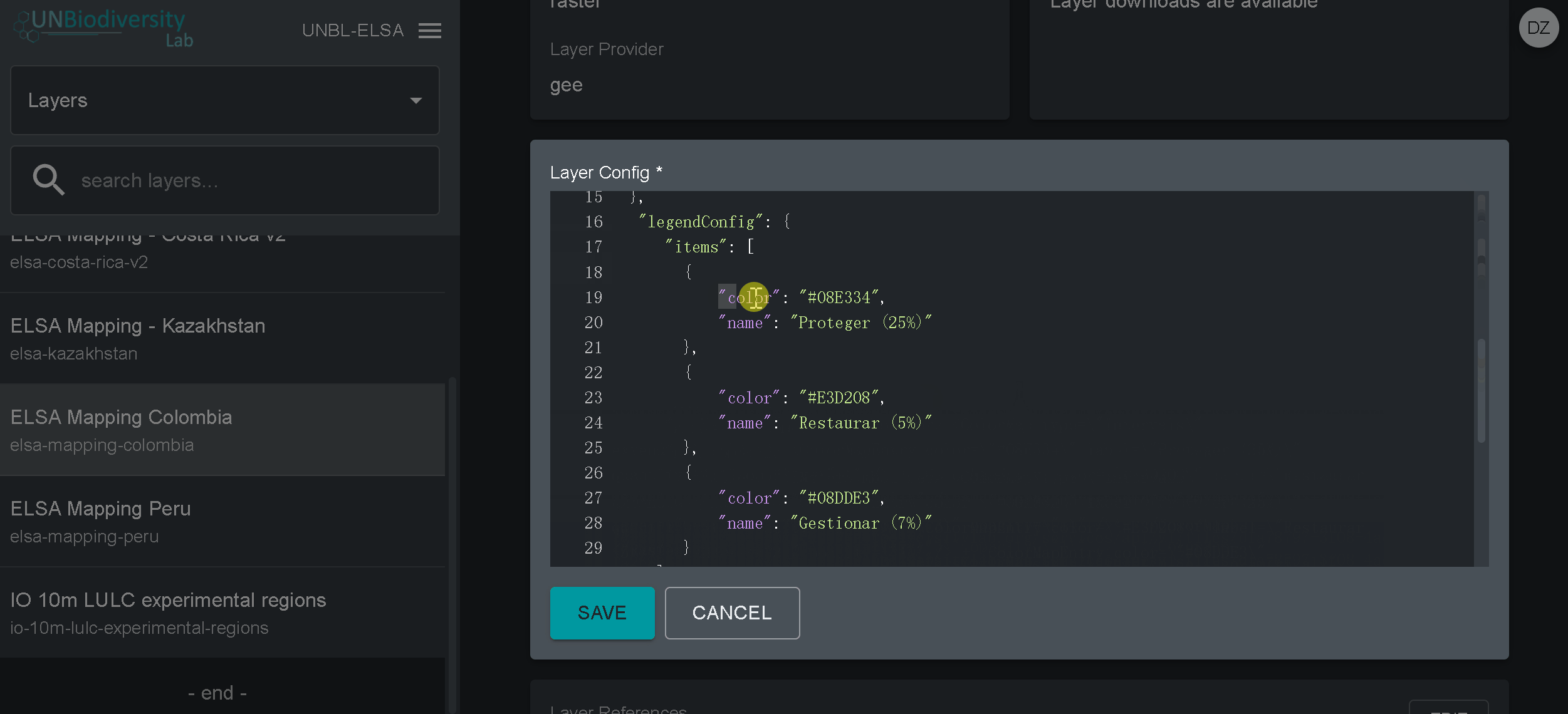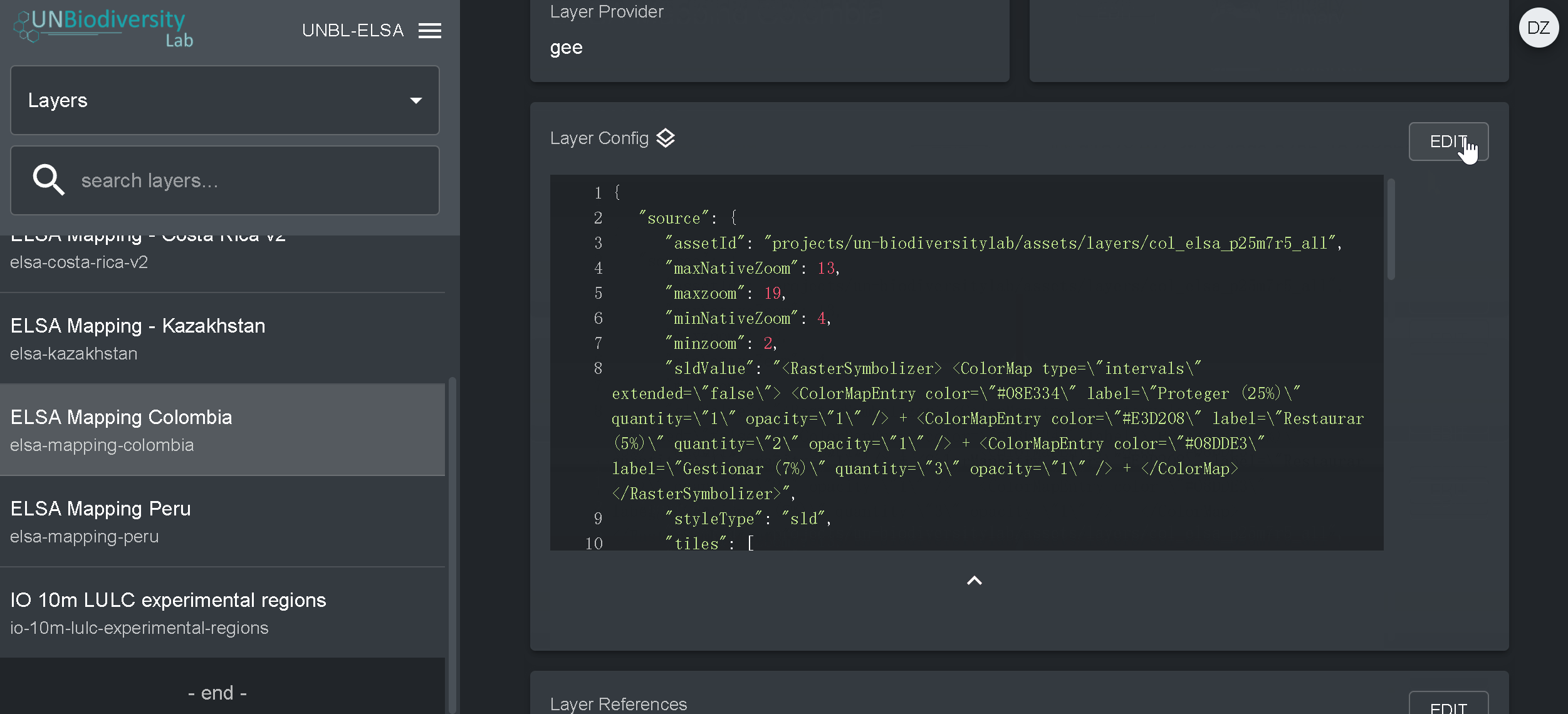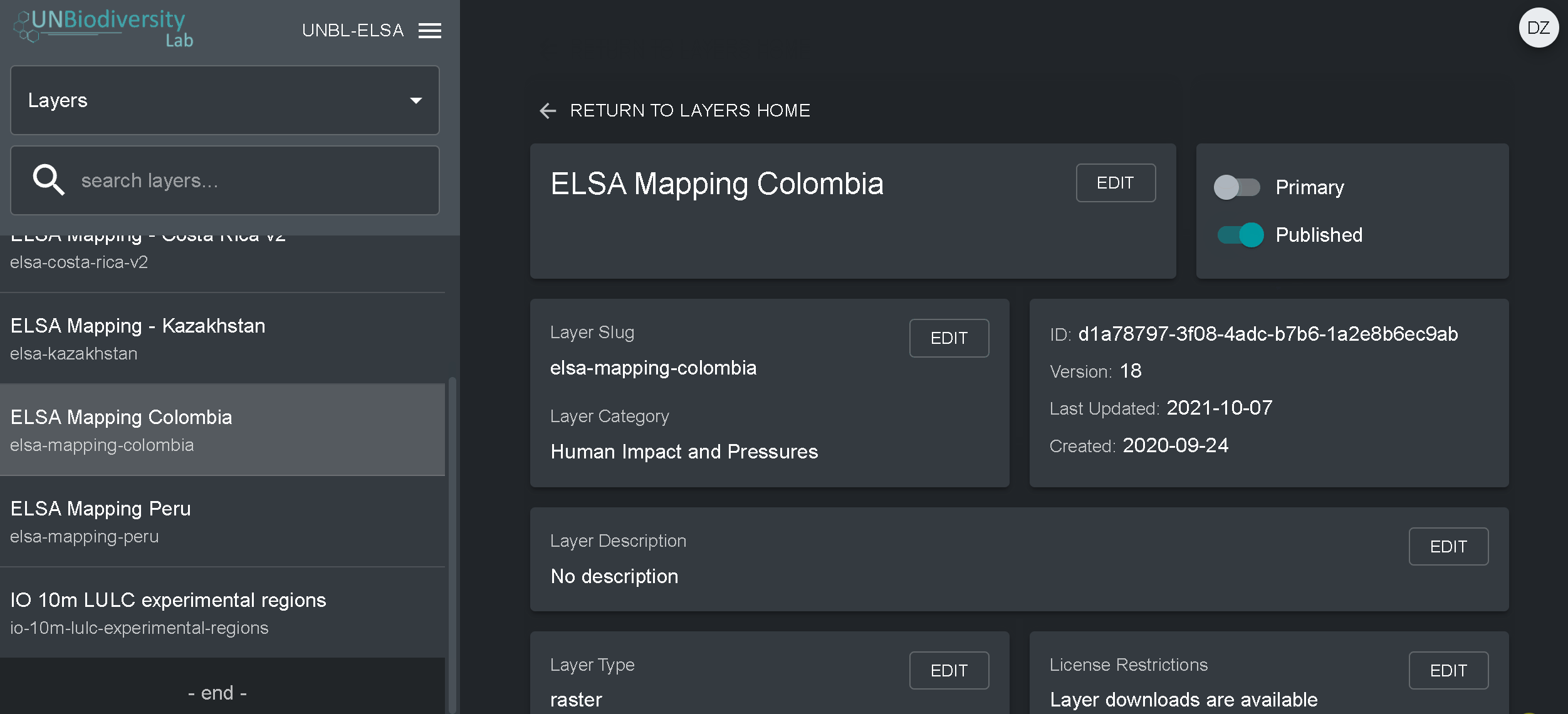
- Clique no botão EDIT na secção Layer config.
- No ecrã do editor de Layer, editar apenas as secções destacadas do código de configuração, como se viu acima. Tudo o resto deve permanecer inalterado ou então receberá um erro.
- Copie e cole aqui, entre aspas (” “), o ID de bens do Motor Google Earth.
- Introduzir o estilo de camadas. O estilo de camadas segue o formato Styled Layer Descriptor (SLD). Este formato permite-lhe alterar a coloração, transparência e a gama de valores da sua camada. Recomendamos que siga estes passos para preencher esta parte da configuração no guia do utilizador.
- Introduzir o estilo de legenda mostrado no guia do utilizador.
- Clique em SAVE LAYER quando tiver o estilo desejado para criar um URL único para a camada. Este URL será adicionado à configuração da camada para completar o processo.
- Alterar o URL. Depois de guardar um valor de ID aparecerá (circulado abaixo). As placas raster são armazenadas com base num identificador único encontrado dentro da Camada URL. Colar este URL na configuração da camada para carregar a camada na vista do mapa.
- Seleccionar Grupo no pulldown do Tipo de Camada.
- Adicionar cada uma das camadas componentes utilizando a caixa de selecção Camadas Incluídas.
- Adicione um dos dois scripts de configuração especiais abaixo, dependendo de como gostaria de apresentar os dados na legenda da camada na vista do mapa. Nota: não é necessária qualquer informação de estilo, url, ou legenda. Quando a camada é marcada como camada de ‘grupo’, toda a visualização é arrancada das camadas componentes.
-
- Botões de rádio: Recomendado para camadas de grupo contendo dois ou três anos/categorias. Colar o código no guia do utilizador na caixa de configuração, sem alterações.
- Barra de descida: Recomendada para camadas contendo mais de três anos/categorias. Colar o código no guia do utilizador na caixa de configuração, sem alterações
Neste momento, se você gostaria de criar uma camada animada, por favor entre em contato com support@unbiodiversitylab.org para assistência.
Baixar o guia do usuário de trabalho seguros : Inglês | Francês | Espanhol | Português | Russo
Espaços de trabalho UNBL
Espaços de trabalho privados
Você está trabalhando para conservar a natureza e promover o desenvolvimento sustentável? Você tem dados nacionais que gostaria de visualizar e analisar em combinação com nossas camadas de dados globais? Oferecemos espaços de trabalho gratuitos para que diversos interessados possam utilizar as ferramentas do UNBL em um ambiente seguro.
Contribua
Contribua

Você tem dados que enriqueceriam a plataforma pública do UNBL? Você está disposto(a) a fazer parte de uma comunidade científica comprometida com o compartilhamento aberto de dados espaciais? Se você tem dados globais que abordam a biodiversidade, as mudanças climáticas ou o desenvolvimento sustentável, gostaríamos de ouvir você.
Consulte os critérios de seleção de dados da UNBL aqui.

Como você está usando os dados espaciais para obter informações e agir em seu trabalho? O UNBL trabalha para dar destaque a diversos casos de uso em todo o mundo. Nossa equipe trabalhará com você para criar um ensaio fotográfico ou uma história no Google Earth para destacar suas conquistas. As histórias de sucesso serão compartilhadas em nossa seção Histórias em Destaque.
Contate-nos
Contate-nos
Por favor, deixe sua mensagem e informações de contato abaixo e responderemos o mais rápido possível. Alternativamente, você pode nos enviar um e-mail para support@unbiodiversitylab.org.
Programa das Nações Unidas para o Desenvolvimento
304 East 45th Street
New York, NY 10017
